Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
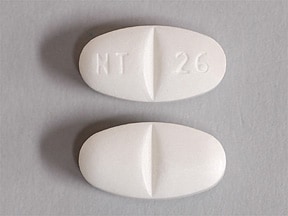
Gabapentin is a drug often used together with opioids to treat chronic pain, and both have been shown to suppress breathing with worsening complications rates in combination. General · In 2019, 16% of overdose deaths involving opioids also involved benzodiazepines · Every day, more than 136 Americans die after overdosing on opioids Expert opinion: Loperamide, gabapentin, and modafinil are becoming drugs of abuse, and as such, should be on the radar of healthcare providers. Recognizing their unique toxicity profiles is imperative in providing optimal resuscitative care. Keywords: Evidence-based emergency medicine; gabapentin; loperamide; modafinil; toxicology. Dr. Hans Rosenberg reviews the evidence for the use of gabapentinoids such as gabapentin and lyrica in emergency medicine on EM Cases' EM Quick Hits Videos series Toxicity from gabapentin and pregabalin overdose is commonly encountered. Treatment is supportive, and the use of extracorporeal treatments (ECTRs) is controversial. The EXTRIP workgroup conducted systematic reviews of the literature and summarized findings following published methods. Disclaimer: This generalized information is a limited summary of diagnosis, treatment, and/or medication information. It is not meant to be comprehensive and should be used as a tool to help the user understand and/or assess potential diagnostic and treatment options. Multiple studies and reviews have examined the efficacy and safety of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal. 22, 56 – 58 A retrospective cohort study of 100 patients who presented to an ED found that those who received high-dose gabapentin (1800 mg/day) during the first two days of hospital admission required a significantly lower total dose of The 2 most commonly used gabapentinoids are gabapentin and pregabalin. Gabapentin has a lower bioavailability, less predictable pharmacokinetics and requires a longer titration duration to reach an effective dose. Effective dose reached in ~ 14 days. Pregabalin. Effective dose reached in ~ 7 days. Gabapentin and pregabalin have now become the new drugs for abuse, with around one of five opioid abusers also using gabapentin. (Drugs 2017;77[4]:403; “Opioids Not the Only Pain Meds that Lead to Abuse,” EMN 2017;39[10]:1; The real mystery is why medical providers are still writing for gabapentin and pregabalin. The use of gabapentin (and pregabalin [Lyrica], a gabapentin precursor) tripled from 2002 to 2015. Some 57 million prescriptions for gabapentin were written in the United States in 2015, a 42 percent increase since 2011, partially in response to the paranoia surrounding physician prescribing during the “opioid crisis.” Gabapentin is available as Gralise, Neurontin, and generic gabapentin in the following dosage forms that are taken by mouth. 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg oral capsules 250 mg/5 mL oral solution EM Quick Hits 1 Massive PE, Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal, Dental Avulsions, Pediatric Eye Exam, Best Resuscitation Fluid In brief, medications shown in randomized trials to reduce pain associated with postherpetic neuralgia include topical lidocaine, 26 anticonvulsant agents (e.g., gabapentin 27 and pregabalin 28 SAEM GRACE-4: Alcohol Use Disorder and Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome Management in the Emergency Department. While the opioid epidemic has garnered much attention, other forms of substance use disorders (SUD) continue to have significant impacts on health and wellness. Gabapentin for acute and chronic pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3. Art. No.: CD005452. Goodman CW, Brett AS. A clinical overview of off-label use of gabapentinoid drugs. JAMA Internal Medicine. Published on-line March 25, 2019. Wiffen PJ, McQuay HJ, Rees J, Moore RA. Gabapentin for acute and chronic pain. Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of seizure disorders, neuropathic pain (eg, postherpetic neuralgia), fibromyalgia, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and restless leg syndrome. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat some types of nerve pain but is classified as an anticonvulsant medicine, not as an opioid or painkiller. Gabapentin is used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type nerve pain that can occur due to an outbreak of shingles, and restless legs syndrome (RLS), an uncomfortable urge to move your legs around The newer anticonvulsant agents include: Gabapentin, Lamotrigine, Levetiracetam, Oxcarbazepine, Pregabalin, Tiagabine, Topiramate and Vigabatrin. These are generally less toxic in overdose causing sedation and non-specific neurological symptoms and patients do well with supportive care. The purpose of this study is to document the clinical manifestations and outcomes of gabapentin exposures reported to poison centers. Methods: A multicenter prospective observational study of all gabapentin exposures reported to three poisoncenters was conducted between 4/1/98 and 4/1/2000. Cases involving gabapentin only were evaluated. Gabapentin side effects. Get emergency medical help if you have signs of an allergic reaction to gabapentin: hives, difficult breathing, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Seek medical treatment if you have a serious drug reaction that can affect many parts of your body. The calcium channel blocker anticonvulsants pregabalin and gabapentin reduce central pain sensitization by preventing voltage-gated postsynaptic neurotransmitter release. 96 Pregabalin functions similar to gabapentin but with increased potency and binding affinity. 97
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |