Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
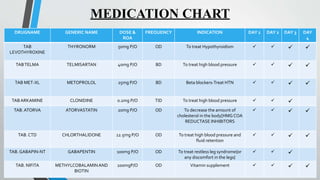
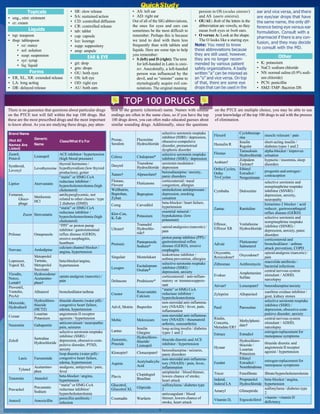
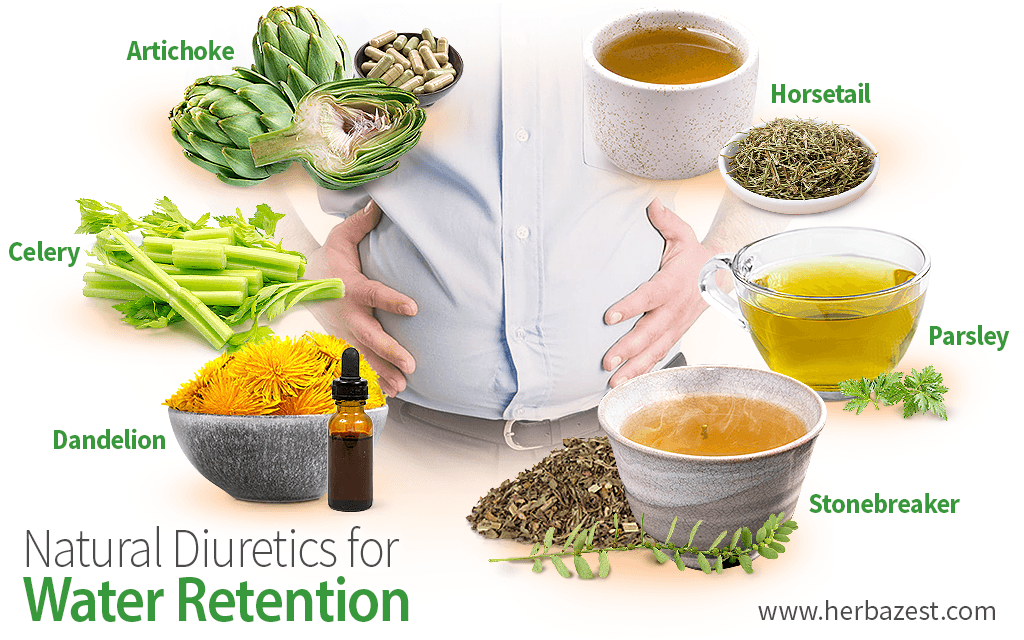
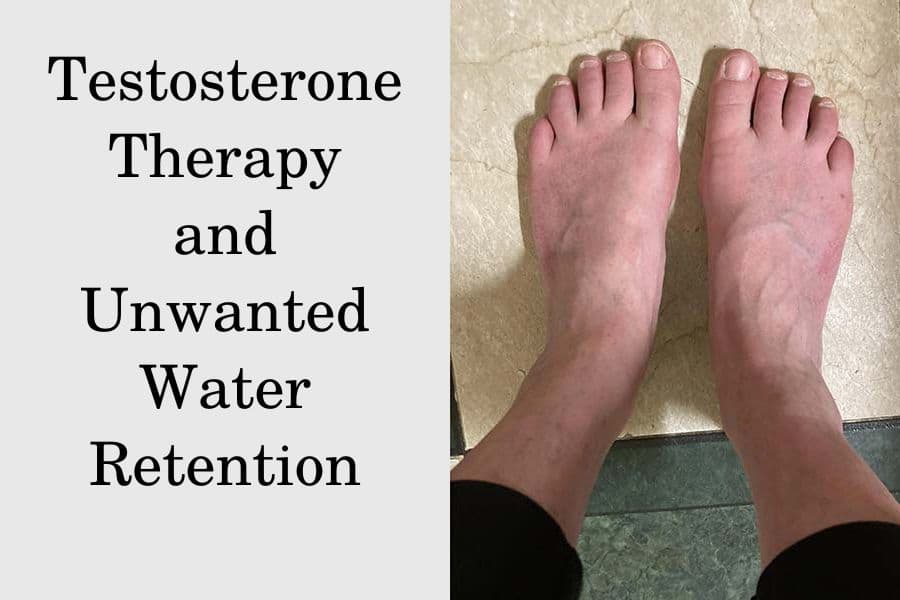
Fluid retention is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 6 - 12 months also take Furosemide, and have Depression. When I was first prescribed gabapentin, I was told to take 300 mg three times a day. It seemed that there was so much fluid collected in my feet that I couldn’t feel the sidewalk under me. If I backed off to take 200 mg three times a day, I didn’t have the clinical benefit for my chronic pain syndrome. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. Seven days after the administration of the gabapentin, the patient complained from pain and edema and scaling and hyperesthesia in his lower extremities and pitting edema, pain and tenderness. The range of motion of the extremities was been increased. According to the patient statement the gabapentin brand has been changed. Fluid retention, or edema, can occur when gabapentin affects vascular permeability or alters kidney function. Edema refers to swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation in tissues. It can occur in various parts of the body but is most commonly seen in the legs, ankles, and feet. Gabapentin can cause fluid buildup in the legs (edema), which can lead to temporary weight gain. You can also gain weight without fluid buildup, though it’s not common. You may be able to avoid weight gain from gabapentin by adjusting your diet and exercising regularly. Gabapentin does help with the pain but, I don’t like the swelling. It also makes me drowsy but I sleep good. The drug has pros and cons about it. I have been on it for about 8.5 years with no fluid retention or other side effects. Thanks for your response but Im not 100% convinced that is true. Edema is a well-described side effect of gabapentinoid drugs (i.e., gabapentin and pregabalin). In this study from Ontario, Canada, researchers used provincial databases to examine whether gabapentinoid use was followed by diuretic prescriptions — a so-called “prescribing cascade” in which a drug is prescribed to treat an adverse effect of another drug. Background. Gabapentin binds to the alpha-2-delta subunit of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels and is used for a wide variety of indications both Food and Drug Administration approved and off-label. 1-3 It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat postherpetic neuralgia and epilepsy 4 with common off-label indications including fibromyalgia, anxiety, mood disorders, and Studies have suggested that gabapentin may interfere with the RAS, leading to an imbalance in fluid regulation. Increased fluid retention can cause edema in certain individuals receiving gabapentin therapy. Gabapentin is a medication used to treat seizures, restless legs syndrome, and nerve pain from shingles. Some people taking it report fluid retention and swelling in their extremities. Swelling may be more likely if you’re older, or if you’re taking a higher gabapentin dosage. Background Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly prescribed medications to treat pain in patients with diabetic neuropathy. Gabapentin and pregabalin can cause fluid retention, which is hypothesized to be associated with cardiovascular diseases. However, whether long-term use of gabapentin and pregabalin is associated with adverse cardiovascular diseases remains unknown. This study aims to Swelling from fluid retention may be reduced by: Sitting with your feet raised; Avoiding standing for long periods of time; If gabapentin is causing you to gain weight, do not stop taking this drug on your own. Stopping the drug suddenly can lead to serious problems, especially if you are taking gabapentin for seizures. However, this medicine can cause a number of side effects including fluid retention. We will also discuss what could be done if you suffer from gabapentin induced fluid retention. Does gabapentin cause fluid retention? Yes, gabapentin may cause fluid retention and induce edema in arms and legs. Experts believe that this side effect can also be Hello! I have been on Gabapentin for Neuropathic back pain only for one month and am at the max dose of 3600 mg a day. It is helping with the pain however I am seeing the water retention. I work out daily and my clothes fit tighter and I can see swelling in my legs and abdominal bloat. Gabapentinoids can cause concentration-dependent peripheral edema of early onset. Reduced myogenic tone is the main mechanism of these non-cardiogenic edemas. In case of peripheral edema or heart failure, a drug etiology should be considered. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. Gabapentin induced edema, just like calcium channel blockers induced edema, is not associated with salt and water retention and hence diuretics are ineffective. Physicians, especially nephrologists, should be mindful of uncommon side effect of this commonly prescribed medication as distinguishing this early can prevent a lot of unnecessary work Gabapentin side effects are usually mild, and they may be less common with gabapentin ER forms. Examples of mild side effects that can happen include: Vertigo (dizziness) Feeling fatigued or sleepy. Fluid retention. Trouble balancing or controlling movement. Diarrhea or constipation. Nausea and vomiting. Brain fog. Headache. Weight gain. Dry mouth For the next 7 days, the patient continued to experience bilateral, painful, 3 to 4+ pitting edema despite compression socks and fluid restriction.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |