Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
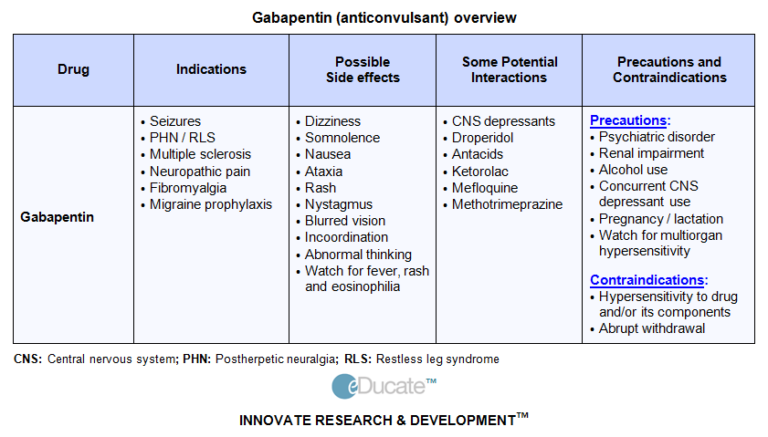
What is gabapentin? Gabapentin is an anti-seizure drug used to treat some types of epilepsy and neuropathic pain when no other pain medications are effective. In recent years, it has become a popular alternative for those who have fibromyalgia. vomiting in an 11-year-old girl and a 4-year-old boy who underwent craniotomies for posterior fossa tumor resection.11 Both patients continued to experience episodes for 2 months following surgery that did not respond to antiemetics. The 11-year-old patient was treated with a gabapentin dose of 300 mg orally twice daily and the 4-year- Prescribing information and the American Addiction Centers recommend tapering gabapentin over a minimum of one week. Using a slow taper by reducing the daily dose at a rate of 300 mg every 4 days may be particularly useful for elderly patients or other patients vulnerable to withdrawal symptoms. See tables 1 through 5 for case reports describing gabapentin tapers. Gabapentin may be given twice a day, but more often is given three times a day. If it is given three times a day, this should be first thing in the morning, early afternoon and at bedtime. Ideally, these times are at least 4 hours apart. Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® Why is it important for my child to take this medicine? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is gabapentin available as? • Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg • Capsules: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg; these contain small amounts of lactose • Liquid medicine: 50 mg in 1 mL; these may contain dose 1-5mg PO q8h. Max 10mg PO q8h Gabapentin PO: 5-40mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses (children ≥3 years old) Neuropathic pain and enhancement of opioid analgesia. Start low and titrate. Amitriptyline PO: Start 0.15mg/kg QHS; may advance over 2-3 weeks to 0.5-2mg/kg QHS Indications: headache prophylaxis, IBS, neuropathic pain,. Can prolong QT Gabapentin is currently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and children over 3 years of age. It is also indicated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia in adults.2,3. There are several studies of gabapentin in children with partial seizures. Learn about the common side effects of gabapentin in elderly patients, including dizziness, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and more. Explore the connection between gabapentin and depression, mechanisms behind gabapentin-related depression, and strategies to manage and mitigate side effects. Discover other significant concerns for elderly gabapentin users and the importance of personalized While there are no strict dietary restrictions for elderly patients on gabapentin, some guidelines can help: 1. Take gabapentin with food to reduce gastrointestinal side effects 2. Maintain a balanced diet and stay well-hydrated 3. Avoid antacids containing aluminum or magnesium within two hours of gabapentin doses I got an old bottle of Gabapentin mixed up with my recently filled bottle, took pills that were 2 years expired for about 3 days and noticed that I didn’t sleep as well. But upon waking after that 3rd dose, my lips were swollen from the inside out, and my head kind of hurt. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Sarah, a 42-year-old female, requests a prescription for an anorexiant to treat her obesity. A trial of phentermine is prescribed. Prescribing precautions include: 1. Understanding that obesity is a contraindication to prescribing phentermine 2. Anorexiants may cause tolerance and should only be prescribed for 6 months 3 Gabapentin has shown benefits for a variety of pain etiologies in adult patients, with off-label use as an adjunctive agent in pediatric patients occurring more frequently. To summarize the studies which evaluate safety and efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of pediatric pain. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Your child needs to take the medicine called gabapentin (say: GA-ba-pen-tin). This information sheet explains what gabapentin does, how to give it and what side effects or problems your child may have when they take this medicine. The nurse will teach the patient and the parents to immediately report which symptoms A. Increasing or severe abdominal pain B. Decreased or foul taste in the mouth C. Pruitus and dry skin D. Bone and joint pain, The nurse is caring for a 72-year-old patient taking gabapentin (Graalise, Horizant, Neurontin) for a seizure disorder. Used to treat restless legs syndrome in adults and occasionally in children/adolescents. Gradual dose increase helps to minimize sedation. May need to adjust dose in renal impairment. Space doses at least 2 hours from antacids (decreases absorption of gabapentin). Adverse effects: somnolence, ataxia, fatigue, and depression. Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is Gabapentin available as? Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg. Capsules: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg; these contain small amounts of lactose. Liquid medicine: 50 mg in 1 mL; these may contain acesulfame K and saccharin sodium (artificial sweeteners), and propylene glycol. If you have any concerns or Gabapentin, like all prescription drugs, does expire. Generally, the expiration date of gabapentin after manufacture is usually 2 to 3 years. After dispensing by a pharmacy to the patient, the expiration date is generally set at 1 year (from the date of dispensing). There is no evidence to suggest that gabapentin turns harmful after it has expired. There is growing use of gabapentin in infants younger than 1 year of age with neuropathic pain, irritability, NAS, feeding intolerance, rescue sedation and visceral hyperalgesia. 1 – 7 In this retrospective single center study, the mean gabapentin dose at initiation was 8.6 mg/kg/day at an initial median interval of every 24 hours and a One 300-mg tablet has produced lethal cardiac dysfunction in a 1-year-old child. 17 The narrow therapeutic margin of chloroquine necessitates careful anticipatory guidance with each prescription. Phenylpropanolamine is a common ingredient in over-the-counter decongestants and has a narrow therapeutic-toxic margin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |