Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
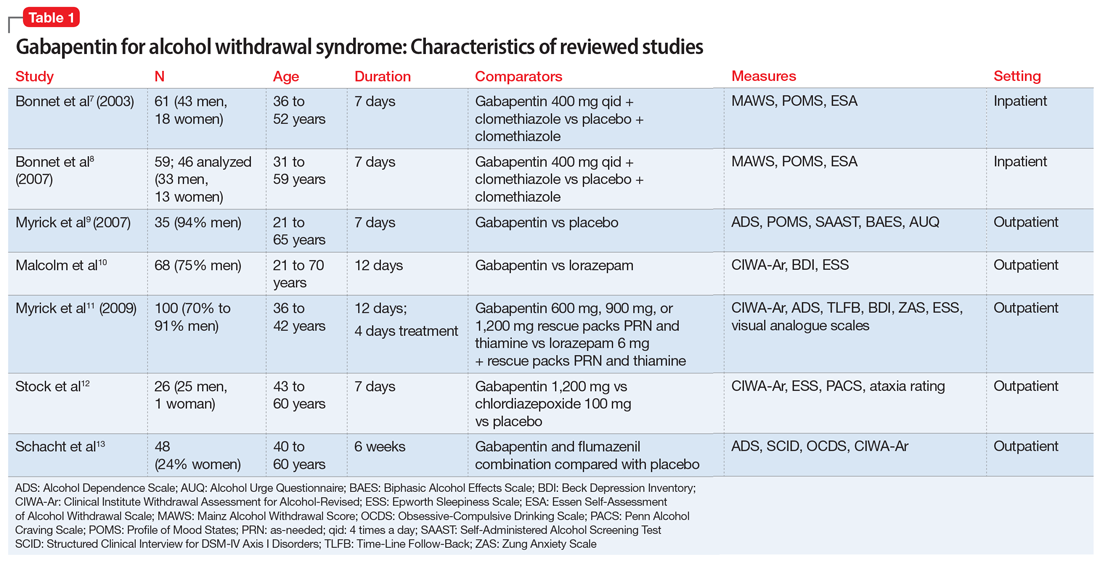
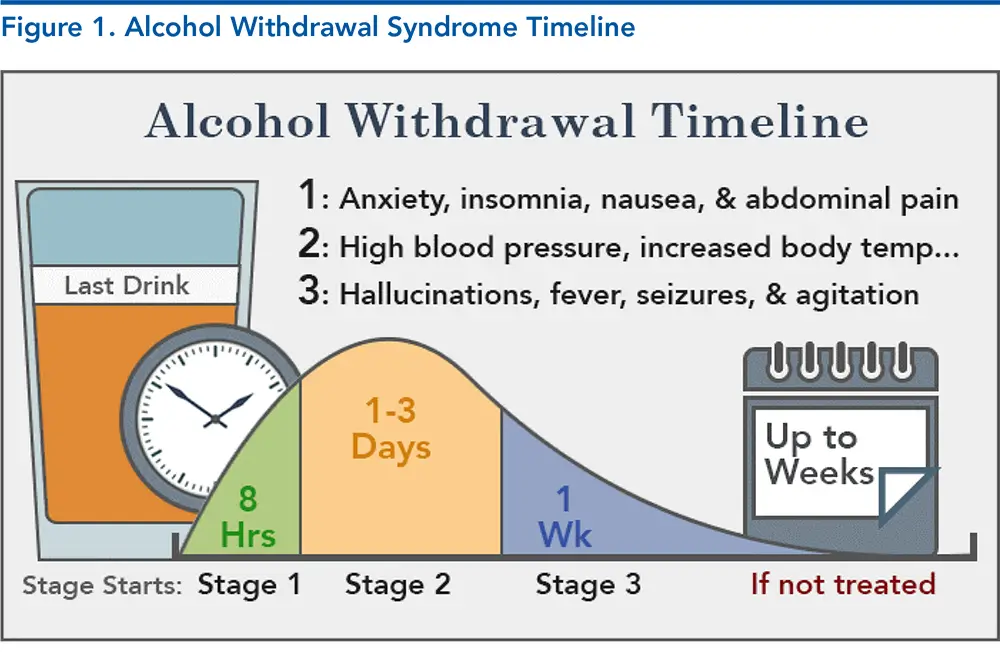
A meta-analysis of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder. AU Kranzler HR, Feinn R, Morris P, Hartwell EE SO Addiction. 2019;114(9):1547. Epub 2019 Jun 5. BACKGROUND AND AIMS Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate Individuals with alcohol use disorder may experience a withdrawal syndrome when they abruptly stop or sharply reduce consumption of alcohol. In some cases, these can progress to life threatening seizures or delirium tremens (DT). Pharmacologic treatment of alcohol use disorder has focused on altering the reinforcing effects of alcohol use. Medication development has focused on several neurotransmitter systems that mediate reinforcement including opioid, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and serotonin systems. Clinicians should be aware of gabapentin’s limitations for treating alcohol use disorder and be attentive to emerging data on risks and benefits. The anticonvulsant drug gabapentin is used off-label to treat alcohol-related withdrawal, cravings, anxiety, and insomnia. Study selection and data extraction: Studies were included wherein gabapentin was used as an adjunctive or primary treatment of alcohol dependence/withdrawal. Studies included participants diagnosed with alcohol use disorder using DSM-IV, DSM-IV-TR, DSM-5, or the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10). Abstract Background. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant medication, has been proposed as a treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD). A multisite study tested gabapentin enacarbil extended-release (GE-XR; 600 mg/twice a day), a prodrug formulation, combined with a computerized behavioral intervention, for AUD. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or -Opioid use disorder, prescribed opioids – For patients with alcohol use disorder and co-occurring opioid use disorder, our preference is to address both disorders with naltrexone (algorithm 1). However, naltrexone can only be started after a sufficient time has elapsed since last opioid exposure. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder. AU Kranzler HR, Feinn R, Morris P, Hartwell EE SO Addiction. 2019;114(9):1547. Epub 2019 Jun 5. BACKGROUND AND AIMS Studies of the efficacy of gabapentin for treating alcohol use disorder (AUD) have yielded mixed findings. The aims of our study were to estimate Evidence from single-site studies lend support to the safety and efficacy of gabapentin as a novel treatment for alcohol use disorder, with unique benefits for alcohol-related insomnia and negative affect, relative to available treatments. Ondansetron may be selectively efficacious in individuals with early-onset subtype of alcohol use disorder (onset of problem drinking prior to age 25 years) and in individuals with family history of alcohol use disorder . Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02349477. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. UpToDate Thus, gabapentin should only be used in mild alcohol withdrawal, including outpatient settings where benzodiazepines can’t be safely administered. Although future research is required to determine optimal dosing, at this point, it seems gabapentin 600 mg thrice-daily provides the best results. Is gabapentin an effective treatment for alcohol use disorder (AUD)? Bottom line. Gabapentin treatment avoided more heavy drinking days (> 5 standard drinks/day) than placebo (27% vs 9%). Gabapentin can be a second-line, off-label option to treat AUD. However, there is mixed evidence and concerns about abuse-misuse, and drug-related harms. Evidence Alcohol use disorders are the most prevalent of all substance use disorders worldwide. The global single-year prevalence has been estimated to be over 100 million individuals [ 1 ]. Additionally, nearly 3 million deaths (5.3 percent of all deaths globally) have been attributed to alcohol-related mortality in a single year [ 2 ]. Alcohol use disorder: Psychosocial management; Alcohol use disorder: Treatment overview; Alcohol withdrawal: Ambulatory management; Approach to the patient with visual hallucinations; Clinical manifestations and diagnosis of alcohol-associated steatosis and cirrhosis; Clinical manifestations and treatment of hypokalemia in adults CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Gabapentin (particularly the 1800-mg dosage) was effective in treating alcohol dependence and relapse-related symptoms of insomnia, dysphoria, and craving, with a favorable safety profile. Increased implementation of pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence in primary care may be a major benefit of gabapentin as In sustained remission: After full criteria for alcohol use disorder were previously met, none of the criteria for alcohol use disorder have been met at any time during a period of 12 months or longer (with the exception that Criterion A4, "Craving, or a strong desire or urge to use alcohol," may be met). Specify if:
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |