Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
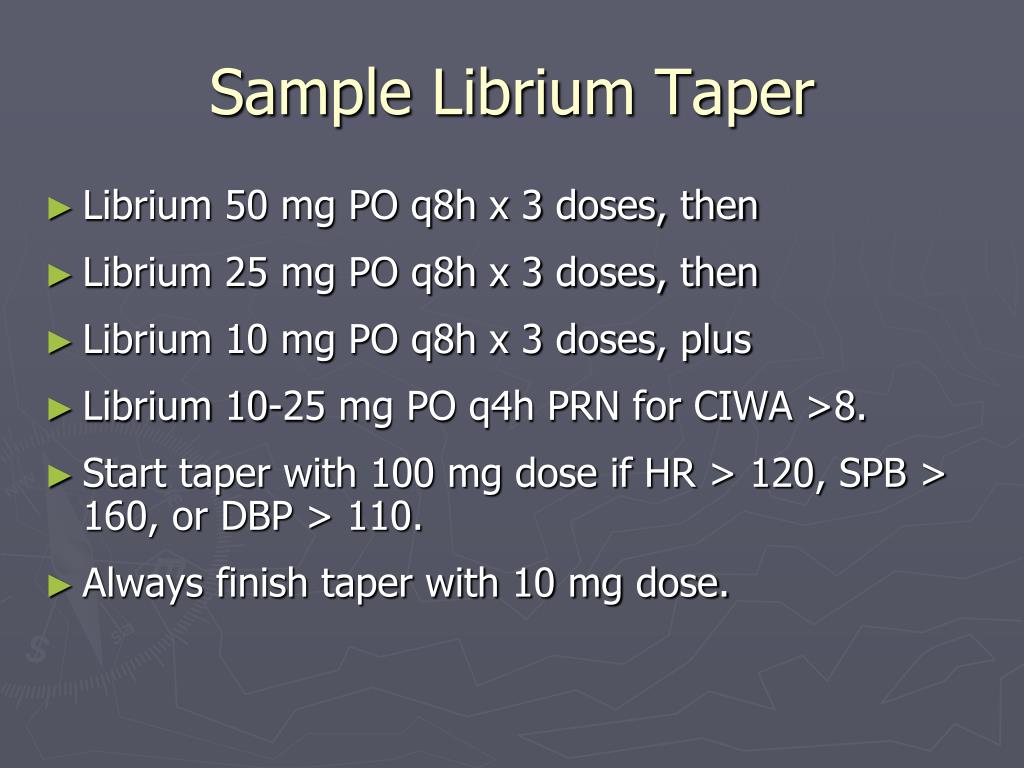
Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. Dosage Information. The following dosage information may be useful if you are considering taking gabapentin for withdrawal: Since it is a generic drug, dosage amount may vary depending on the brand and different brand name tablets are not interchangeable. 600-1800 mg per day is typically effective to mitigate symptoms. alcohol withdrawal.12,14,15 Gabapentin for Alcohol Withdrawal at VAPORHCS Although not currently included in the alcohol withdrawal protocol at Veterans Affairs Port-land Health Care System (VAPORHCS), gaba-pentin has been added to the standard of care in select patients per the discretion of the at-tending physician. Anecdotal reports of patients We hypothesized that patients treated with fixed-dose gabapentin taper would experience shorter clinically significant alcohol withdrawal with equivalent safety compared with those treated with CIWA-triggered benzodiazepines. Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Pharmacologic treatment of alcohol use disorder has focused on altering the reinforcing effects of alcohol use. Medication development has focused on several neurotransmitter systems that mediate reinforcement including opioid, glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, and serotonin systems. is useful only for milder forms of alcohol withdrawal. Hence, subsequent efforts on the use of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal have focused on outpatients. Outpatient trials reveal benefi ts over benzodiazepines Myrick et al3 compared gabapentin vs lorazepam in 100 outpatients seeking treatment for alcohol withdrawal. Participants Gabapentin may cause side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and dizziness. It is important to follow the prescribed dosage and seek medical attention if experiencing serious side effects or changes in mood or behavior. Gabapentin is prescribed by healthcare professionals and should only be taken under medical supervision. Objective: The current meta-analysis synthesizes previous findings on the effect of gabapentin on alcohol withdrawal and craving. Data Sources: Using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) methodology, a search for relevant English-language literature published between January 1999 and February 2019 was conducted using PubMed and Google Scholar with the Benzodiazepines are considered the drugs of choice for treating alcohol withdrawal. Gabapentin has been studied as a potential treatment for acute alcohol withdrawal, based on its modulatory action on brain excitatory (i.e., glutamergic) and inhibitory (i.e., GABAergic) pathways. Gabapentin appears to be more beneficial for mild rather than severe alcohol withdrawal. High dose Gabapentin (1800 mg/day) is also associated with decrease in percentage of heavy drinking days. CIWA protocol adapted from San Francisco General Hospital CIWA protocol form. Dixit D, Endicott J, Burry L, et al. Management of Acute Alcohol Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, especially gabapentin dose schedule (300 mg capsules four times per day with rapid titration to 600 mg three to four times per day as necessary) in conjunction with an alcohol withdrawal protocol utilizing a symptom-triggered benzodiazepine, versus management with lower dose (or no dose) gabapentin in conjunction with an alcohol Typically, Gabapentin is prescribed for alcohol withdrawal in doses ranging from 300 to 800 mg, three times daily, with adjustments made based on symptom severity and patient response. The precise dosage and treatment duration are determined by a healthcare professional, taking into account the individual’s alcohol use history and overall health. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. In the first double-blind, dose-response, controlled trial of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal, investigators randomized 100 treatment-seeking outpatients with alcohol dependence and moderate alcohol-withdrawal symptoms to 4 days of treatment with one of three gabapentin doses (200, 300, or 400 mg three times daily, tapered to twice daily on Gabapentin is an off-label medication for alcohol use disorder, sold under the brand names Neurontin, Gralise, and Horizant, among others. The medication was originally developed to treat epilepsy and is now FDA-indicated for a variety of additional uses, including the treatment of conditions like postherpetic neuralgia and restless leg syndrome.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |