Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 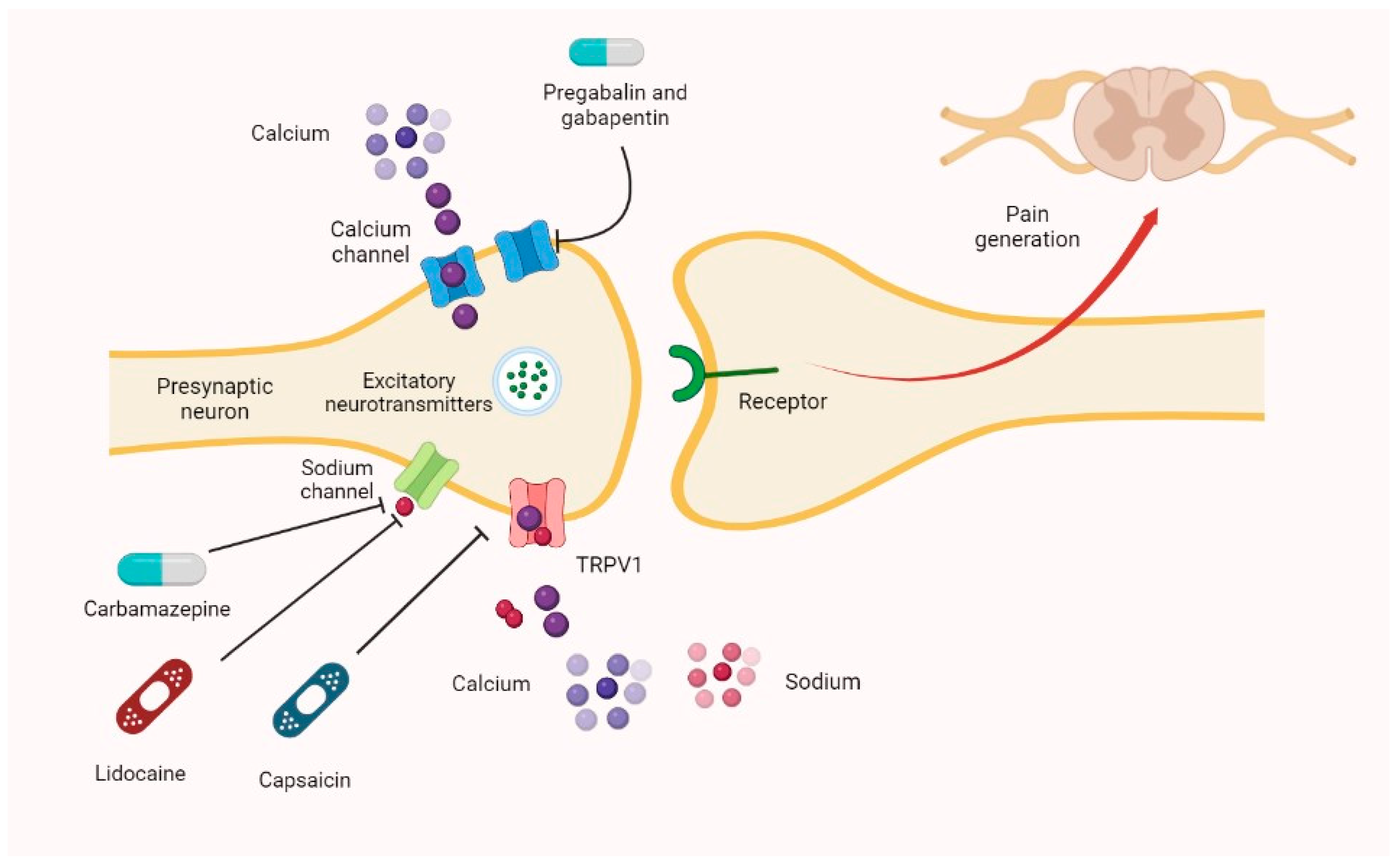 |
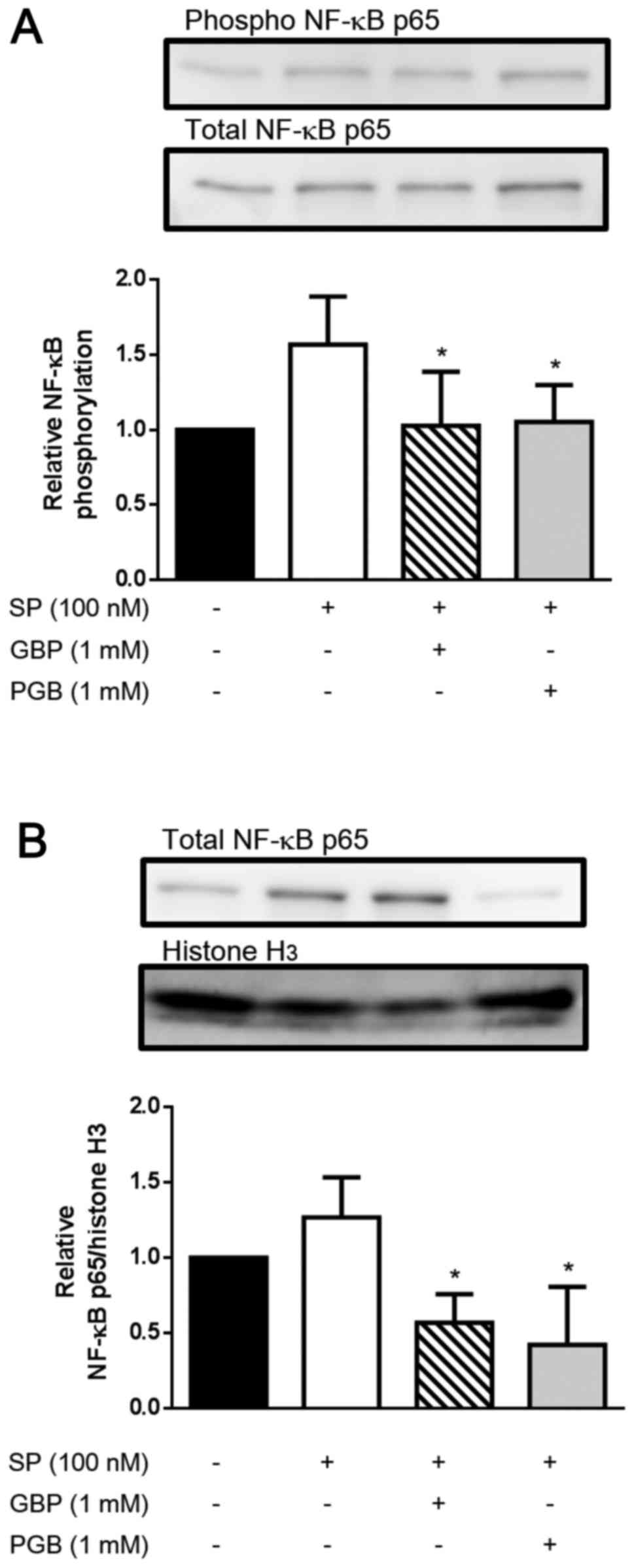
Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. Gabapentin is used to relieve neuropathic pain. They reduce pain by changing the way by which the nerves send messages to the brain. They also have an anti-inflammatory effect. They help in relaxing muscles. They work by reducing the frequency and severity of muscle cramps. Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) exert antinociceptive effects on chronic nociceptive responses with neuropathic or inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, it is considered that GBP and PGB exhibit anti‑inflammatory effects by modulating the substance P (SP)‑mediated neurokinin‑1 receptor (NK1R; a SP receptor) response. Thus, in the present study, the effects of GBP and PGB on SP Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that is also used for post-herpetic neuralgia and neuropathic pain. Recently, gabapentin showed anti-inflammatory effect. Nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) is a regulator of the inflammatory process, and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) i These studies suggest gabapentin has anti-inflammatory properties through various mechanisms, including regulating mast cell signaling, inhibiting pro-inflammatory cytokines, and modulating specific signaling pathways. Gabapentin exhibits significant anti-inflammatory properties through various mechanisms, including the activation of PPAR-gamma, reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and modulation of oxidative stress. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that is also used for post-herpetic neuralgia and neuropathic pain.Recently, gabapentin showed anti-inflammatory effect. Nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB) is a regulator of the inflammatory process, and Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor gamma (PPAR-gamma) is an important receptor involved in NFκB regulation. Technically, gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication although it's thought to possibly have some anti-inflammatory effects. It's not classified as a non-steroidal inflammatory drug like aspirin or ibuprofen. Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant and nerve pain medication. Learn more about whether or not it is effective against arthritis pain. Gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB) exert antinociceptive effects on chronic nociceptive responses with neuropathic or inflammatory conditions. Furthermore, it is considered that GBP and PGB exhibit anti‑inflammatory effects by modulating the substance P (SP)‑mediated neurokinin‑1 receptor (NK1R; Gabapentin has shown anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic properties in a mouse model of ovalbumin-induced asthma. The treatment significantly reduced lung inflammatory cell counts, serum LDH, and catalase activities, while increasing lung GSH concentration and SOD activity. The study indicates that gabapentin has no analgesic effect in normal skin, but may reduce primary mechanical allodynia in acute inflammation following a thermal injury. These observations suggest a clinical potential of gabapentin in the treatment of postoperative pain. Gabapentin was initially introduced in 1994 as an antiepileptic drug (AED), mainly due to partial seizures. It is an anticonvulsant whose side effects are well tolerated end well absorbed after oral administration with the maximum plasma concentration observed after 2–3 h. 2,5 Some of the most commonly reported side effects of gabapentin include dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue, ataxia, and the following nonprescription products may interact with gabapentin: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin, others) and naproxen (Aleve). Be sure to let your doctor and pharmacist know that you are taking these medications before you start taking gabapentin. Inflammatory pain is a very common component of most pain syndromes, making the inclusion of anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs [NSAIDs] or piprants [grapiprant]) an integral component of chronic pain therapy for all patients, unless use of these drugs is contraindicated (e.g., gastrointestinal ulceration, renal Gabapentin is primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain but may also have anti-inflammatory properties. It may be beneficial for managing conditions with an inflammatory component, such as fibromyalgia and rheumatoid arthritis. The short answer is that gabapentin is primarily a painkiller, specifically for neuropathic pain, rather than a direct anti-inflammatory. While some research suggests potential anti-inflammatory effects, these are secondary and not the drug’s primary mechanism of action. Gabapentin as an anti-inflammatory. Gabapentin, primarily used as an anticonvulsant and a medication to treat nerve pain, has also been found to possess anti-inflammatory properties. This means that it can help reduce inflammation in the body, offering potential benefits for individuals suffering from inflammatory conditions.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |