Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-this-normal-how-long-will-it-last-80197_final-01-61e907a86b19467487b731d369f8c978.png) |  |
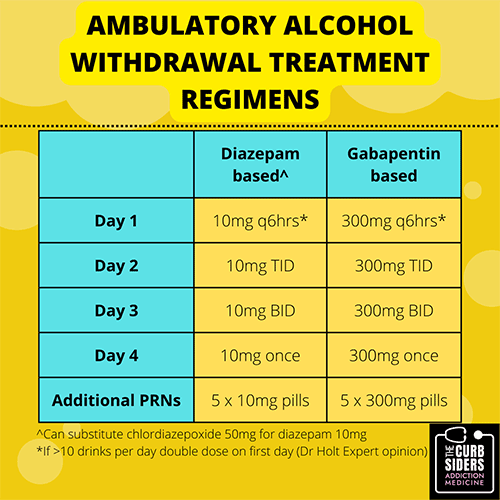
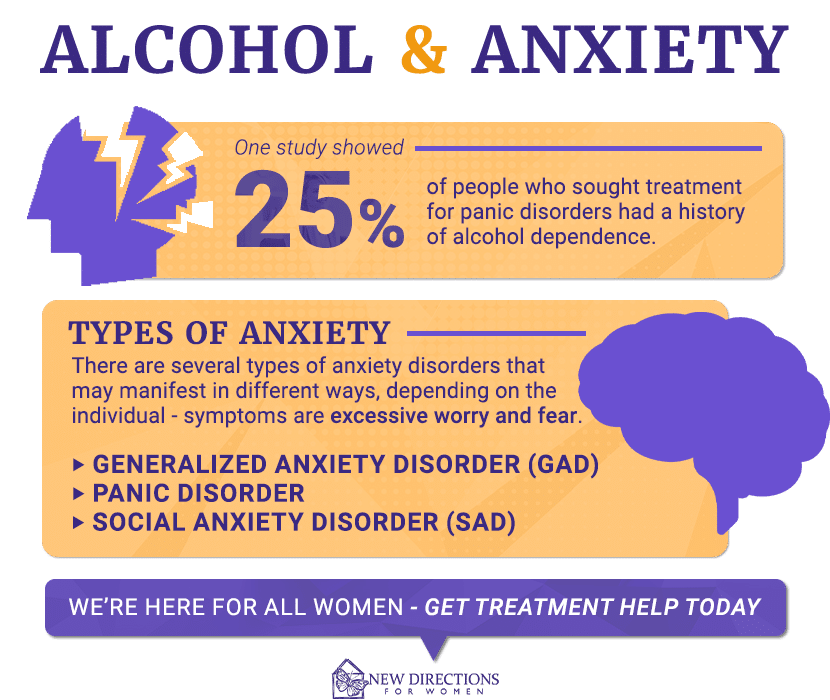
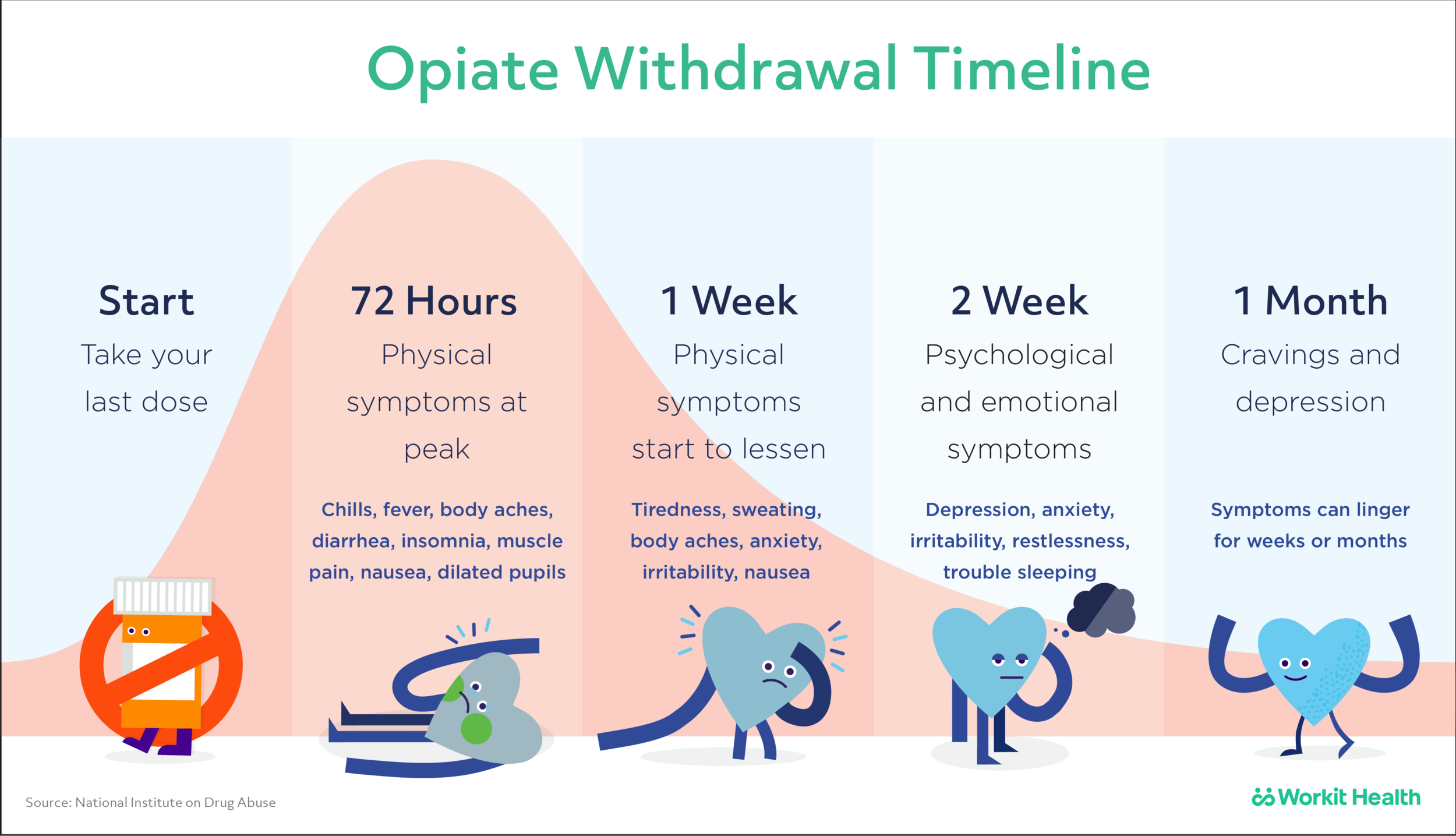
Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to People whose anxiety levels are very high during alcohol withdrawal may get relief from their symptoms by taking gabapentin, which has minor anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) properties. This medicine can work very well at boosting emotional regulation by affecting brain neurotransmitters. Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Conclusions: Our analysis of pooled data provides evidence that the use of gabapentin to manage alcohol withdrawal symptomatology and related cravings is at least moderately effective. However, given the limited number of available well-designed studies, these findings require further support through more rigorously designed studies. Evidence also suggests gabapentin is more effective in reducing the symptoms of alcohol withdrawal and certain types of anxiety than conditions like bipolar disorder, panic disorder, or panic attacks. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that helps to control and reduce severe epileptic seizures. According to a 2020 study, people who took gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal tolerated it well. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation. A study published this week concluded that gabapentin can relieve alcohol withdrawal symptoms but is most effective for people with a history of more severe symptoms after a few days of Baseline drinking levels and anxiety levels may be associated with the protracted withdrawal syndrome, previously implicated in the clinical response to gabapentin. However, these analyses underscore motivation for change and self-efficacy as predictors of clinical response to GE-XR, suggesting these established constructs should receive is useful only for milder forms of alcohol withdrawal. Hence, subsequent efforts on the use of gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal have focused on outpatients. Outpatient trials reveal benefi ts over benzodiazepines Myrick et al3 compared gabapentin vs lorazepam in 100 outpatients seeking treatment for alcohol withdrawal. Participants This study showed that gabapentin is efficacious in promoting abstinence and reducing drinking in individuals with alcohol use disorder and especially so in those with more alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Although an estimated 30 million people meet criteria for alcohol use disorder (AUD), few receive appropriate pharmacotherapy. Gabapentin is used off-label use for fibromyalgia, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, resistant depressants, mood disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, alcohol withdrawal, postoperative analgesia, migraine prophylaxis, interstitial cystitis, painful diabetic neuropathy, social phobia, generalized tonic-clonic seizures, pruritus, insomnia Gabapentin and Withdrawal Gabapentin withdrawal can occur when someone who has been taking gabapentin for a long period of time suddenly stops taking the medication. Gabapentin withdrawal can cause a number of unpleasant symptoms‚ including⁚ Anxiety; Insomnia; Tremors; Seizures; Gabapentin withdrawal can be severe in some cases. However, recent comprehensive reviews of the extant literature conclude that gabapentin should not be considered a stand-alone treatment for severe alcohol withdrawal because of ineffectiveness in suppressing alcohol withdrawal-related seizures.[79,80] Initiating gabapentin dose titration in conjunction with alcohol detoxification may assist in Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or More broadly, gabapentin is considered clinically useful in treating anxiety, insomnia, neuropathic pain, some other pain conditions, and alcohol withdrawal. It can be especially helpful in curbing alcohol use if you struggle with any of these other conditions at the same time. Evidence supports gabapentin as a treatment for alcohol withdrawal and alcohol use disorder. There is sufficient evidence to consider gabapentin as a third-line treatment for social anxiety disorder and severe panic disorder. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. Study selection and data extraction: English-language prospective studies evaluating gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and dependence were evaluated. Data synthesis: A total of 10 publications utilizing gabapentin in alcohol withdrawal (n = 5) and alcohol dependence (n = 5) were included in this review. Limited data suggest that gabapentin can
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/is-this-normal-how-long-will-it-last-80197_final-01-61e907a86b19467487b731d369f8c978.png) |  |