Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
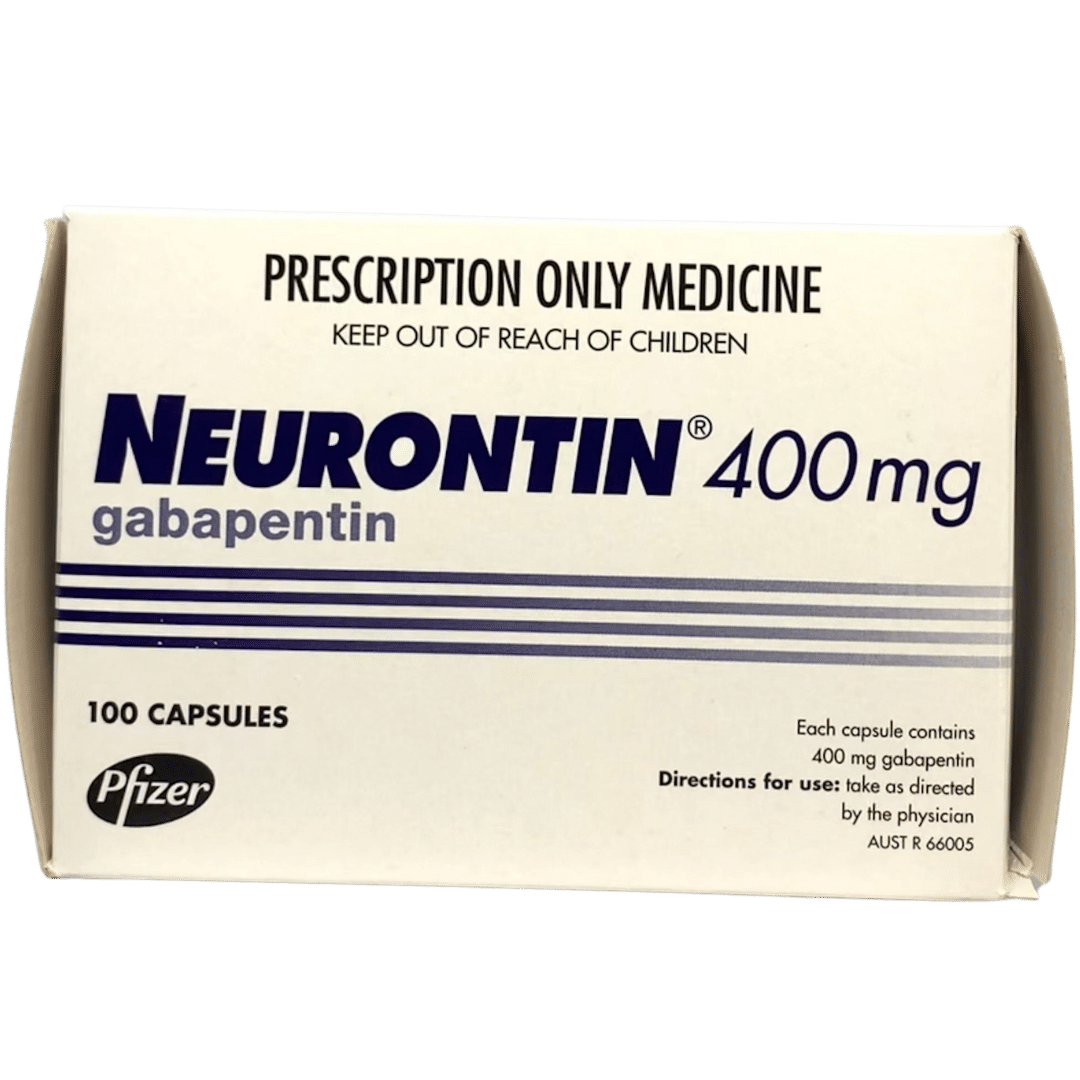
Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there Gabapentin, while slower, may still be effective for individuals with specific anxiety profiles, such as social anxiety. It may also be a better option for individuals who have both anxiety and chronic pain or those seeking a medication with a lower risk of misuse. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA approved to treat seizures and nerve pain from shingles. It has many off-label uses as well, including treatment for alcohol use disorder and anxiety. We don’t know exactly how gabapentin works. But we know it mimics a chemical called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Gabapentinoids are an efective treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy; there is increasing evidence that they are not efective for people with sciatica or non-specific low back pain. There is also growing concern of a rise in gabapentinoid misuse and dependence. What are gabapentinoids? The New Zealand Formulary. The NZF is an independent resource providing healthcare professionals with clinically validated medicines information and guidance on best practice, enabling healthcare professionals to select safe and effective medicines for individual patients. Conversely, gabapentin is not a first-line treatment for anxiety and may work better for some individuals who have chronic anxiety or comorbid conditions. The effectiveness can vary based on individual response, so it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment option for anxiety management. The potential synergistic effects of gabapentin on sleep quality when used for both sleep and anxiety are particularly interesting. By reducing anxiety levels, gabapentin may help create a more relaxed state conducive to falling asleep and staying asleep throughout the night. One medication that is being used off-label for anxiety is called gabapentin. Here we’ll look at the use of gabapentin for anxiety, and explore the pros and cons of this protocol. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin belongs to the group of drugs called anticonvulsants, sold under the brand name Neurontin to treat chronic nerve pain. A clear pattern of remission or mild anxiety on total daily doses of gabapentin ≥ 900 mg/day and severe anxiety at doses < 600 mg/day was observed. In the absence of randomized controlled trials, these findings may offer clinically important clues about dosing and effectiveness of gabapentin in GAD. Stopping gabapentin suddenly may worse your condition or increase your chance of experiencing withdrawal symptoms, such as sleeplessness, headache, nausea (feeling sick), anxiety or excessive sweating. Gabapentin may be effective for anxiety, but it’s usually not a first-choice medication for this use. Other medications have been studied more for anxiety, and they’re typically tried first. The recommended gabapentin dosage for anxiety and other conditions can range from 300 mg to 3,600 mg per day. Gabapentinoids are an effective treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy; there is increasing evidence that they are not effective for people with sciatica or non-specific low back pain. There is also growing concern of a rise in gabapentinoid misuse and dependence. What are gabapentinoids? Whether you’re already taking gabapentin for an anxiety disorder or are curious if you might benefit from it, you may be wondering how effective it is, how it works, and if there are side effects. Here we’ll cover everything you need to know about gabapentin for anxiety. What is Gabapentin? Gabapentin was originally approved to treat epilepsy in humans. However, gabapentin became more useful as a drug to control nerve pain. More recently, the inhibitory (reducing brain activity) effects of gabapentin have been useful to control anxiety in animals, especially when being transported. Generalised anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders. Anxiety is a normal human emotion that affects most people at some time. 1 It becomes a disorder when it is of greater intensity and duration than expected and if it leads to impairment/avoidance behaviours or disability. 1 Anxiety disorders are the most prevalent mental health condition in the community, yet many Timing: Take gabapentin at the same times each day. You can take gabapentin with or without food. Try taking it with food if it makes you feel sick (nauseous). Swallow the capsules whole, with a glass of water: If you have problems swallowing the capsule, you can open it and mix the contents with apple sauce or orange juice, just before taking it. Gabapentin users with GAD have been demonstrated to have fewer irritable episodes, cut back on alcohol use as a self-medication, also experience fewer symptoms of depression, feel less anxious when thinking about the future, and improve their phobic avoidance (going out in public more often). Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Sedation is the main potential side effect of gabapentin, and the level of sleepiness varies from patient to patient. Although evidence is limited, some studies show gabapentin can help with anxiety symptoms. One 2020 review suggests gabapentin may help with different types of situational anxiety,
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |