Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
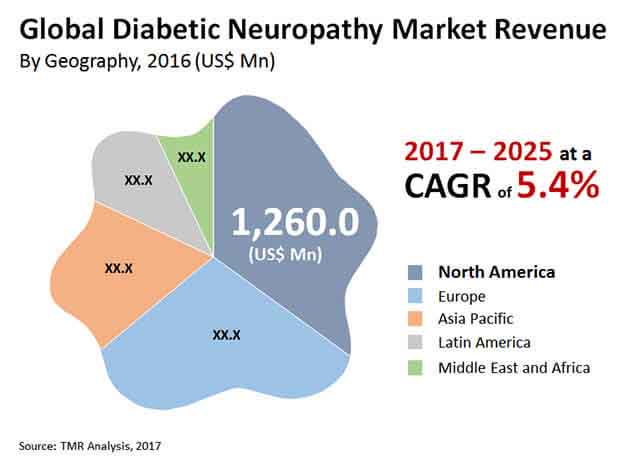
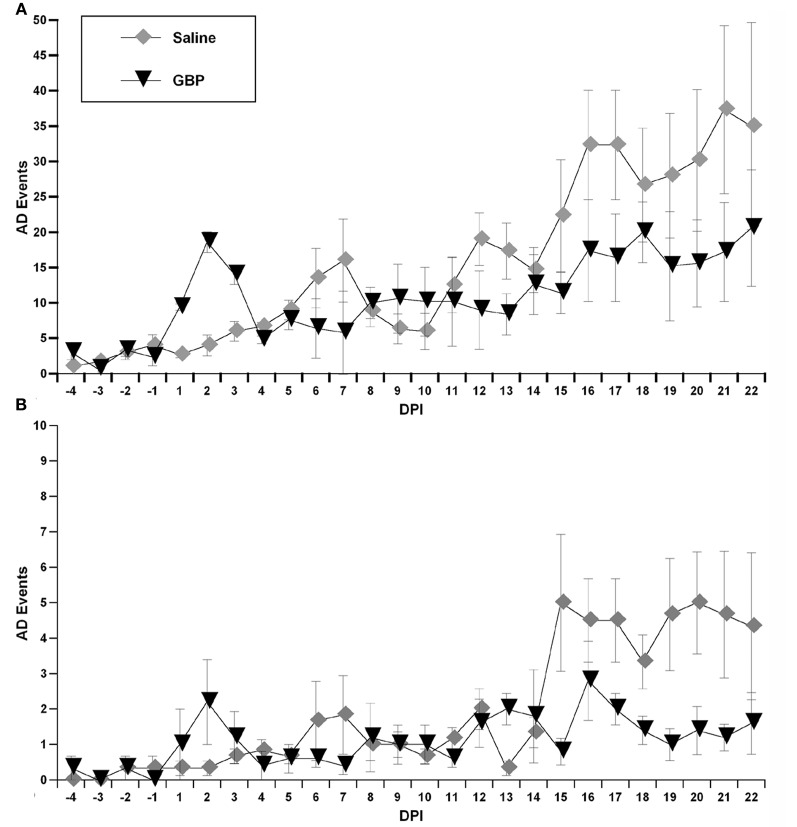
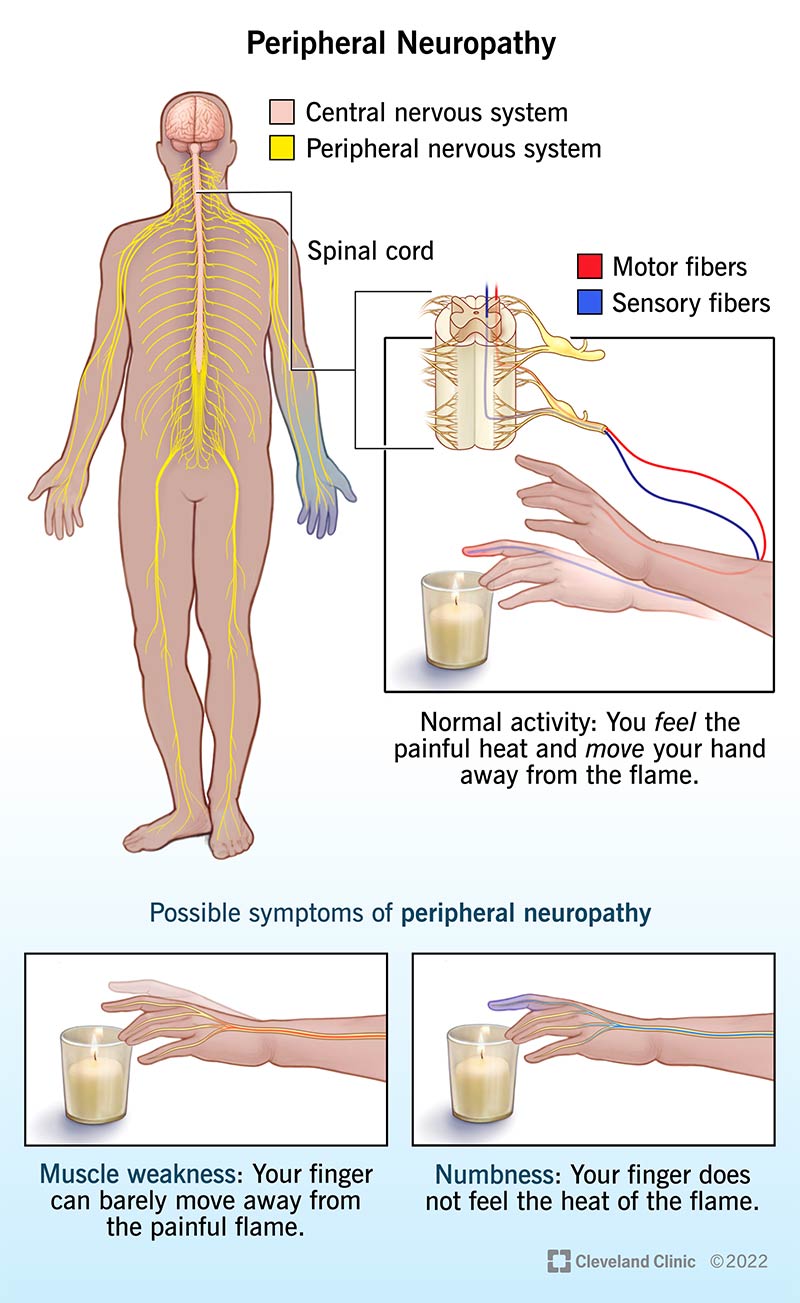
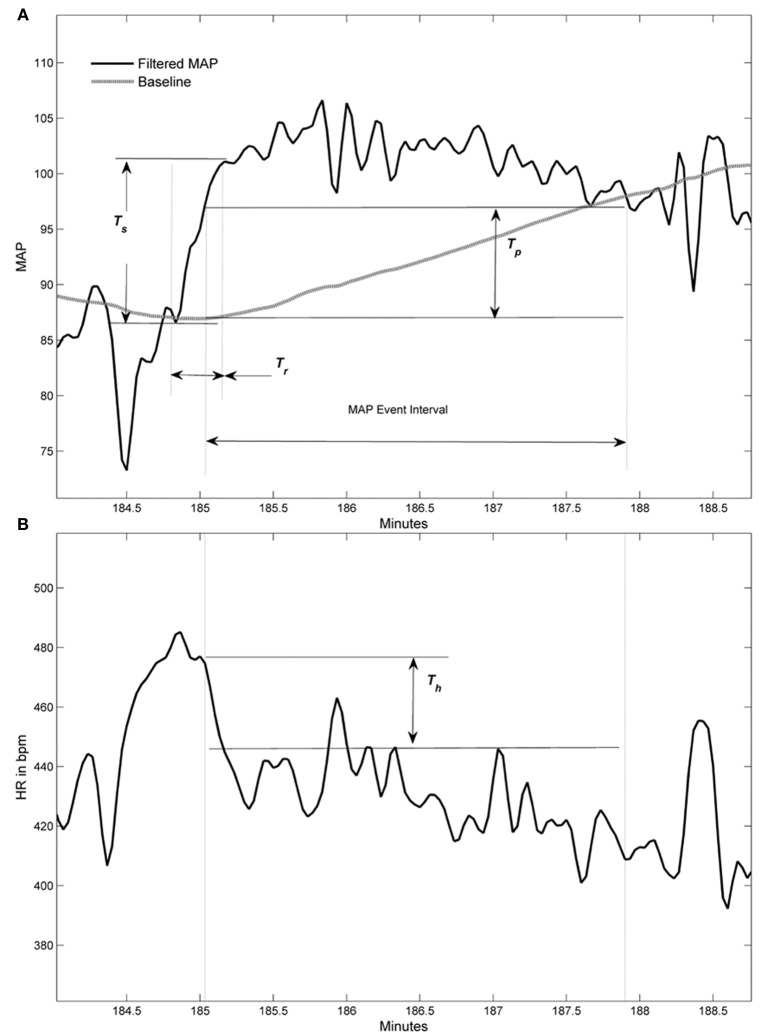
The drug gabapentin, most often used as a pain reliever, has been found in mice models to prevent autonomic dysfunction if applied early enough after injury. Treatment of autonomic neuropathy includes: Treating the underlying disease. The first goal of treating autonomic neuropathy is to manage the disease or condition damaging your nerves. If diabetes is causing your nerve damage, you'll need to tightly control blood sugar to prevent damage from progressing. Sensory neuropathy affects these groups of nerves. Autonomic nerve neuropathy. Autonomic nerves control functions that you are not conscious of, such as breathing and heartbeat. Damage to these nerves can be serious. Combination neuropathies. You may have a mix of 2 or 3 of these other types of neuropathies, such as a sensory-motor neuropathy. Gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) also is an option. Side effects may include drowsiness, dizziness, and swelling in the hands and feet. Antidepressants. Some antidepressants ease nerve pain, even if you aren't depressed. Tricyclic antidepressants may help with mild to moderate nerve pain. The three systematic reviews summarized in this report examined the efficacy and safety of treatments for patients with any type of neuropathic pain, 8 painful diabetic neuropathy, 9 or fibromyalgia. 10 All the reviews included gabapentin, pregabalin, TCAs, and SNRIs. Small fiber neuropathy is a condition that affects the small nerve fibers in the skin, causing various sensory symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness. Additionally, SFN can affect autonomic nerve fibers, which control functions such as blood pressure regulation, sweating, and digestion. Most patients with DPN will remain pain-free; however, painful DPN (PDPN) occurs in 6–34% of all DM patients and is associated with reduced health-related-quality-of-life and substantial economic burden. Symptomatic treatment of PDPN and diabetic autonomic neuropathy is the key treatment goals. For short-term treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be as effective as tricyclic antidepressants, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, or pregabalin (based on indirect evidence). Summary: Overall ratings: 3.3/5 Long term ratings: 3.5/5 This is a phase IV clinical study of how effective Gabapentin (gabapentin) is for Autonomic neuropathy and for what kind of people. “Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. This paper presents six subjects with dysautonomia following extremely severe traumatic brain injury where gabapentin controlled paroxysmal autonomic changes and posturing in the early post‐acute phase following limited success with conventional medication regimens. Sometimes other terms are used, including cryptogenic neuropathy or chronic polyneuropathy of undetermined cause. For some people, neuropathy is due to diabetes, alcohol abuse, medications, or other conditions. But in nearly half of all cases, sensory polyneuropathy is idiopathic. No cause, no cure I was just wondering if it is possible that gabapentin can sometimes make neuropathy pain worse. My EMG and biopsy results are negative for short fiber neuropathy so far. Interested in more discussions like this? Go to the Neuropathy Support Group. Gabapentin can be an effective treatment for brain damage symptoms such as neuropathy, seizures, and autonomic dysfunction. However, it is not without side effects or risks. Therefore, consult with your doctor carefully before trying it, and alert your doctor immediately if any side effects appear. Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy may affect the nerves controlling the automatic functions of the heart and circulation system (cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy). You may need treatment to increase your blood pressure or, in rare cases, a pacemaker. Find out more about complications of peripheral neuropathy. Different types of peripheral neuropathy If your lab tests show no condition that's causing the neuropathy, your health care professional might recommend watchful waiting to see if your neuropathy stays the same or gets better. Medicines. Medicines can be used to treat conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy. There also are medicines used to improve peripheral neuropathy Rarely, procedural studies such as autonomic testing and nerve biopsies may be necessary to aid in the diagnosis and management of peripheral neuropathy. Autonomic testing may be indicated because A Cochrane review of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults confirmed that gabapentin is associated with greater rates of pain relief compared with placebo in post-herpetic neuralgia and diabetic peripheral neuropathy, but it concluded that evidence for other neuropathic pain conditions was weak . The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |