Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/379962-bipolar-disorder-symptoms-and-diagnosis-5b1150af3418c60037552e47.png) |
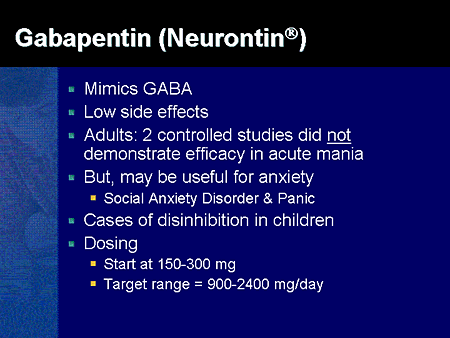 |  |
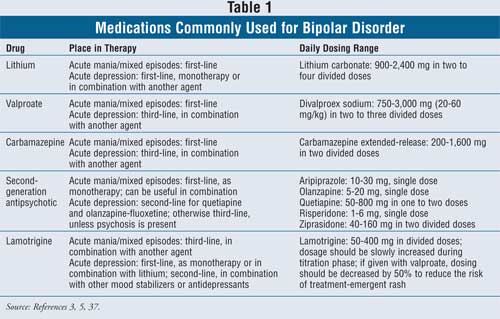
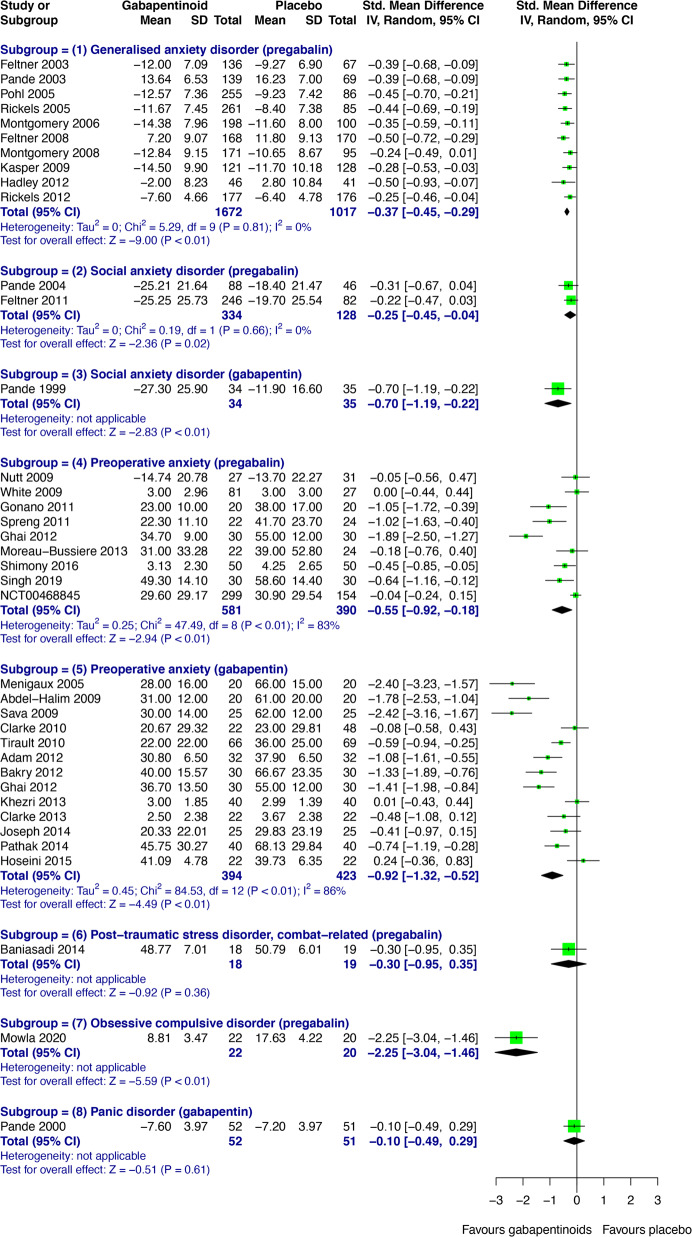
Gabapentin was effective in the treatment of mania and hypomania in patients with bipolar and schizoaffective disorders. If confirmed in controlled studies, these findings suggest that gabapentin represents a well-tolerated, rapidly acting antimanic agent. Researchers found that gabapentin does not help people with bipolar disorder. Learn more about the history of why some doctors prescribe gabapentin for bipolar as an adjunct therapy, even though there’s no evidence that it works for bipolar treatment or maintenance. Lithium and gabapentin. Gabapentin is currently being studied as a treatment for bipolar disorder, and there have been favorable reports regarding its potential as a mood stabilizer (82, 83). The advantages of gabapentin include the lack of interactions with other drugs in the cytochrome P450 system and the lack of protein binding . Since there "In my opinion, gabapentin has been a lifesaver. Conventional drugs for bipolar never have worked well for me. I have bipolar 1, OCD, GAD, PTSD, and a picking disorder. With my bipolar, I have mixed mania and rapid cycling. Since taking gabapentin, my family has noticed a 100% improvement. Recent anecdotal single case reports have suggested that the new antiepileptic drug gabapentin might be effective in the treatment of manic episodes and in the prophylaxis of bipolar disorder. In the present open trial, 14 patients with acute mania were treated for up to 21 days with gabapentin in a dose range from 1200 to 4800 mg/day. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Despite of the lack of evidence, reviews of gabapentin prescribing patterns in the United States show that this medication is still being used with alarming frequency for bipolar disorder. There are now five medications with specific, FDA approval for acute bipolar depression. A systematic search strategy employing different combinations of the keywords (bipolar, mania, hypomania, gabapentin, neurontin, gralise, gabarone, fanatrex, pregabalin, lyrica) was developed and performed in five databases namely OVID Medline, PubMed, ProQuest, PsychInfo and ScienceDirect from database inception to 7 June 2021. was a case report of a single patient with acute mania who improved with gabapentin alone,8 and another a case se-ries of moderate to marked improvement in 4 of 5 patients with bipolar or schizoaffective disorders receiving adjunc-tive gabapentin.9 Only 2 studies defined their diagnostic methods using DSM-IV criteria and utilized rating scales with bipolar I, bipolar II, and treat-ment-resistant depression.3 Thus, the new FDA approvals for bipolar mania for quetiapine and ziprasidone and pending for aripiprazole mean the possibility of adding new options to the treatment formula for bipolar spectrum disorders, including some with less risk of weight gain and per- A recent survey using the US-based TriNetX electronic health records network showed that gabapentin had been prescribed at least once in 13.6% of patients with bipolar disorder (BD), 11.5% with More specifically, can it prevent future episodes of mania and depression? Right now, there is no good evidence that gabapentin can be used for treating people with bipolar disorder. A psychiatrist answers common questions about mood stabilizers for bipolar depression. Topamax) or gabapentin (Neurontin), may be prescribed in some cases when other treatments haven’t For the acute treatment of BD, our primary outcome was the efficacy of gabapentin or pregabalin as measured by the following: (i) number of hospital admissions during the study period, (ii) length of hospital admission, (iii) change on validated manic or depressive symptom rating scales from baseline, (iv) change on validated psychotic symptom Gabapentin is FDA-approved for adjunctive treatment of partial complex seizures in individuals over 12 years old: June, 1995: Depakote, an anticonvulsant drug, is approved to treat bipolar mania: August, 1996: Lawsuit filed by a former Parke-Davis employee against Warner-Lambert for illegal marketing of gabapentin for off-label uses: December, 1999 The drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are sometimes prescribed for people with bipolar disorder or insomnia. Research found little evidence that they are effective. The drugs have side effects and can be addictive; the team calls for further trials. Gabapentin and pregabalin (collectively known as gabapentinoids) are licensed in the UK to treat pain and seizures. performed in epileptic patients make gabapentin an at-tractive medication choice for bipolar and schizoaffective patients. At this time, the effectiveness of gabapentin as a treatment for affective disorders has been studied very little. Stanton et al.7 described a successful treatment of acute mania with gabapentin (at 3600 mg/day) mono- Gabapentin appears to have acute anti-manic and anti-depressant properties as an adjunctive agent for refractory bipolar illness. Prospective double-blind studies are needed to further delineate its acute efficacy when used as monotherapy and its prophylactic efficacy as monotherapy or in conjuction Case series suggest benefit of adjunctive gabapentin for mood symptoms in bipolar disorder, though the existing randomized controlled trials do not support this finding. Gabapentin’s role in acute mania is equivocal, and limited data exist on its use as prophylaxis in bipolar disorder. We identified 40 open-label studies on the use of GBP in at least 600 patients with bipolar disorder (BP), manic, depressed, or mixed episodes and unipolar depression and four controlled studies.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/379962-bipolar-disorder-symptoms-and-diagnosis-5b1150af3418c60037552e47.png) |
 |  |