Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
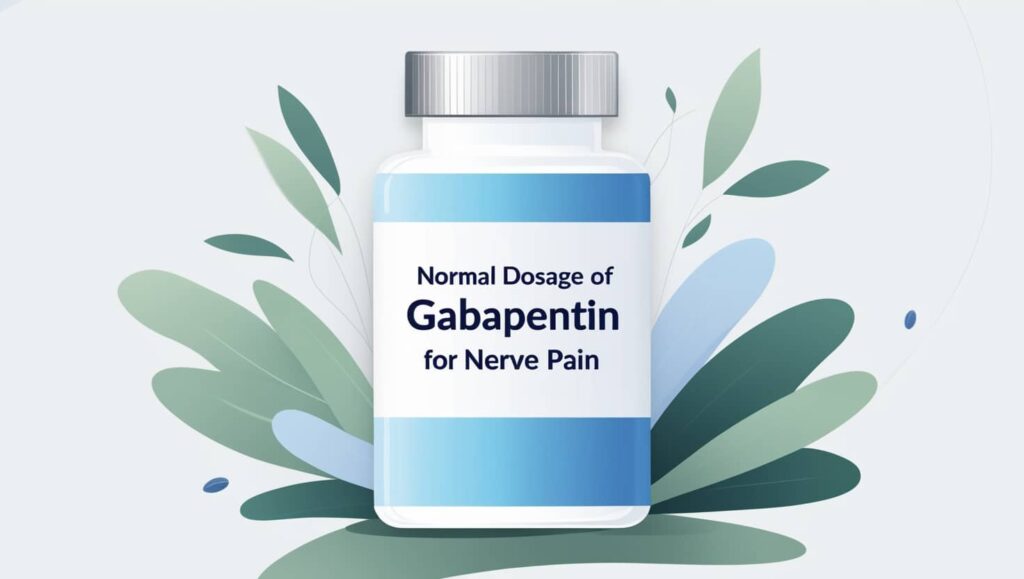
That’s the situation for millions of people who suffer from idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. The term “idiopathic” means that no cause can be identified; “sensory” refers to the type of nerve, in this case those carrying nerve signals such as pain or temperature; “poly” means “many” and “neuropathy” means nerve disease. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Neuropathic pain tends to be chronic, is complex, and can be difficult to treat effectively. Roughly 30% to 60% of people over age 60 who get shingles go on to develop a chronic pain syndrome called post-herpetic neuralgia. Learn about treatment options from a pain management specialist. Gabapentin can help relieve nerve pain in some people with postherpetic neuralgia (nerve pain after shingles) and peripheral diabetic neuropathy (nerve pain in the feet in people with diabetes). Nerve pain medications. A variety of drugs can be added to conventional pain relievers to reduce nerve pain. Adding one of these nerve pain medications won't completely take the pain away, but it may help. Anticonvulsants: These medications were developed to control seizures, but they also help to blunt pain signals in the nerves. Several are If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Gabapentin can usually be taken continuously for months or years to manage nerve pain, if providing benefits. Follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and report any side effects while on long-term gabapentin. Pregabalin is also used to treat nerve pain. It's often prescribed to people whose nerve pain hasn't improved with other medicines. Pregabalin may help reduce the pain you feel by changing Mechanism of Action: Gabapentin modulates nerve signals to alleviate pain. Conditions Treated: Effective for neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, and more. Dosing Guidelines: Start low and increase dosage based on individual response. Side Effects: Common effects include dizziness and fatigue; monitor closely. Comprehensive Care:Comprehensive Care: se your gabapentin dose. You may increase it more slowly if you feel you are getting side effects, for example by going back a step for an extra wee. before increasing again. You can stay at a lower dose if you are getting good pain relief (you don’t have to keep increasing the do. ilar manner . with a glass of water. You can take gabape. Gabapentin was shown to be better than placebo across all studies for IMMPACT outcomes. The review concentrated on gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater and reported that doses at or above this threshold were reasonably effective for treatment of various neuropathic pain types. The established therapeutic dosing for gabapentin in neuropathic pain is 1800-3600 mg/day in 3 divided doses in patients with normal renal function. Using antidepressants for nerve pain can have an added benefit, considering that chronic pain often coincides with depression.Chronic pain can make a person depressed, and depression can often Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burning. To evaluate the analgesic effectiveness and adverse effects of gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain management. Neurontin (gabapentin) is an immediate-release form used to treat seizures in adults and children who are at least 3 years old, in addition to nerve pain due to shingles. It comes as 100, 300, or 400 mg oral capsules; 600 mg and 800 mg oral tablets, and as a 250 mg per 5 mL oral solution. Why have I been prescribed Gabapentin? Gabapentin is used to treat some types of persistent pain. It is especially good for nerve pain, such as sharp, shooting, burning and stabbing types of pain. Gabapentin belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants which are also used to treat epilepsy. Nerve pain: Treats the sharp burning nerve pain often experienced after a shingles outbreak, from diabetes, or nerve pain following a spinal cord injury The typical starting dose of gabapentin 3. Medication Doesn't Address Underlying Causes of Nerve Pain. One of the most significant drawbacks of relying solely on gabapentin for neuropathy is that it doesn't tackle the root cause of your nerve pain. It's a symptomatic treatment—meaning it may mask the pain without addressing why you're experiencing neuropathy in the first place. Treatment for nerve pain generally requires a prescription, but these four OTC medications are also available. burning, or pain. Serious problems appear to be uncommon, even with highly
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |