Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
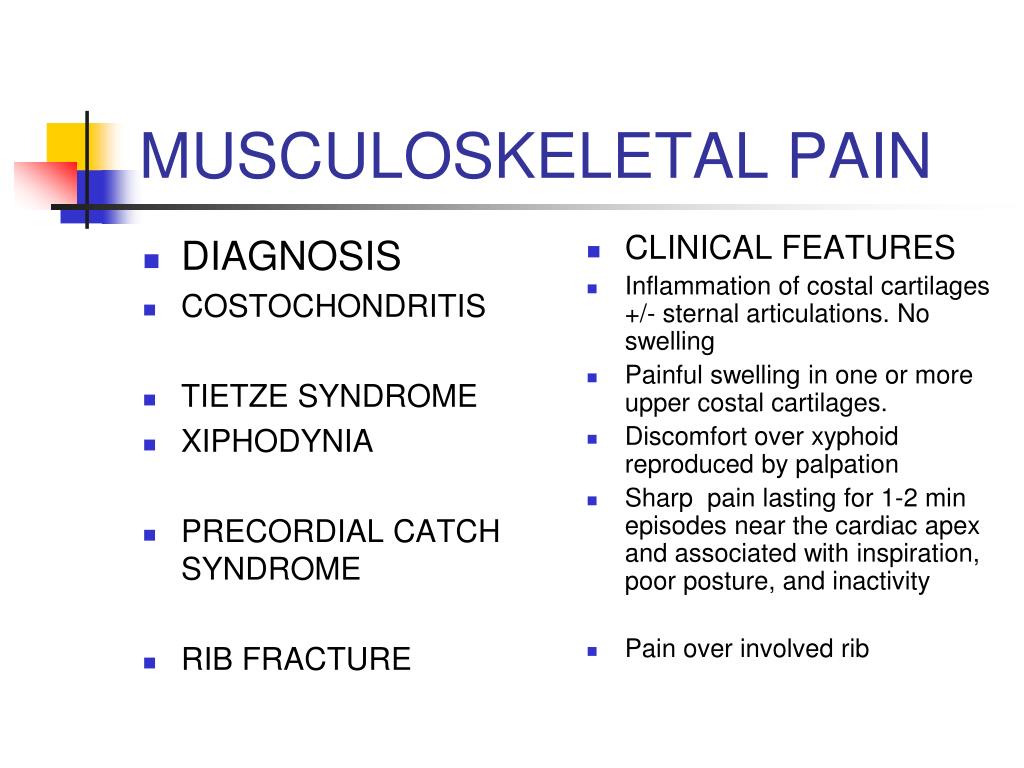 |  |
In 108 patients included in this study, both gabapentin and diclofenac were found to be effective and safe on the treatment of post-sternotomy chest pain and paresthesia (p<0,001). Adverse effects were observed in four patients with gabapentin (%7) and in two patients with diclofenac (%4). 3. Ochroch EA, Gottschalk A. Impact of acute pain and its management for thoracic surgical patients. Thorac Surg Clin. 2005;15:105-121. 4. Bayman EO, Brennan TJ. Incidence and severity of chronic pain at 3 and 6 months after thoracotomy: meta-analysis. J Pain. 2014;15(9):887-897. 5. Perkins FM, Kehlet H. Chronic pain as an outcome of surgery. Gabapentin may relieve refractory chest wall pain in some of these patients, particularly those with more severe pain. Further studies are warranted to define the role of gabapentin in cardiothoracic surgical practice. Sihoe et al. investigated the effectiveness of gabapentin for post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients . They reported that severe pain and chest wall paresthesia decreased in 73.3% and 75% of patients, respectively. Repeated minor trauma to your chest wall; Persistent chest pain of any type when you also have nausea, sweating, or pain in your left arm. usually gabapentin (Neurontin), may help with Gabapentin has also been shown to reduce immediate postoperative pain following mastectomies and other breast surgeries, and is often a component of ERAS protocols. 35,36 In their randomized control trial, Fassoulaki et al found that combining perioperative gabapentin and local anesthesia led to a significant decrease in chronic pain 3 months Pre- and postoperative gabapentin administration as part of a multimodal analgesic regimen may decrease postoperative pain, opioid consumption and demand for a “rescue drug”, as well as improve patient satisfaction. The Ravitch procedure is the reconstructive operation of an anterior chest wall deformity [1]. Chest wall pain or costochondritis, also called Tietze’s syndrome, is an inflammation which occurs between the tissues that connect the rib to the sternum. (Neurontin) has also shown some There are times when rib and chest pain may indicate a life-threatening condition. Intercostal neuralgia can cause severe and debilitating pain that makes it hard to breathe. Sometimes, rib cage pain or chest area pain can be a sign of a condition that may require emergency medical treatment. For example, chest pain may indicate a heart attack. Chest wall pain syndromes can emerge following local therapies for lung cancer and can adversely affect patients’ quality-of-life. This can occur after lung surgery, radiation therapy, or percutaneous image-guided thermal ablation. This review describes the multifactorial pathophysiology of chest wall pain syndromes that develop following surgical and non-surgical local therapies for lung Like heart pain, chest wall pain can be intense. Unlike heart pain, The discomfort from costochondritis can often be reproduced by pushing on the chest wall. Chest wall pain is usually not worsened by physical exertion (unless the rib cage is being stretched or compressed, as described above). Chest wall pain can last throughout the day Gabapentin appears safe and well tolerated when used for persistent post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients, although minor side effects do occur. Gabapentin may Summary: Chest pain is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Aspirin, and have Multiple sclerosis. Gabapentin appears safe and well tolerated when used for persistent post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients, although minor side effects do occur. Gabapentin may relieve refractory chest wall pain in some of these patients, particularly those with more severe pain. This chest wall pain, caused by inflammation, usually improves on its own. The epilepsy medication gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin) has also proved successful in Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that can be considered for patients with neuropathic pain refractory to non-opioid oral analgesics. 48 Gabapentin reduces pain by inhibiting the upregulation of α2δ-1 subunits that occurs following nerve injury to the dorsal horn neurons. 49 Sihoe et al. 50 used gabapentin to treat 45 patients with Chronic post-sternotomy chest pain and paresthesia (PCPP) are frequently seen and reduce the quality of life. We aimed to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of gabapentin compared with diclofenac in the treatment of PCPP and to elucidate the similarities of PCPP to neuropathic pain syndromes. Gabapentin is effective, safe and well tolerated when used for persistent postoperative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients: 33 patients (73.3%) noted reduction of pain Chest wall paraesthesia distinguishable from wound pain was relieved in 24 (75.0%) of 32 affected patients We study how severe was Chest pain, when it was recovered, drug effectiveness, race, and more among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin). This phase IV clinical study is created by eHealthMe based on reports submitted to eHealthMe, and is updated regularly. A 74 year old gentleman with neuropathic pain in the T5dermatome of the chest wall, was seen in the pain clinic, which had started since an episode of shingles earlier in the year. The previous treatment for his severe neuropathic pain had included Diclofenac, Paracetamol, Capsaicin and Amitriptyline.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |