Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
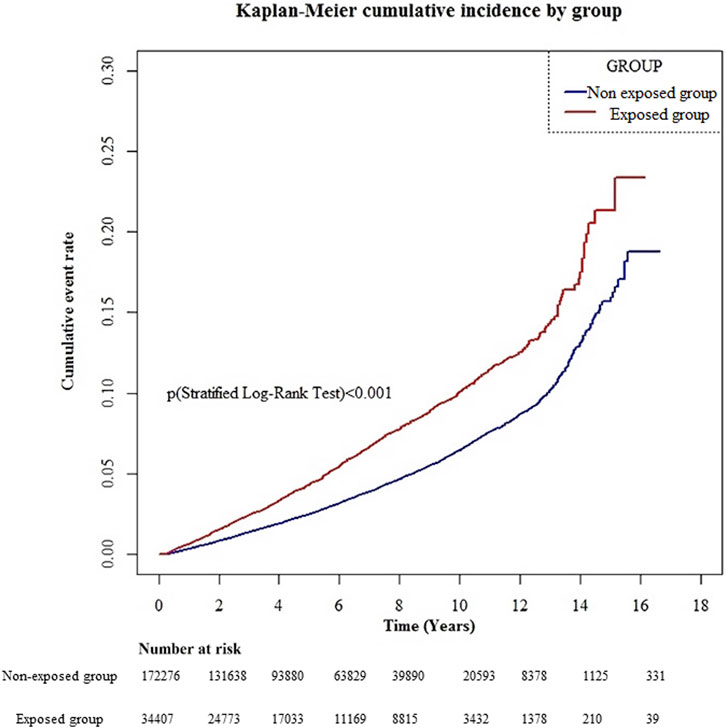
Applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria yielded 201,492 patients for the study: 25,373 in the dementia cohort and 174,930 in the non-dementia cohort. Post 1:1 matching, and after excluding recent gabapentin use (within three months of the index date), the study comprised 22,769 individuals in the dementia cohort and 22,644 in the non-dementia Long-term Gabapentin therapy for chronic pain is not associated with a differential risk of dementia across dosage levels, irrespective of age or gender. Further study into its potential cognitive impacts is essential. 1. Introduction. Gabapentin has been administered to several geriatric patients with bipolar disorder and patients with dementia. It has also been reported to be successful in the treatment of a 13-year-old boy with behavioural dyscontrol, a finding that suggested a possible role for gabapentin in the treatment of other behavioural disorders. Gabapentin use was significantly associated with decline in cognitive and functional status among older adults with initially normal cognition. Further studies are needed to examine the association. AD, VaD, dementia of traumatic brain injury, anoxic brain damage dementia, dementia NOS, alcoholic dementia, Parkinson's dementia: Gabapentin: 1318 mg day −1 average (300–3600 mg day −1) OASa, OASSYb, CMAIc, CGI-Id: 5-very much improved 12- much Improved 4-Minimally Improved 1-Unchanged 2-Dropout: Excessive sedation, 2: 4: Herrmann et al We present the case of a patient with incipient vascular dementia accompanied by nocturnal agitation, which was successfully treated with gabapentin. Gabapentin appears to be useful and well-tolerated in this indication. dementia patient was only followed for three weeks. Next, it is unclear whether gabapentin is equally efficacious in Alzheimer’s dementia versus concomitant Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia. Additionally, the age difference of 17?years may have also contributed to the 97-year old’s limited response to gabapentin. Preliminary low-grade evidence based on case series and case reviews suggests possible benefit of gabapentin and pregabalin in patients with BPSD in Alzheimer's disease. These benefits cannot be confirmed until well-powered randomized controlled trials are undertaken. The evidence of gabapentin and dementia is mixed, with two studies looking at hundreds of thousands of people and coming to completely different conclusions. TABLE 1. Dementia Patients Treated for Aggressive Behavior With Gabapentin ICD-10 Age and SexDiagnosis Behavioral Problem Vascular Risk Factors Brain Imaging Psychotropic Medication Before Treatment With Gabapentin Dose of Gabapentin Length of Follow-Up 74-year- old man Vascular dementia Physical and verbal aggression The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Gabapentin is an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain but may cause dizziness, drowsiness, and confusion in some older adults. Dementia: 3,153 (9.2 The adjusted odds ratio for dementia risk associated with gabapentin use was 0.91 (95 % C.I. 0.83-1.01), indicating no substantial increase in risk. Conclusion: Long-term Gabapentin therapy for chronic pain is not associated with a differential risk of dementia across dosage levels, irrespective of age or gender. Further study into its The first patient with Alzheimer's Dementia was followed for months while the second patient with mixed dementia patient was only followed for three weeks. Next, it is unclear whether gabapentin is equally efficacious in Alzheimer's dementia versus concomitant Alzheimer's and vascular dementia. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The results revealed that the risk of dementia associated with gabapentin or pregabalin exposure was significant in all subgroups except for the strata having depression or head injury. The risk of dementia development was higher in the younger group (age <50 years) than that in the older group. The prevalence of gabapentin use increased from 2006 to 2019, both in overall population and within every subgroup (i.e., cognitive status, age group, and sex). About 10–30% of gabapentin users reported to concurrently use gabapentin with opioids. Over one-half of gabapentin users with dementia concurrently used gabapentin with antidepressants. The authors describe the use of gabapentin in the treatment of 4 outpatients with dementia-associated agitation. On the basis of clinical case reports and the Overt Agitation Severity Scale, all 4 patients had reduced agitation with gabapentin. Three of 4 patients were successfully titrated to a full dose of 2,400mg/day. These findings suggest a possible role for gabapentin in the behavioral Especially in older adults, gabapentin is prescribed to treat behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD) (Kim et al., 2008). Several studies have reported that gabapentin has a deleterious effect on cognition (Leach et al., 1997; Meador et al., 1999; Shem et al., 2018). Aim: To evaluate low dose gabapentin in treatment of disruptive behavioral symptoms in patients with moderate- severe dementia with Lewy bodies. Findings: Improvement in symptoms seen by clinician and caregivers supported by changes on respective scales.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |