Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
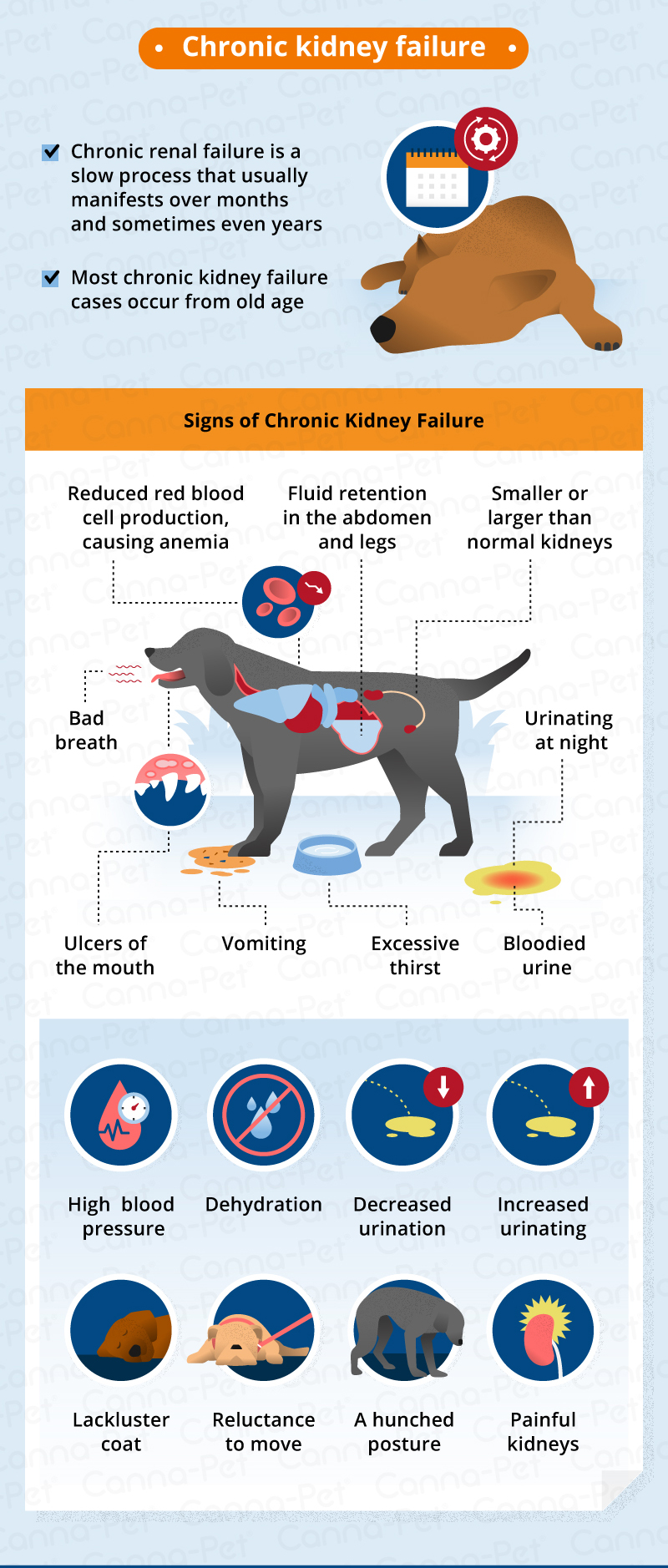
Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common side effects, how to manage them, and what Gabapentin Side Effects and Warnings. Gabapentin can cause side effects in dogs, including lethargy and dizziness. In addition, there are some warnings that you should be aware of when using this medication. What are the side effects of gabapentin in dogs? Anytime you notice side effects from a medication, you should consult with your veterinarian. Gabapentin is generally safe for dogs as long as dog parents follow guidelines and veterinary instructions. Typical side effects include: Less common, more serious side effects may occur. What Are the Side Effects of Gabapentin in Dogs? Sedation is the main potential side effect of gabapentin, and the level of sleepiness varies from patient to patient. Veterinarians will prescribe a starting dose, and if this results in the dog becoming a little too sedate, the veterinarian will taper the dose down to the most effective one. Although dogs with kidney disease may need a lower dose due to slower excretion, gabapentin does not seem to have adverse effects on the kidneys like NSAIDs do. One of the drawbacks to gabapentin as a pain medication, however, is that it does not have anti-inflammatory effects like NSAIDs do. It should be used with extreme caution in dogs with kidney or liver disease. The most common side effects of gabapentin in dogs include: Drowsiness; Loss of Serious side effects in dogs are uncommon when gabapentin is used at prescribed doses. Higher doses may cause more sedation and problems with walking and balance. Careful use of gabapentin is important for dogs with significant liver or kidney disease. While it’s generally safe for dogs with kidney disease, close monitoring is still essential to avoid potential side effects like sedation or constipation. Acetaminophen (Under Strict Vet Guidance) : While typically avoided in dogs, low-dose acetaminophen can be prescribed in specific cases where other options are insufficient, especially for Pre-existing Conditions: Dogs with kidney disease may require lower doses because gabapentin is primarily eliminated by the kidneys. Concurrent Medications: Gabapentin can interact with other drugs, potentially exacerbating side effects. Dogs with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, may require a lower dose or should not take gabapentin at all. Additionally, gabapentin should not be abruptly discontinued, as this can cause withdrawal seizures in dogs with epilepsy. Potential Side Effects of Gabapentin. The most reported side effects described by owners administering gabapentin to their dogs are sedation and ataxia (loss of coordination). What is gabapentin? Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. Gabapentin is used for dogs and is commonly prescribed by veterinarians to treat seizures, pain, and anxiety. It has a low risk of side effects. What is gabapentin used for in dogs? Gabapentin can treat and reduce the frequency of seizures and is commonly used as an anticonvulsant to treat or prevent seizures in dogs. Plus, the side effects are temporary. Since Gabapentin is a short-acting medication, its effects diminish after 24 hours of administration. However, the effects may persist longer in dogs with liver and kidney disease. Therefore, Gabapentin should be used with caution in dogs with: Liver and kidney problems ; Young puppies What is gabapentin? Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. **Answer:** Gabapentin can be used safely in senior dogs, but it is important to monitor them closely for any signs of side effects, as older dogs may be more susceptible to certain side effects. 13. **Concern:** Can gabapentin be used in dogs with liver or kidney disease? Serious side effects include cases of systemic hypersensitivity such as skin rashes, fever, swelling of the lymph nodes, mouth, tongue, and throat, and hypotension. The effects of this short-acting drug should stop within 24 hours, although they may last longer in pets with liver or kidney disease. So dogs with kidney or liver problems may have more prolonged side effects. Your veterinarian may want to monitor kidney and liver blood values when using gabapentin long-term. Recommended doses Is Gabapentin Safe For Dogs? That depends on what you mean by safe and your dog’s individual medical conditions. Most dogs tolerate gabapentin well, but sedation is a common side effect 1. Especially when starting or increasing a dose, monitor your dog around environmental dangers (stairs, pools, anything you would not let a toddler near). While gabapentin itself is unlikely to cause direct kidney damage, it’s essential to be aware of its metabolism, potential side effects, and how it interacts with dogs that have pre-existing kidney conditions. This article will explore these aspects in detail, providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions about your
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |