Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
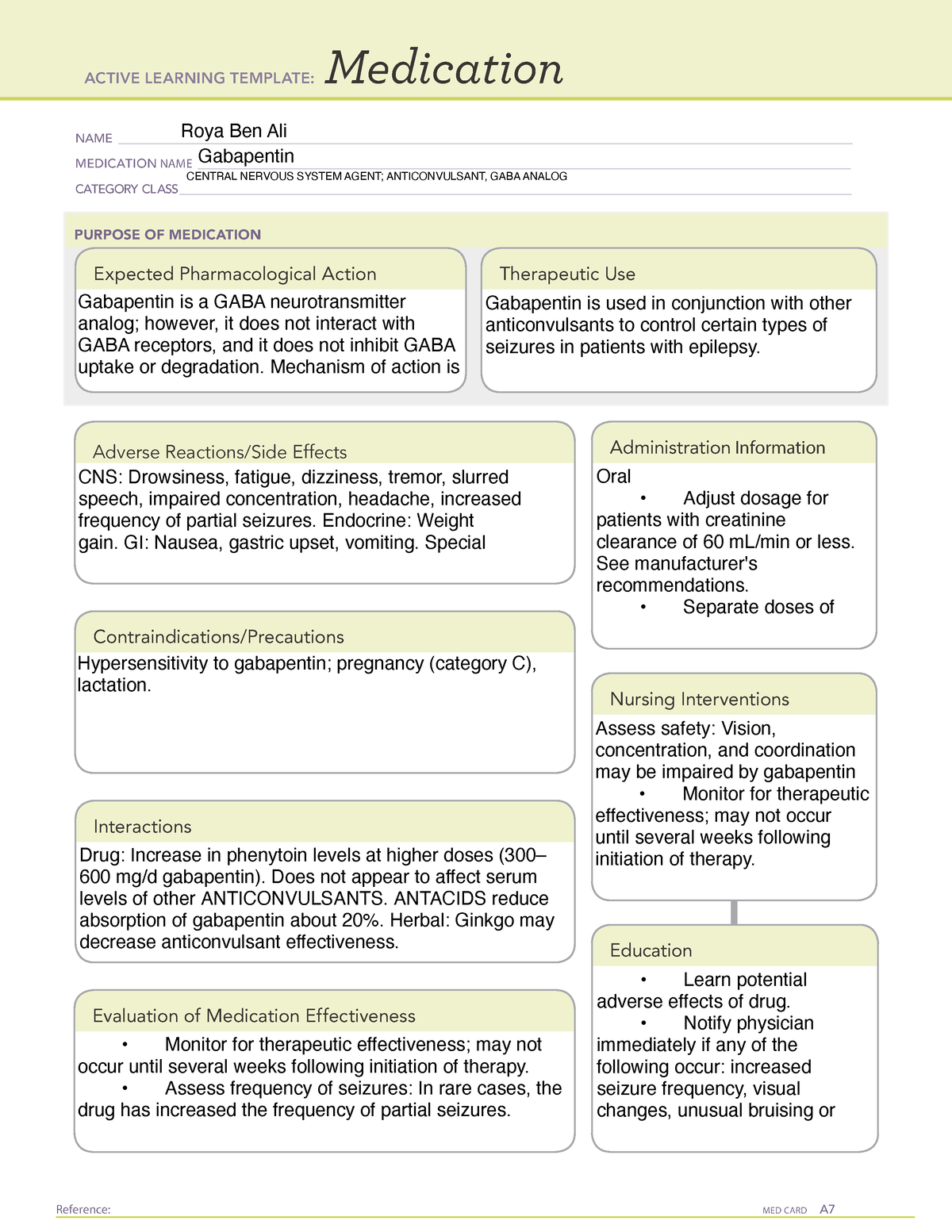
Gabapentin is effective for the treatment of alcohol dependence and can be used for treating anxiety, insomnia, headaches, and/or pain in patients who have comorbid substance use disorders (SUDs) or who are at high risk of substance abuse. Gabapentin has been shown to lead to dependence, addiction and withdrawal in some people, although when it was first approved in 1993 this risk was thought to be minimal. . Gabapentin has been increasingly associated with drug abuse, particularly in people who mix it with opioids, alcohol or other substanc Gabapentin, also known by the brand name Neurontin, is an anticonvulsant used for seizure disorders, as well as certain neuropathic pain conditions. It belongs to its own drug class, gabapentinoids. It is most commonly used to treat epilepsy, restless leg syndrome, hot flashes, and neuropathic pain. 33 recent users of gabapentin among non-medical users in Kentucky identified in two cohort studies: 67% (n = 22) reported use of prescription opioids, 15% reported use of gabapentin to get high Pregabalin: Snellgrove et al., 2017 : 2012–13: Germany: Cross-sectional study Structured questionnaire and urine samples – Gabapentin is approved to prevent and control partial seizures, relieve postherpetic neuralgia after shingles and moderate-to-severe restless legs syndrome. Learn what side effects to watch for, drugs to avoid while taking gabapentin, how to take gabapentin and other important questions and answers. The gabapentinoid drugs, gabapentin and pregabalin, are first-line treatments for neuropathic pain. The epidemics of chronic pain and opioid misuse have given rise to the widespread use of non-opioid drugs such as the gabapentinoids for treatment. Unfortunately, the widespread use of gabapentinoid drugs has resulted in reports of misuse and abuse. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is a “novel anticonvulsant” and is FDA indicated for partial seizures and post-herpetic neuralgia. But the drug has long been heavily marketed to psychiatrists to treat a range of conditions from bipolar disorder to anxiety to alcohol withdrawal. When one drug becomes less available, drug users historically seek out alternatives, he said. “What is most surprising is the sheer magnitude of its use.” The share of Appalachian drug users who reported using gabapentin to get high increased nearly 30-fold from 2008 to 2014, according to a 2015 study in the American Journal of Psychiatry. Gabapentin (often prescribed under its brand name Neurontin) is an anti-convulsant/sedative medication used to treat a wide range of medical issues, ranging from partial seizures to shingles-related nerve pain and restless leg syndrome. 1 It is also commonly used off-label to treat an even wider variety of physical and mental health concerns, in Gabapentin is a prescription anticonvulsant used to treat epileptic seizures, postherpetic neuralgia, and restless legs syndrome. Postherpetic neuralgia is pain caused by shingles, which can last many months after having the illness. Brand names for Gabapentin include Gralise, Horizant, and Neurotin. Additional questions related to gabapentin misuse included, “During the past 90 days, on how many days have you used gabapentin for fun, to get high, to relax, or to come down,” “In the past 90 days, about how many gabapentin pills did you use in a typical month,” and “How old were you the first time you used gabapentin for fun, to Gabapentin use can result in a number of physical and psychological effects, including suicidal thoughts and behaviors. If you or a loved one is using gabapentin, be aware of warning signs of suicide, such as: 7. Talk: Talking about being a burden to others. Talking about having no reason to live. Talking about killing themselves. Behavior: What are gabapentin side effects? While gabapentin can be helpful in a number of circumstances, some of the common side effects associated with taking the drug as directed include drowsiness The current work is targeted to review the risks of gabapentin misuse, its potential interactions with other drugs, side effects and use contraindications. This review consists of a total of 99 biographical references (from the year 1983 to 2016). Gabapentin is one of the recommended mainstays of evidence-based treatment. 3. Unfortunately, our clinical experience suggests that gabapentin is now prevalent as a drug of abuse. The drug’s effects vary with the user, dosage, past experience, psychiatric history, and expectations. Since its market release, gabapentin has been presumed to have no abuse potential and subsequently has been prescribed widely off-label, despite increasing reports of gabapentin misuse. This review estimates and describes the prevalence and effects of, motivations behind, and risk factors for gabapentin misuse, abuse, and diversion. Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. In fact, certain recreational users have gone as far as to suggest that Gabapentin or Neurontin is their new “drug of choice.” Why Gabapentin’s Recreational Use Has Increased. There are several reasons why Gabapentin (Neurontin) has become a target drug for recreational use. Gabapentin, a prescription medication approved for the treatment of seizures and neuralgia, is often prescribed off-label for substance use treatment, mental health problems, and pain. Emerging reports also suggest it is misused for the purpose of getting high.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |