Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-1317124199-9ff17073b0ba45099a2c6e0e779d7639.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
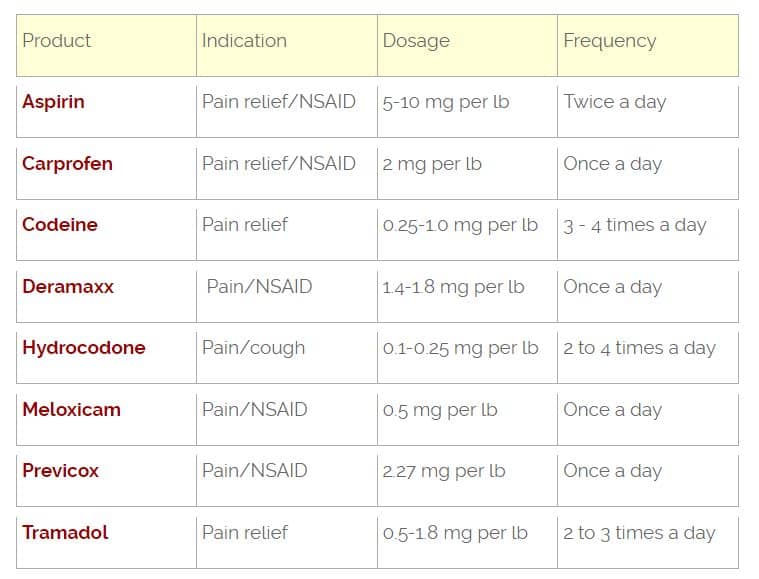
When your dog is suffering from pain, whether due to arthritis, surgery, or injury, you’ll likely hear about medications like Carprofen and Gabapentin. Both drugs are widely prescribed by veterinarians, but they work in different ways and are suited for different types of pain. Understanding the key differences between Carprofen and Gabapentin can help you make informed decisions about managing levels of pain can easily be underestimated. There are several good choices available to clinicians for pain management; effective choices for the management of otitis media/externa are listed in Table 2. Advise owners to monitor for less obvious indicators of pain, such as decreased interaction, anorexia, and lethargy, in combination Gabapentin is a commonly prescribed medication for dogs dealing with chronic pain, seizures, or anxiety. However, understanding the right dosage and how to use it safely can be challenging for pet owners. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed to dogs for pain management, particularly for conditions like arthritis, neuropathic pain, or to control seizures. While it’s an effective treatment for many dogs, it’s essential to understand the potential side effects that may occur, especially with long-term use. In this guide, we’ll explore the most common side effects, how to manage them, and what Gabapentin—Your vet might recommend giving carprofen and gabapentin for dogs together to increase your dog’s pain relief. This is a helpful combination because carprofen and gabapentin work differently in your dog’s system and have an additive effect to decrease pain. Effective treatment with gabapentin involves ongoing communication with a veterinarian. Regular check-ups and discussions about the dog’s response to the medication, behavior changes, and any side effects are vital. This open dialogue ensures the safe and effective use of gabapentin in managing your dog’s health conditions. Side Effects Veterinarians commonly prescribe gabapentin to treat pain, seizures, and anxiety in dogs. Gabapentin is a human medication, and its use in veterinary medicine is “off-label,” meaning it is not FDA-approved for pets. Key takeaways: Gabapentin is a medication that is approved for use in humans but is sometimes used off-label for dogs. For dogs, it is used for chronic pain management and is prescribed alone or together with another sedative to reduce anxiety and fear during certain events, such as travel or fireworks. Gabapentin (brand names: Neurontin®, Aclonium®, Equipax®, Gantin®, Gabarone®, Gralise®, Neurostil®, Progresse®) is an anti-seizure and pain medication that is used with other medications to treat seizures and chronic pain, primarily nerve pain, in dogs and cats. Gabapentin can treat and reduce the frequency of seizures and is commonly used as an anticonvulsant to treat or prevent seizures in dogs. Gabapentin may also be used to provide pain relief for dogs, particularly when other medications have proved ineffective or are not well tolerated. Gabapentin for dogs is an anti-seizure and pain medication commonly prescribed to dogs by veterinarians. Gabapentin for dogs may be helpful for treating chronic pain especially nerve pain that is secondary to neurological diseases such as slipped discs. The most common side effects of gabapentin in dogs include sedation and dizziness. Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for dogs with chronic pain from conditions like osteoarthritis, spondylosis, intervertebral disc disease, and many more. It’s particularly effective when used in combination with other pain-relievers, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications like meloxicam, firocoxib, and carprofen. Gabapentin can also be used as a pain medication for dogs, specifically in the case of chronic nerve-related pain. Your veterinarian might prescribe gabapentin if your dog has intervertebral disk disease, any other condition leading to compression of the nerves or spinal cord, or even in some cases of arthritis pain. For dogs, it’s used to treat seizures, anxiety, and nerve pain. It works by blocking calcium channels in the brain to suppress overly stimulated neurons that cause anxiety, nerve Gabapentin works best for managing neuropathic pain – pain that stems from issues like extruded discs and nerve injuries. It is also very efficient in managing joint pain and postoperative pain. When used together with NSAIDs and opioids, it boosts their efficacy and allows lowering their doses. The effectiveness of gabapentin can vary from one dog to another, and it may not provide sufficient pain relief for all types of pain. For more severe or acute pain in dogs, stronger pain medications like opioids (e.g., tramadol) or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often prescribed.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | /GettyImages-1317124199-9ff17073b0ba45099a2c6e0e779d7639.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |