Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
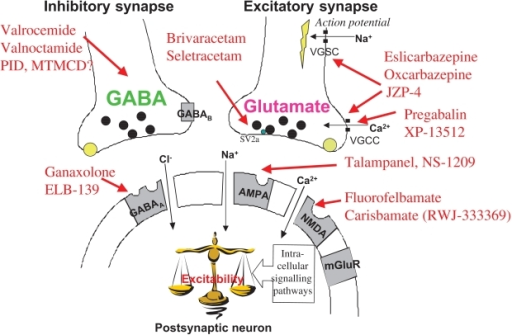
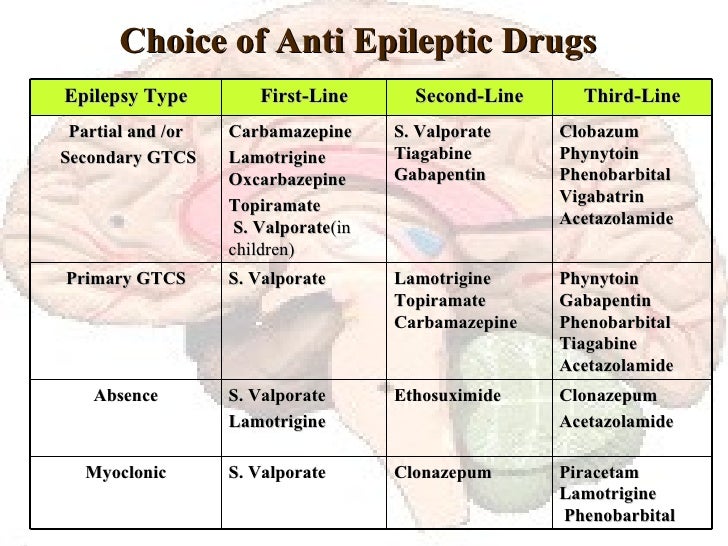
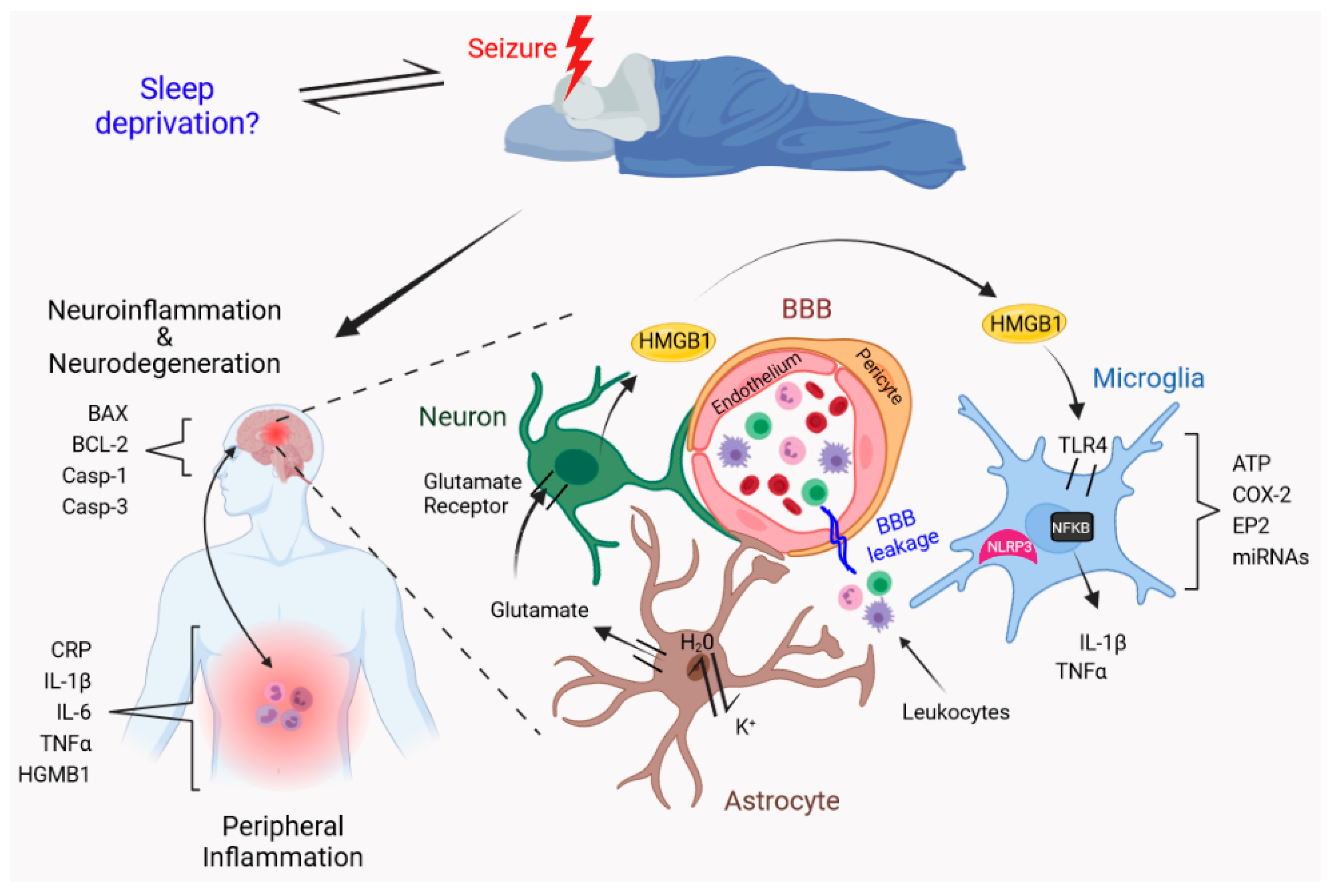
However, the AAN/AES guidelines recommend gabapentin and lamotrigine, as first‐line monotherapy in patients aged ≥60 years with new‐onset focal epilepsy. 22 A recent systematic review and network meta‐analysis showed that lacosamide, lamotrigine, and levetiracetam had the highest probability of ranking best for achieving seizure freedom Only two trials comparing gabapentin to placebo reported seizure freedom data (Appleton 1999; Yamauchi 2006). Yamauchi 2006 reported no participants attaining seizure freedom, whereas Appleton 1999 reported 3/119 participants receiving gabapentin as seizure‐free compared to 1/128 participants receiving placebo. Due to the very small numbers Gabapentin is FDA-approved as Neurontin to treat partial seizures in adults and children with epilepsy. Partial seizures are convulsions that originate from a single location in the brain. Neurontin is also approved to treat a type of nerve pain called postherpetic neuralgia, or PHN. Gabapentin Effectiveness as Initial Monotherapy for Epileptic Seizures and Syndromes. Adults with partial-onset seizures: Derived from existing evidence, GBP is effective as initial monotherapy for adults with recently diagnosed or untreated partial-onset seizures. 38, 42, 43 Children may be treated with gabapentin 23 to 78 mg/kg per day. Based on controlled and open trials, the majority of patients will tolerate gabapentin well enough for an adequate therapeutic assessment. Titration to effect can be accomplished rapidly, if necessary; however, as with other AEDs, optimal seizure control may take months to achieve. Epilepsy is a common, complex disease in which abrupt, abnormal synchronous or excessive electrical activity in the brain causes seizures. Seizures may manifest as variable motor, autonomic, and/or behavioral clinical signs. 1 The seizures are typically episodic and short but may change in frequency, length, and severity over time. Gabapentin is 1 of many antiseizure medications available for the treatment of epilepsy in adults; however, there are potential risks associated with its use. Therefore, it is important to determine the place of therapy of gabapentin in the treatment of epilepsy. Gabapentin . Gabapentin is a recent addition to the human anti-convulsant market, which has primarily been used as an adjunctive drug for humans with uncontrolled partial seizures with and without secondary generalization. Gabapentin is well absorbed from the duodenum in dogs with maximum blood levels reached in 1 hour after oral administration. Gabapentin - Brand name: Neurontin. Read about how gabapentin treats epilepsy and nerve pain and how to take it. Gabapentin for partial seizures: According to the guidelines from the American Epilepsy Society, clinicians might consider gabapentin as a potential option for patients aged 60 and older with new-onset focal epilepsy, as it could be similarly effective and better tolerated compared to carbamazepine. In this review we summarised the evidence from randomised controlled trials of gabapentin used as monotherapy for the treatment of focal epilepsy, both newly diagnosed and drug-resistant, with or without secondary generalisation. Gabapentin (GA ba PEN tin) has been approved by the FDA as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of focal onset seizures, with and without secondary generalization, in pediatric patients 3 years and older with epilepsy. The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin only as adjunctive treatment for refractory focal seizures in children, young people, and adults and for treatment of children and young people with benign epilepsy with centrotemporal spikes, Panayiotopoulos syndrome, or late‐onset childhood occipital epilepsy A 17-year-old man presents with myoclonic seizures followed by generalized a tonic-clonic seizure after awakening. He denies any recent head trauma or substance abuse. He reports to being sleep deprived for the past week due to final examinations. Routine EEG testing is significant for 5-Hz bilateral polyspike and slow wave discharges. Gabapentin. Gabapentin is a recent addition to the human anti-convulsant market, which has primarily been used as an adjunctive drug for humans with uncontrolled partial seizures with and without secondary generalization. Gabapentin is well absorbed from the duodenum in dogs with maximum blood levels reached in 1 hour after oral administration. Gabapentin is available in Canada by prescription only. Known as. Neurontin. Uses. Effective against partial seizures (including secondary generalized tonic-clonic). Somewhat effective against primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Ineffective or worsens absence, myoclonic or tonic/atonic type seizures. How to Use Numerous studies have investigated the efficacy of gabapentin in epilepsy treatment. Clinical trials and retrospective studies have consistently demonstrated the beneficial effects of gabapentin in reducing seizure frequency and improving overall seizure control. Gabapentin is used to help control partial seizures (convulsions) in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine cannot cure epilepsy and will only work to control seizures for as long as you continue to take it. Gabapentin is also used to manage a condition called postherpetic neuralgia, which is pain that occurs after shingles. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is FDA-approved to treat focal onset seizures. The way gabapentin works for seizures also isn’t quite clear. But it’s thought to act similarly to a brain chemical called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is believed to help soothe nerves in the brain. Gabapentin comes as an oral capsule, tablet, and liquid. Gabapentin is a Pfizer-made medication for focal aware and impaired seizures. For more information, visit the Epilepsy Foundation online.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |