Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
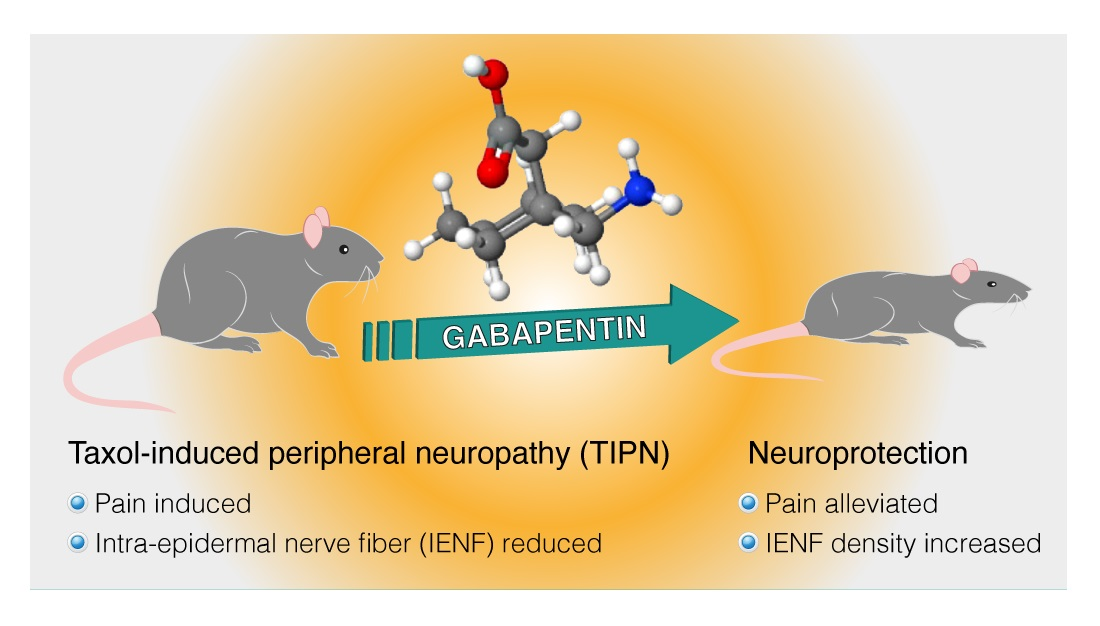
In this review, based on a systematic search of relevant literature, we aim to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Neuropathic pain, which occurs as a result of damage to neural tissue, includes phantom limb pain, compression neuropathies, peripheral neuropathies (e.g. due to Diabetic complications, chronic excessive alcohol intake, HIV infection, chemotherapy, idiopathic neuropathy), trauma, central pain (e.g. pain following stroke, spinal cord injury, and syringomyelia), and postherpetic neuralgia Other medicines that may be used include topiramate (Qudexy XR, Topamax, others), pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant). If the anti-seizure medicine you're using becomes less effective, your healthcare professional may increase the dose or switch to another type. Gabapentin is an oral antiepileptic agent with a proven analgesic effect in various traumatic neuropathic pain syndromes. We retrospectively examined the analgesic effect of gabapentin on non-dental and non-traumatic orofacial neuropathic pain. This study included 12 patients. Instead, get help from a doctor -- preferably an expert in treating nerve pain, like a neurologist or a pain management specialist. Together, you can come up with a treatment plan that will help Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN), or tic douloureux, is a rapid onset of stabbing, unilateral facial pain, lasting seconds to minutes, triggered by simple activities such as eating, brushing teeth, talking, or being exposed to a burst of cold air. If you have chronic pain in the face, we might prescribe you a medicine called gabapentin. Chronic pain (also called persistent pain) is long-term pain that lasts for more than 3 months. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is used to treat epilepsy, or to treat nerve pain. review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. Of the 92 who had received a trial of gabapentin, 43 reported reduction in facial pain. This benefit was Anti-seizure medications (anticonvulsants) were originally designed to treat people with epilepsy. But the nerve-calming qualities of some of these medications can also help quiet the burning, stabbing or shooting pain often caused by nerve damage. This procedure, unlike MVD, is intended to produce permanent facial numbness, which completely relieves the TN pain in most patients. For some patients, the nerve will gradually regrow, the numbness will disappear, and the pain will recur. If that happens, your physician will simply repeat the 10-minute procedure. Carbamazepine has also been shown to potentiate gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors made up of alpha1, beta2, and gamma2 subunits. This may be relevant to its efficacy in neuropathic pain. 24 In newly diagnosed cases of TN, the usual starting dose is 100 to 200 mg twice daily. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Treating trigeminal neuralgia often begins with medications. “Anticonvulsants such as carbamazepine, gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used to manage the pain. Muscle relaxants like baclofen and in some cases Botox injections or steroids may also be prescribed,” Dr. Jaikumar says. Accordingly, gabapentin has been shown to interact with the α 2 δ subunit of voltage-dependent Ca 2+ channels and to increase the concentration and possibly also the rate of synthesis of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) within the brain. 16, 19, 29 Potentiation of GABAergic neurotransmission is believed to be important in suppressing pain of It can take a few weeks – or sometimes many months – to notice any change after stereotactic radiosurgery, but it can offer pain relief for some people for several months or years. Facial numbness and pins and needles in the face are the most common complications associated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Trigeminal neuralgia most frequently affects people older than 50, and the condition is more common in women than men. Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common cause of facial pain and is diagnosed in approximately 15,000 people per year in the United States. Nerve pain medications: Medications such as amitriptyline and gabapentin are used to treat many types of nerve pain, including nerve damage caused by TMJ disorders. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. An overview of TN is presented here. Other causes of facial pain are discussed separately. (See "Overview of craniofacial pain".) ETIOLOGY AND PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Anatomy — The trigeminal nerve provides sensation to the face and portions of the mouth as well as motor control to the muscles of mastication. It has three major divisions:
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |