Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
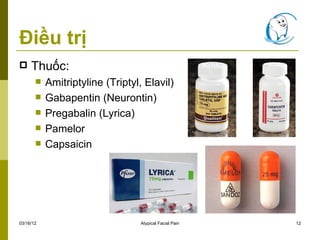
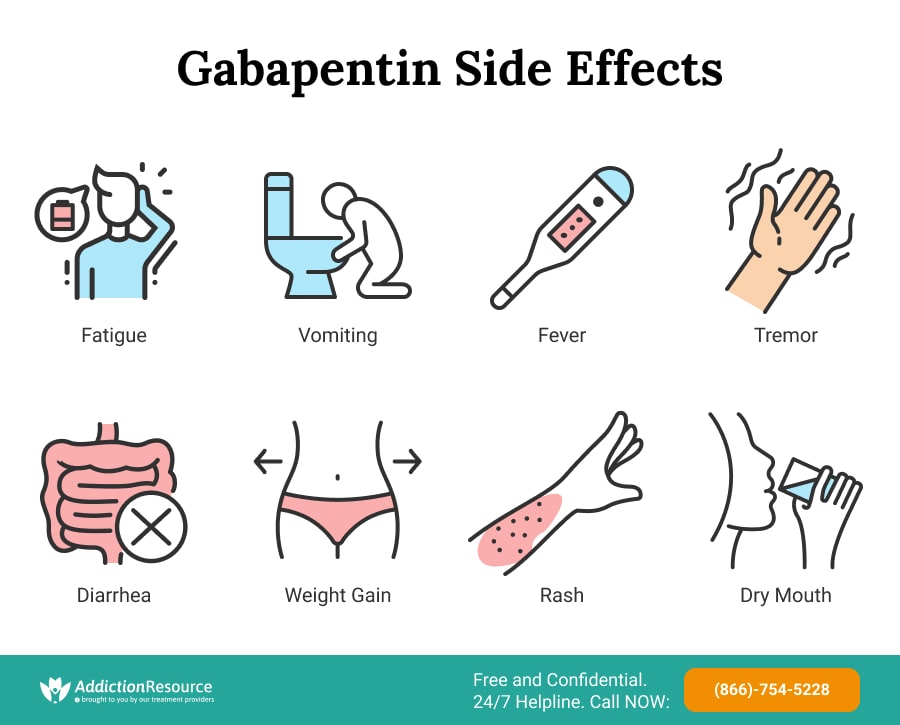
Purpose of Review Acute facial pain presents a complex challenge in medical practice, requiring a comprehensive and interdisciplinary approach to its management. This narrative review explores the contemporary landscape of treating acute facial pain, delving into pharmacological, non-pharmacological, and advanced interventions. The significance of tailored treatment strategies, rooted in the Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with trigeminal neuralgia (TN) advocate for a multidisciplinary team approach to improve the care of patients with acute and chronic TN. Evidence-based discussions and decisions are encouraged to establish care pathways for prompt diagnosis and treatment, and long-term outcomes data collection to improve care. The guidelines include ptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysma. facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple me. The pain can last for a few seconds to a few minutes, and it can be triggered by activities such as brushing your teeth, touching your face, eating or even the wind blowing on your face. Trigeminal Neuralgia Symptoms and Diagnosis. The primary symptom of trigeminal neuralgia is sudden, severe facial pain. Gabapentin has been associated with minor dose-related adverse effects but no serious events. 16, 19, 23 Clinical trials of gabapentin monotherapy for epilepsy have reported dizziness in 7% to 15% and somnolence in 3% to 7% of patients taking from 300 to 1,800 mg/day. 6 Higher doses of 900 to 3,600 mg/day in patients with neuropathic pain have TN is a chronic pain disorder of the trigeminal nerve that causes sudden, intense facial pain. TN may be caused by vascular contact with the trigem-inal nerve (classic TN), an underlying pathology such as multiple sclerosis or tumor (secondary TN), or no known cause (idiopathic TN). Once dental causes for facial pain are ruled out, prompt Persistent idiopathic facial pain. Combination of antidepressants and anticonvulsants (e.g. amitriptyline and/or gabapentin) Neuropathic facial pain. Combination of antidepressants and anticonvulsants (e.g. amitriptyline and/or gabapentin) Trigeminal neuralgia If you have chronic pain in the face, we might prescribe you a medicine called gabapentin. Chronic pain (also called persistent pain) is long-term pain that lasts for more than 3 months. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is used to treat epilepsy, or to treat nerve pain. Neuropathic pain, which occurs as a result of damage to neural tissue, includes phantom limb pain, compression neuropathies, peripheral neuropathies (e.g. due to Diabetic complications, chronic excessive alcohol intake, HIV infection, chemotherapy, idiopathic neuropathy), trauma, central pain (e.g. pain following stroke, spinal cord injury, and syringomyelia), and postherpetic neuralgia Treatment options for atypical facial pain normally begin with medications, followed by other forms of treatment. Here we briefly list the main forms of treatment recommended for the condition of ATFP: A) Medications • Amitriptyline (Triptyl, Elavil) • Gabapentin (Neurontin) • Pregabalin (Lyrica) • Capsaicin . B) Hot and cold compresses “We really don't use gabapentin a great deal for migraine — it is used more for other headache disorders, like occipital neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and facial pain,” says Dr. Ailani. “Not only is it off-label, but it’s considered Level U evidence in guidelines.” All 42 patients having persistent facial pain with tenderness of regional muscles were first prescribed amitriptyline, but those with side effects were subsequently transferred to nortriptyline. In patients where no response to TCAs was observed, gabapentin was initiated. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant to previous surgical interventions or treatment with multiple medications. Gabapentin relieved facial pain in 6 of the 11 patients who had never taken carbamazepine and in 37 of the 81 who had previously taken carbamazepine. A typical initial dose was 100 mg 3 times a day, and some patients were started on as little as 100 mg daily. Several studies have reported that gabapentin is effective in the treatment of postradical neck pain syndrome, postherpetic neuralgia, and postsurgical facial pain 3, 4. We examined the analgesic effect of gabapentin on non-dental and non-traumatic orofacial trigeminal neuropathic pain. In this review, based on a systematic search of relevant literature, we aim to provide current, evidence-based, knowledge about the use of gabapentin and other α2δ ligands in patients with trigeminal neuralgia. Lemos L, Flores S, Oliveira P, Almeida A. Gabapentin supplemented with ropivacain block of trigger points improves pain control and quality of life in trigeminal neuralgia patients when compared with gabapentin alone. Most patients respond well to pharmacotherapy; carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are first line therapy, while lamotrigine and baclofen are considered second line treatments. Other drugs such as topiramate, levetiracetam, gabapentin, pregabalin, and botulinum toxin-A are alternative treatments. Other medicines that may be used include topiramate (Qudexy XR, Topamax, others), pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant). If the anti-seizure medicine you're using becomes less effective, your healthcare professional may increase the dose or switch to another type. Neuralgic facial pain Trigeminal neuralgia. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is perhaps the most well-known neuralgia. However, in the case of this nerve, the definition of classic TN (CTN) has come to be associated with a suspected cause reflecting a fundamental shift in our understanding of the disease and the definition of it.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |