Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
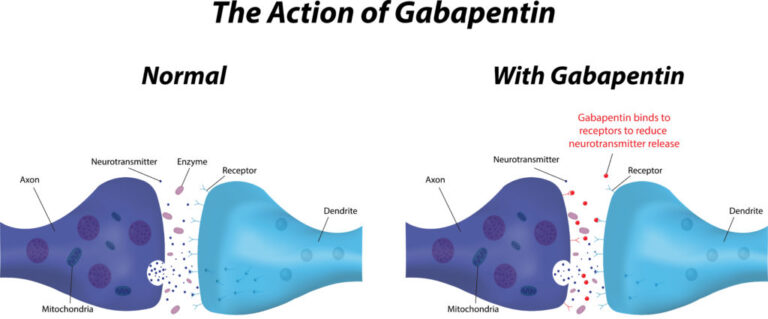
The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. For healthcare professionals. Applies to gabapentin: compounding powder, oral capsule, oral solution, oral tablet, oral tablet extended release. General adverse events. The most common adverse reactions associated with the use of this drug were dizziness, somnolence, and peripheral edema. Gastroenterologists at Massachusetts General Hospital have begun prescribing low-dose gabapentin for patients with functional dyspepsia because it is thought to be capable of relieving visceral pain. We aimed to study the antiinflammatory effects of gabapentin on carrageenan-induced paw edema and to determine its gastric side effects on gastric mucus secretion in Wistar rats. Since intestinal microbiota alteration is one of the most common shared hallmarks of inflammation-related GI disorders [104], [105], a better comprehension of GABA effect in the intestinal inflammatory event could reveal a possible functional interplay among the microbiota, the immune system and the enteric nervous system in the physiopathology It also found that gabapentin, as an adjunctive drug, plus omeprazole could play a significant role in GI symptom improvement, such as pain, reflux, and indigestion. It’s thought that gabapentin impacts bowel function through its effects on calcium channels and opioid receptors in the GI tract. By altering GI motility and secretion, gabapentin can disrupt normal bowel habits. Yes, gabapentin can cause gastrointestinal problems like nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, constipation, flatulence and bloating etc. It can also trigger acid reflux. Make sure you talk to your healthcare provider as soon as you start noticing your side effects getting worse or if you begin to experience any unusual or unexpected side effects. Gabapentin can also affect the digestive system, leading to various gastrointestinal issues in elderly patients. Common complaints include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Common complaints include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Dizziness is similarly common with Horizant. But it may be slightly less likely with Gralise. Along with causing dizziness, gabapentin can worsen your coordination. We sought to determine the efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of functional dyspepsia among an observational cohort of patients. Gabapentin has an established role in the treatment of neuropathic pain, with evidence supporting a benefit in visceral hypersensitivity. Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). Keywords: Functional dyspepsia, gabapentin, gastrointestinal disorders. Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). In this regard, gabapentin as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and may be effective in controlling the symptoms of GI disorders. When it comes to finding the best dog food for small dogs, owners need to consider their unique nutritional needs. With smaller stomachs but often faster metabolisms than larger breeds, small dogs need high-quality protein, moderate fat levels, and balanced nutrients in smaller, bite-sized pieces. Whether your small dog is a puppy, adult, or senior, this guide will cover Can gabapentin cause gastrointestinal issues? Yes, gastrointestinal side effects are common among users of gabapentin. Patients may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and constipation. These issues arise due to changes in gut motility influenced by altered neurotransmitter signaling within the enteric nervous system. Central neuromodulators (antidepressants, antipsychotics, and other central nervous system−targeted medications) are increasingly used for treatment of functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), now recognized as disorders of gut−brain interaction. However, the available evidence and guidance for the use of central neuromodulators in these conditions is scanty and incomplete. In this Goals: We sought to determine the efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of functional dyspepsia among an observational cohort of patients. Background: Gabapentin has an established role in the treatment of neuropathic pain, with evidence supporting a benefit in visceral hypersensitivity. In this regard, gabapentin as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analog used in the treatment of neuropathic pain and may be effective in controlling the symptoms of GI disorders. Gastrointestinal Issues Related to High Gabapentin Doses. High doses of gabapentin can lead to various gastrointestinal complaints. Nausea, vomiting, and constipation. These symptoms can be troubling and often occur in about 25% of patients taking high doses. Managing these effects often requires additional medications, complicating treatment.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |