Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
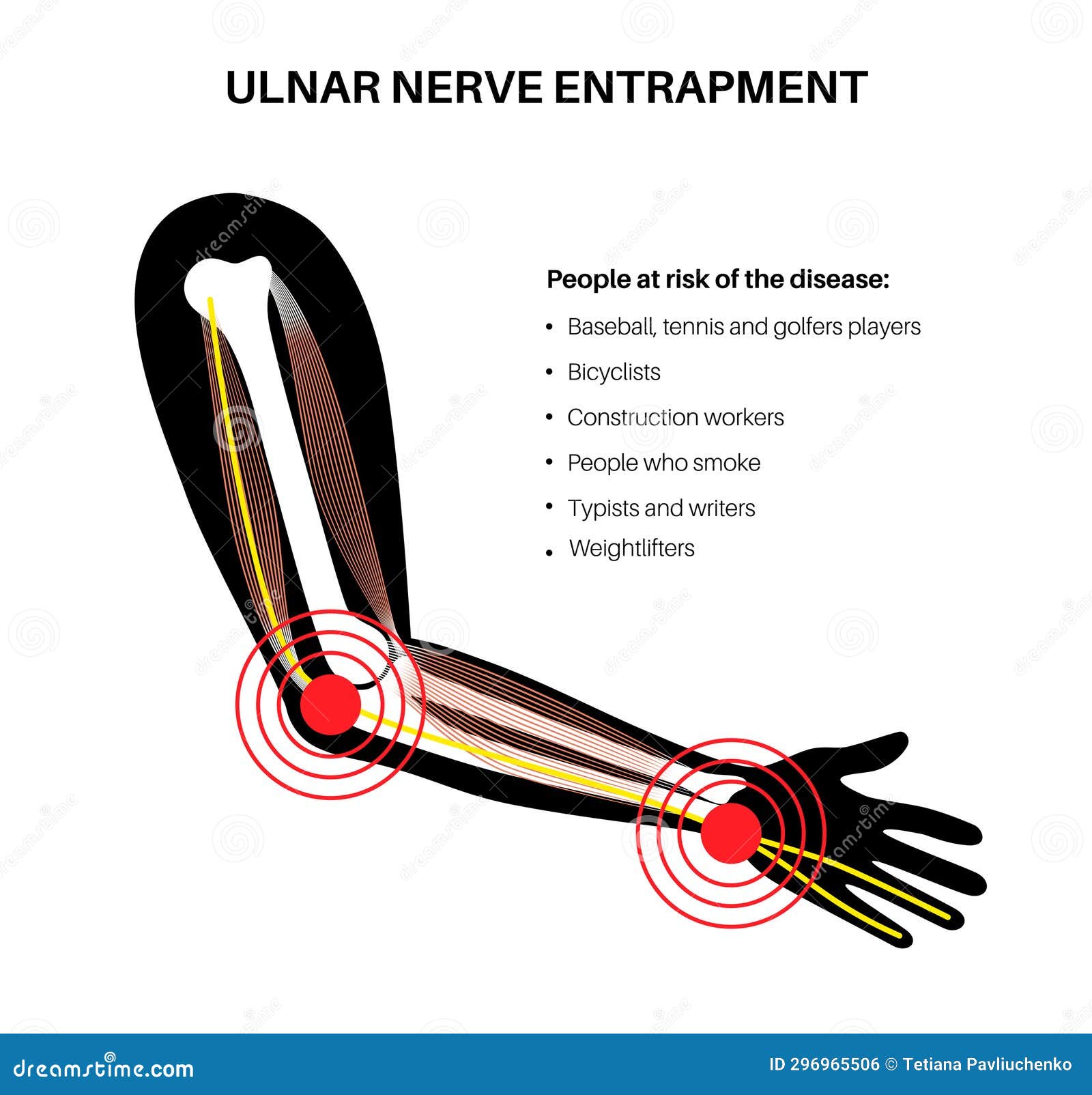
The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Rare but serious gabapentin side effects include mood changes in children. Gabapentin was effective in alleviating steady burning pain as well as lancinating pain and allodynia. Conclusions: The results suggest that gabapentin may be effective in the management of some cases of neuropathic pain in the head and neck. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Neurontin (gabapentin), generally prescribed for the treatment of nerve pain, is sometimes used to relieve severe pain caused by knee osteoarthritis (OA). Osteoarthritis, also known, as wear-and-tear arthritis, can often become so severe that joint replacement surgery is needed. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. The pain can be on one side or both sides of the head. Pain can come with numbness or changes in sensation over the area and sensitivity to normal touching of the head or hair. There is often tenderness over the nerve branches and/or trigger points (areas that when pressed cause pain) around the greater and/or lesser occipital nerve(s). It is believed that gabapentin may reduce the release of inflammatory neuropeptides implicated in headache pain, such as calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and substance P; it could The symptoms of occipital neuralgia can come on suddenly and without warning. Symptoms include a shooting, throbbing, burning, or aching pain that can last from seconds to minutes. The pain often starts at the back of the head and spreads to one or both sides of the head. It can be felt in your scalp, upper neck, and behind your eyes and ears. Focused on reducing the need for opioids while identifying more effective pain relief and increasing quality of life for patients with head and neck cancer, a research team at Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center explored the use of gabapentin as an effective alternative to narcotics in managing treatment-related symptoms caused by Head-to-Head Comparison: Gabapentin vs. Cymbalta for Nerve Pain Effectiveness in Pain Relief. Both gabapentin and Cymbalta can be effective in reducing nerve pain, but their effectiveness varies among individuals and specific pain conditions. Some people respond better to one medication over the other. Gabapentin is most commonly prescribed for nerve pain such as with peripheral neuropathy, various types of nerve damage, nerve pain following shingles, injury, or multiple sclerosis. It can be used as an anticonvulsant medication to treat partial seizures as well and is often prescribed for restless leg syndrome (RLS). Gabapentin is a prescription antiepileptic medication commonly used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain, and other neuropathic pain conditions. Learn more about how long it takes to treat nerve pain and what to expect when you're prescribed it. Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study. In 2010, a study published in Head and Neck (Bar Ad, V. B. et al., 2010) examined the role of gabapentin to treat the neuropathic pain syndrome in radiation induced OM. This retrospective study evaluated the effectiveness of gabapentin as a co analgesic in patients undergoing intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) to the head and neck. We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. We delineate its pharmacological, laboratory and clinical profiles, with a review of the world literature. Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the By week 7, the median pain score in the treatment group was below the 0.25 quantile of the control group. Conclusion: Prophylactic use of gabapentin during chemoradiation for HNC patients resulted in a decrease in pain, neurosensory symptoms, and general systemic symptoms. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. “We really don't use gabapentin a great deal for migraine — it is used more for other headache disorders, like occipital neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and facial pain,” says Dr. Ailani. “Not only is it off-label, but it’s considered Level U evidence in guidelines.” In this trial, the pain was measured using the Vanderbilt Head and Neck Symptom Survey’s pain subscale, a combination of 4 questions related to pain severity individually reported on a 0–10 scale. These investigators identified a difference in pain scores in favor of gabapentin usage (OR = 0.549, 95% CI: (0.364, 0.827), p = 0.004
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |