Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) | 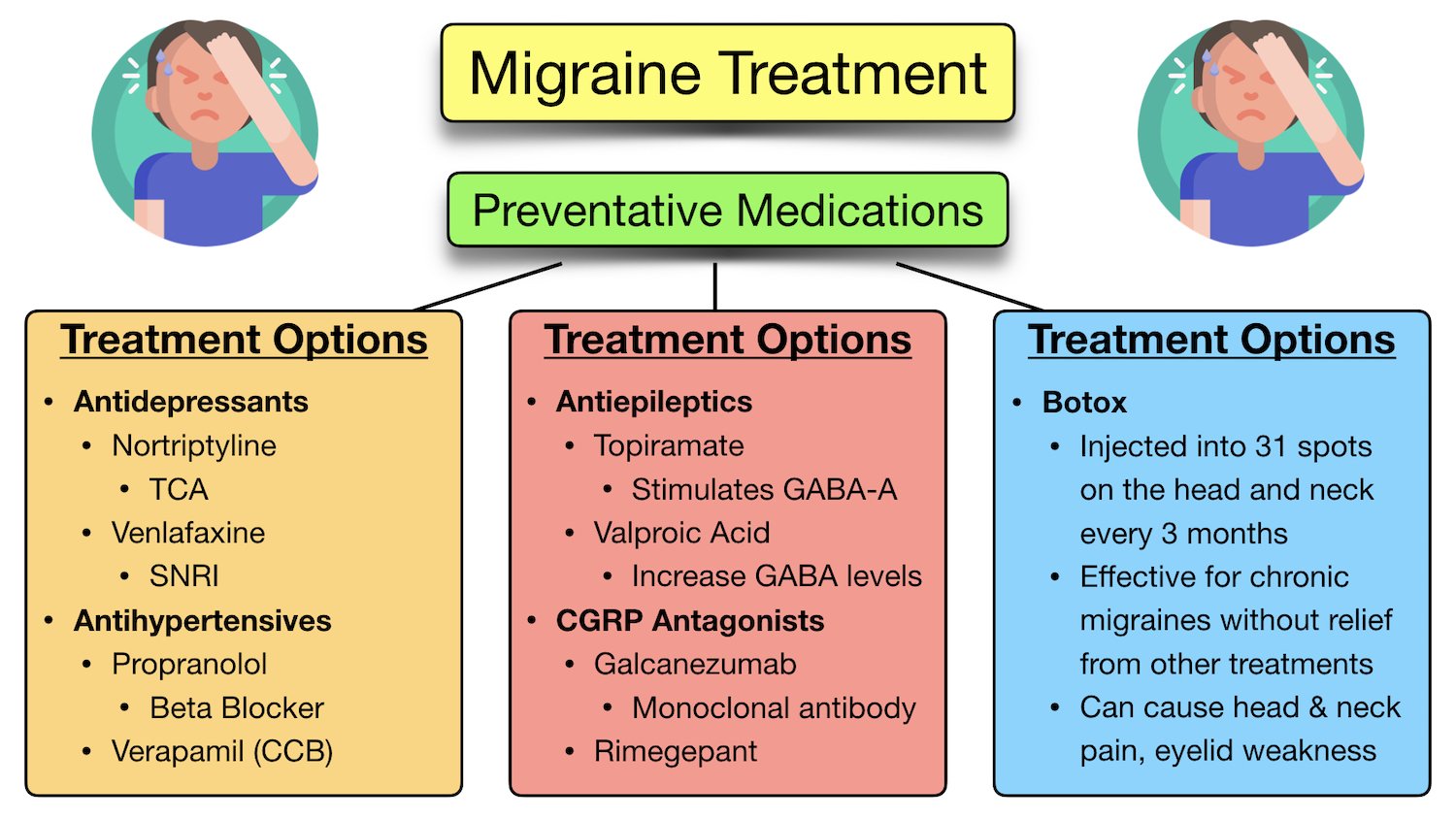 |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 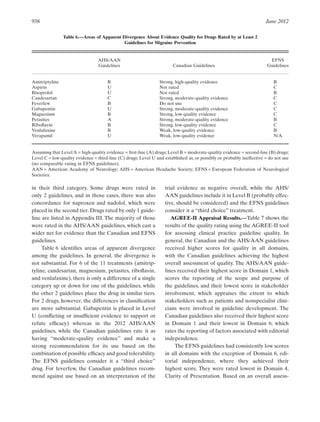 |
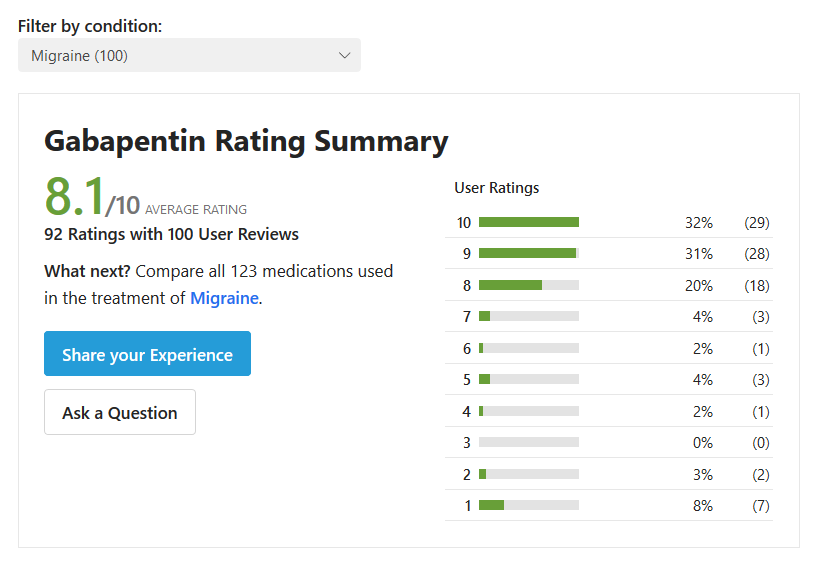
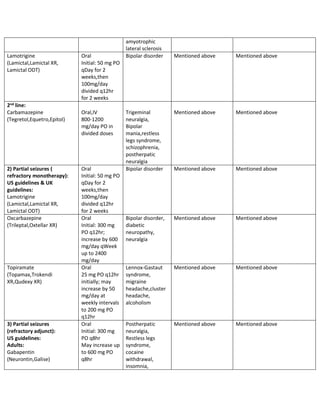
Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. The 2021 American Headache Society consensus guideline recommends that preventive pharmacologic therapy should be considered for patients with 4 or more migraine headache days per month or those with 2 or more migraine headache days per month that are associated with substantial disability despite use of acute medication. 2 Preventive treatment Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1 , 2 . One trial each of gabapentin 900 mg (53 patients), and gabapentin titrated to 1200 mg (63 patients) and 1800 mg (122 patients) failed to show a statistically significant reduction in headache frequency in the active treatment group as compared to the placebo group, whereas one trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 to 2400 mg (113 patients The recommendations on treatment of menstrual-related migraine are based on the clinical guidelines Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management , Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015], National headache management system for adults , and Pharmacological management of migraine , consensus statements from the Danish One trial each of gabapentin 900 mg (53 patients), and gabapentin titrated to 1200 mg (63 patients) and 1800 mg (122 patients) failed to show a statistically significant reduction in headache frequency in the active treatment group as compared to the placebo group, whereas one trial of gabapentin titrated to 1800 to 2400 mg (113 patients A 2016 study found that gabapentin showed some benefits for migraine headaches. However, it concluded that there wasn't enough evidence to recommend it as a primary therapy. Another study review in 2023 found that gabapentin was no more effective than a placebo in reducing monthly migraine days. Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. (Strength of Recommendation: B, based on inconsistent or Gabapentin for Headache Relief. Gabapentin has a wide range of off-label applications, including as a treatment option for neuropathic pain, migraine prevention, and headaches, including tension and cluster types. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Treatment. Some people with tension-type headaches don't see a health care professional and try to treat the pain on their own. But repeated use of pain relievers available without a prescription can cause another type of headache known as medication overuse headache. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. For cluster headache prevention, monthly subcutaneous injection of galcanezumab increases the likelihood of a 50% reduction in headache frequency with a number needed to treat of 6. Gabapentin shows to have an effective therapeutic action in the prophylactic treatment of migraine. Our observations indicate that gabapentin is well tolerated by patients and that reduces headache frequency and use of symptomatic drugs in both groups. The 2000 US Headache Consortium defined the following goals for preventive treatment: (1) decrease attack frequency by 50% and decrease intensity and duration; (2) improve responsiveness to acute therapy; (3) improve function and decrease disability; and (4) prevent the occurrence of a medication overuse headache (MOH) and chronic daily A treatment plan should consider not only the patient’s diagnosis, symptoms, and coexistent or comorbid conditions, but also the patient’s expectations, needs, and goals.1 Effective migraine treatment begins with making an accurate diagnosis, ruling out alternate causes, ordering appropriate studies, and addressing the headache’s impact Some indications for preventive therapy include four or more headaches a month, eight or more headache days a month, debilitating headaches, and medication-overuse headaches. Identifying Type Features Treatment; Short duration: Brief headache syndromes: Hypnic: Develops during sleep; lack of autonomic symptoms; must have 2 of 3 criteria: (1) occurs more than 15 times per month, (2 Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
.jpg) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |