Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 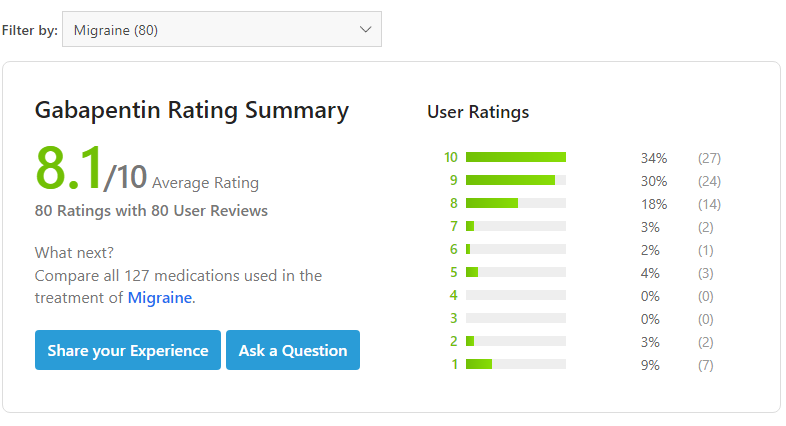 |
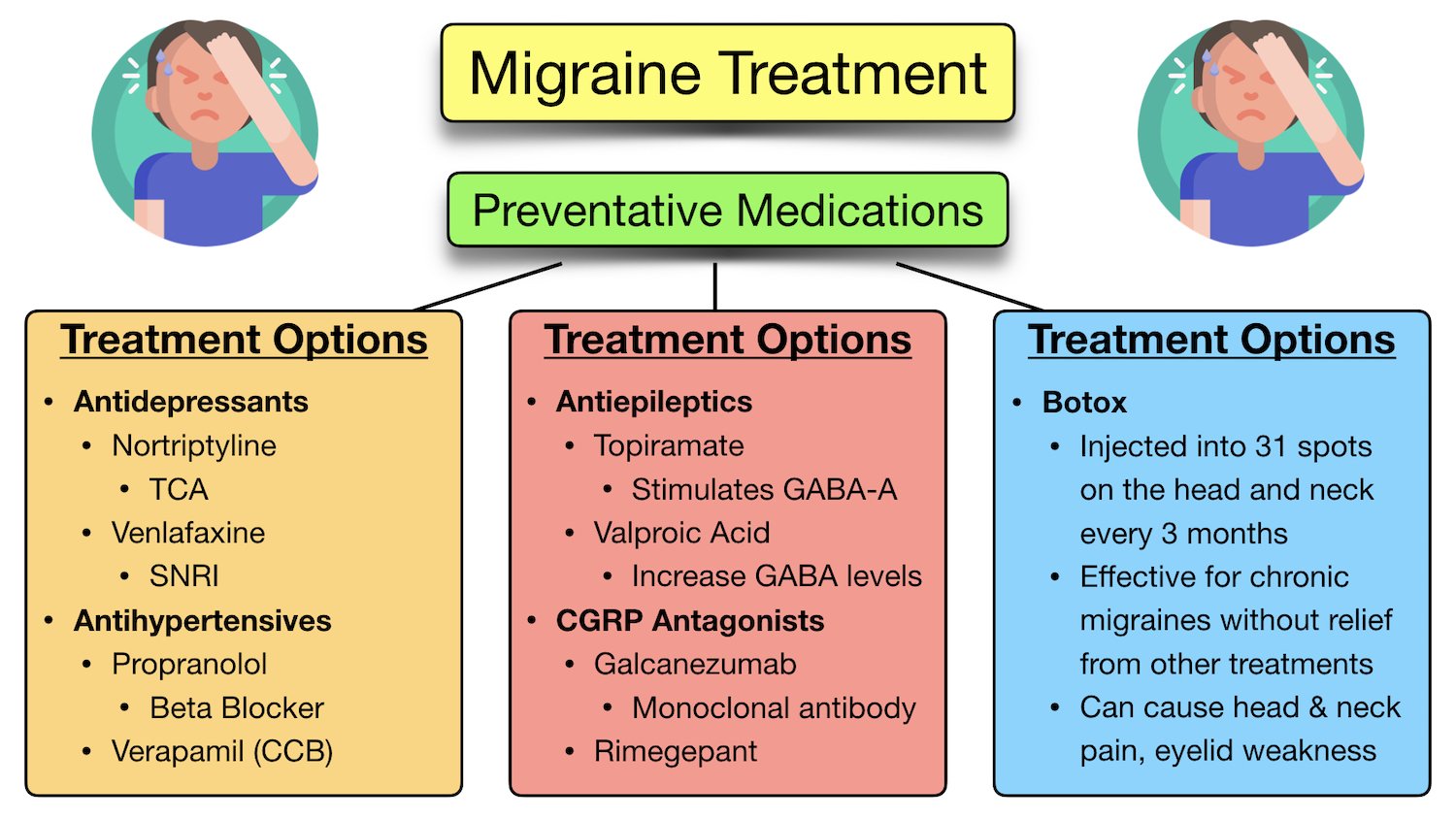
Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Despite the conflicting evidence surrounding select studies, a significant amount of evidence shows that GBP has benefit for a majority of primary headache syndromes, including chronic daily headaches. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention. graine in a 12-week open-label study (35). Gabapentin was not effective in one placebo-controlled double-blind study (65). In a second randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial (36), gabapentin 1800 to 2400 mg was superior to placebo in reducing the frequency of migraine attacks. The responder rate was 36% for gabapentin and 14% for The studies showed that neither gabapentin nor gabapentin enacarbil was more effective than placebo at reducing the frequency of migraine headaches. Gabapentin commonly caused side effects, especially dizziness and somnolence (sleepiness). Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant used off-label to help prevent migraine attacks. Learn about why it’s used and how it works. There is limited evidence for nebivolol, bisoprolol, pindolol, carbamazepine, gabapentin, fluoxetine, nicardipine, verapamil, nimodipine, nifedipine, lisinopril, and candesartan. Acebutolol, The 2021 American Headache Society consensus guideline recommends that preventive pharmacologic therapy should be considered for patients with 4 or more migraine headache days per month or those with 2 or more migraine headache days per month that are associated with substantial disability despite use of acute medication. 2 Preventive treatment Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Objective While there are several trials that support the efficacy of various drugs for migraine prophylaxis against placebo, there is limited evidence addressing the comparative safety and efficacy of these drugs. We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis to facilitate comparison between drugs for migraine prophylaxis. Methods We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, and The recommendations on what information and self-care advice should be given to people with migraine are based on clinical guidelines National headache management system for adults [], Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management [], Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015] and Pharmacological management of migraine [], the American Headache Society updated consensus The studies showed that neither gabapentin nor gabapentin enacarbil was more effective than placebo at reducing the frequency of migraine headaches. Gabapentin commonly caused side effects, especially dizziness and somnolence (sleepiness). No studies of pregabalin were identified, and research on this drug is desirable. Gabapentin (Neurontin) for prophylactic treatment of migraines and headaches, how it works, dosage, review of clinical trials on the effectiveness of gabapentin. Many medications claim to relieve migraine pain, but some are more helpful than others. In a large study looking at real-world data on 25 drugs, migraine sufferers rated the most and least helpful options. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. Chronic daily headache is diagnosed in approximately 3% to 5% of patients presenting with acute headache. 1, 3 For patients with migraine, modifiable risk factors for progression to chronic
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |