Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |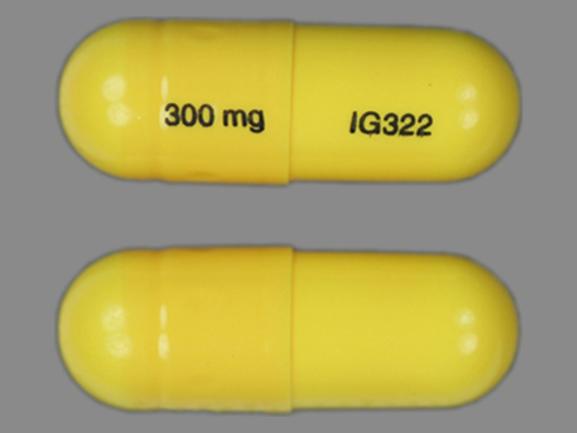  |
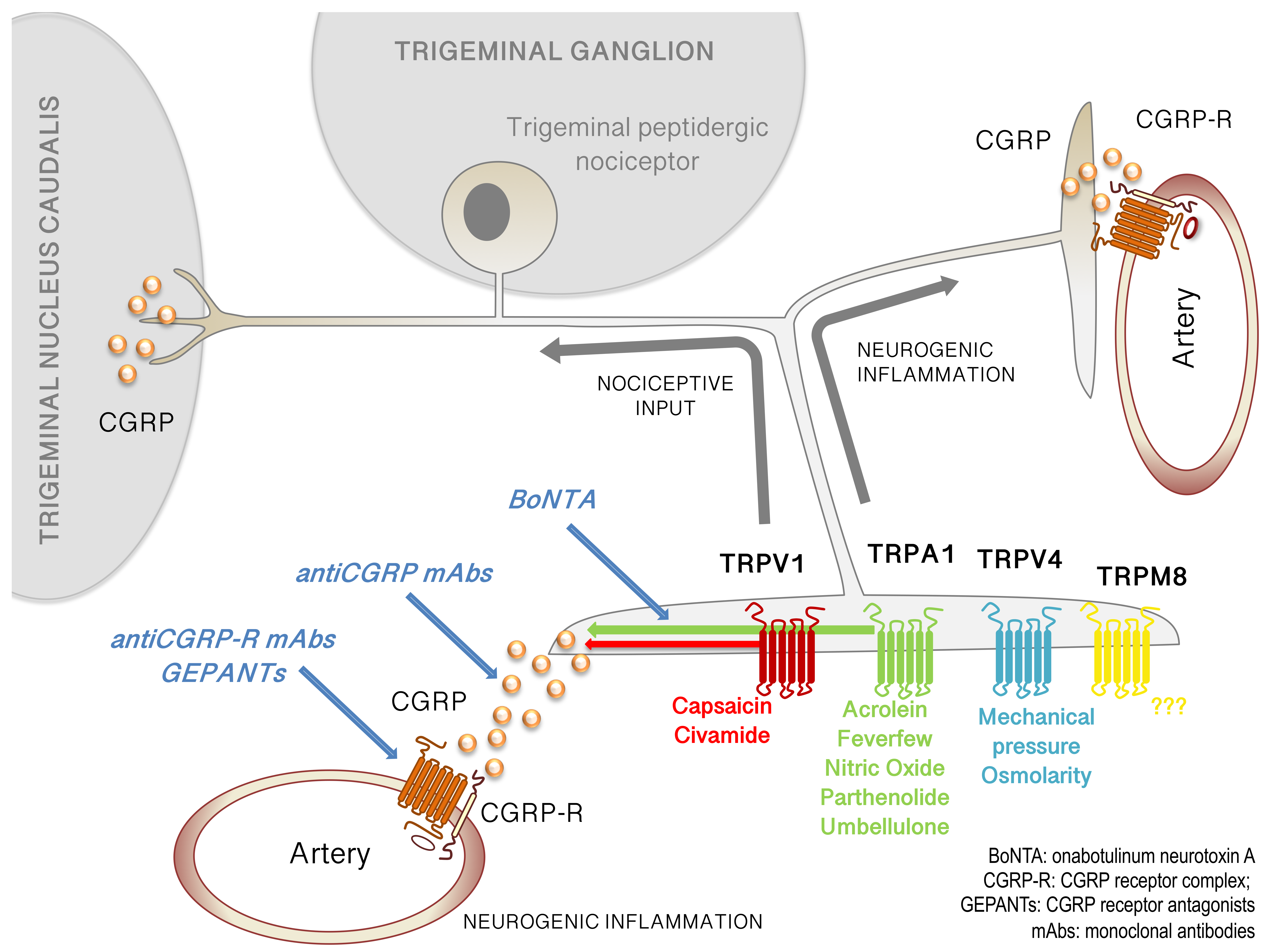
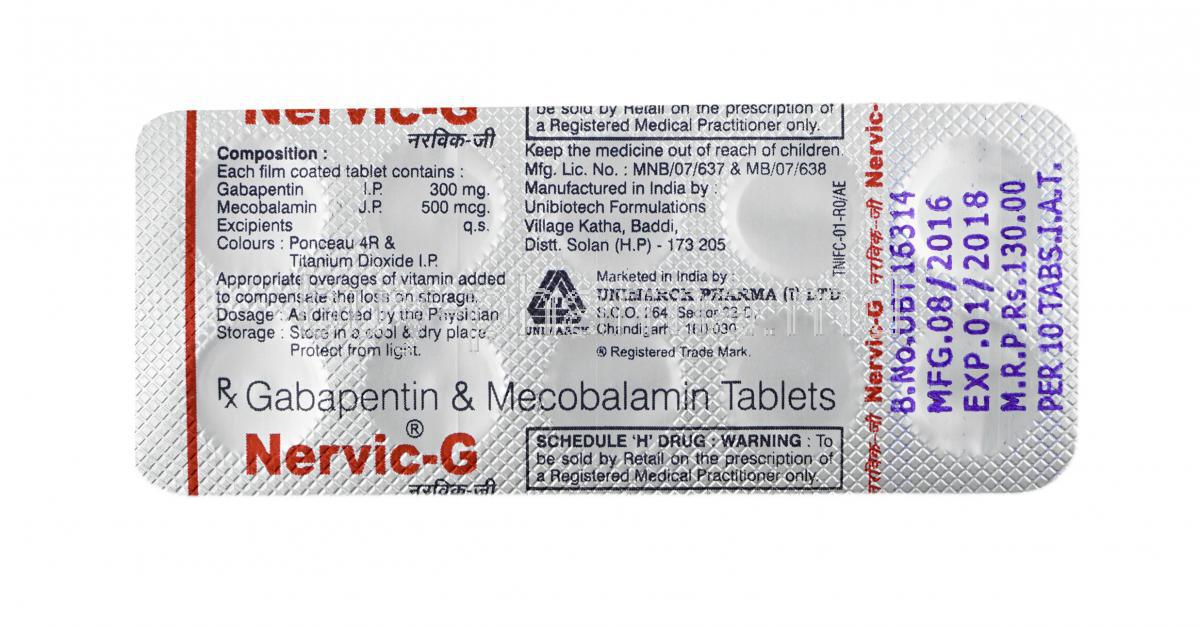
Does gabapentin (Neurontin) help prevent episodic migraine? Evidence-Based Answer Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. First-line medications established as effective based on clinical evidence include divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol. Medications such as amitriptyline, Objective.—To compare gabapentin with placebo for use as a prophylactic agent in patients with migraine (with or without aura). Study Design and Treatment.—After screening, a 4-week, single-blind, placebo baseline period was followed by a 12-week, double-blind, treatment period. Despite the conflicting evidence surrounding select studies, a significant amount of evidence shows that GBP has benefit for a majority of primary headache syndromes, including chronic daily headaches. GBP has some efficacy in migraine headache, but not sufficient evidence to suggest primary therapy Objective While there are several trials that support the efficacy of various drugs for migraine prophylaxis against placebo, there is limited evidence addressing the comparative safety and efficacy of these drugs. We conducted a systematic review and network meta-analysis to facilitate comparison between drugs for migraine prophylaxis. Methods We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, CENTRAL, and Objective.—To compare gabapentin with placebo for use as a prophylactic agent in patients with migraine (with or without aura). Study Design and Treatment.—After screening, a 4-week, single-blind, placebo baseline period was followed by a 12-week, double-blind, treatment period. Gabapentin is used "off-label" for migraine prevention and treatment, including migraines with or without aura, vestibular migraines. It reduces the frequency of headaches, pain intensity, and the use of symptomatic medications 1 , 2 . To describe and assess the evidence from controlled trials on the efficacy and tolerability of gabapentin/gabapentin enacarbil or pregabalin for preventing migraine attacks in adult patients with episodic migraine. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) has some benefit in reducing the frequency, severity, and duration of chronic migraine and chronic tension-type headache. B: 22: Gabapentin (Neurontin) increases the number Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Gabapentin has a wide range of off-label applications, including as a treatment option for neuropathic pain, migraine prevention, and headaches, including tension and cluster types. Many medications claim to relieve migraine pain, but some are more helpful than others. In a large study looking at real-world data on 25 drugs, migraine sufferers rated the most and least helpful options. The migraine headache rate during the second 4 weeks of the SP2 for patients maintaining a stable dose of 2400 mg/day gabapentin is presented in Table 3 for the placebo- and gabapentin-treatment groups. Gabapentin is an effective prophylactic agent for patients with migraine. In addition, gabapentin appears generally well tolerated with mild to moderate somnolence and dizziness. Propranolol decreases the number of days with a migraine headache. Calcium channel blockers do not appear effective. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention. sign in; Don't have an account ? Create one now; Enjoy faster checkout, create ideaboards, earn My Funds and become a Beyond+ member! track order; my offers The migraines continued until I was over 40 years of age. I would have to go to the ER for shots to help with the pain and the nausea. My life was literally miserable because I would only be pain-free a few days a month. Then, when in my 40s, after having migraines for over 25 years, I was put on Neurontin, not for migraines, but as a mood Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |