Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fibromyalgia-myofascial-pain-syndrome-716183_color-d5762d991873409490990230d00c4e79.gif) |  |
 |  |
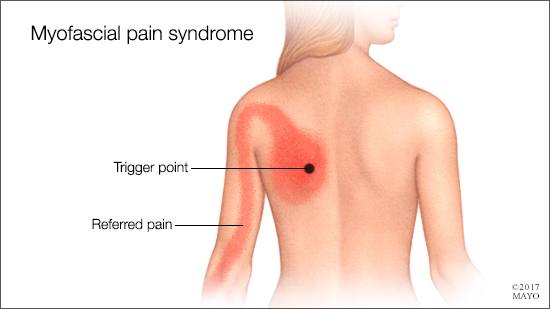
Jennifer is a 37-year-old woman who was medically retired from the Air Force five years ago due to her persistent pain and fatigue, which resulted in an inability to do her job as an air traffic controller. She was diagnosed with fibromyalgia syndrome seven years ago, six months after returning from an Air Force deployment to Afghanistan. Figure. Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is defined as a regional pain syndrome that is estimated to affect nearly 44 million US residents. 1 The prevalence of MPS in adults ages 30 to 60 years is approximately 37% among men and 65% among women, with estimates reaching 85% in the older adult population. 2 MPS is characterized by its most notable feature, the presence of myofascial trigger points PDF | Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is characterized by myofascial trigger points and fascial constrictions. Tölle TR, Phillips T, Moore RA. Gabapentin for chronic . neuropathic pain in Aims: To evaluate, in an open trial, the pharmacotherapeutic efficacy of tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) drugs and gabapentin in patients with persistent myofascial pain and to identify patient and pain characteristics that may predict treatment outcome. I take Gabapentin, 900 mg/day, (300 mg x3/day FOR Myofascial Pain. Myofascial Pain was described to me as nerve pain. This is how It was explained to me: The Fascia is part of the muscle; the Fascia sometimes 'binds' up the muscle, & the nerves in the muscle & Fascia cause the pain. To evaluate, in an open trial, the pharmacotherapeutic efficacy of tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) drugs and gabapentin in patients with persistent myofascial pain and to identify patient and The goal of medication for patients with cervical myofascial syndrome is to reduce pain. Avoid the use of opioid analgesics. If the clinical picture is one of more chronic pain accompanied by sleep dysfunction, consider the use of a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). Gabapentin is a medication often used for nerve pain and seizures, but its role in myofascial pain syndrome is less clear. While some people report improvement, others find it less effective or experience side effects. It's important to understand the full picture before considering this treatment. Percentage of members reporting each side effect. For those who are currently suffering with myofascial pain syndrome, and who have tried other methods for relieving your pain, then talking to your doctor is the first step you should take. It could be that gabapentin is the perfect treatment for you, and offers the relief that you desire. Treatment for myofascial pain syndrome typically includes medicines, shots into the trigger points and physical therapy. Exercise is a big part of any treatment plan. Discuss treatment options and what you prefer with your healthcare professional. Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a common cause of chronic musculoskeletal pain characterized by myofascial trigger points and fascial constrictions. MPS often We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Myofascial pelvic pain syndrome (MPPS) is a pelvic pain syndrome that is defined by short, tight, tender pelvic floor muscles that can include palpable nodules or trigger points. The treatment of MPPS is multimodal and tailored to the individual patient. Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is defined as pain that originates from myofascial trigger points in skeletal muscle. It is prevalent in regional musculoskeletal pain syndromes, either alone or in combination with other pain generators. The appropriate evaluation and management of myofascial pain is an important part of musculoskeletal Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) refers to a type of chronic pain syndrome that recurs in muscles, fascia or related soft tissues and can be accompanied by obvious emotional disorders or dysfunctions. MPS is characterized by myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) and fascial constrictions. Purpose of Review Myofascial pain syndrome (MPS) is a musculoskeletal pain condition that stems from localized, taut regions of skeletal muscle and fascia, termed trigger points. The purpose of this comprehensive review is to provide updated information on prevalence, pathophysiology, and treatment modalities with a focus on interventional modalities in managing MPS. Recent Findings Though MPS Non-pharmacologic treatment modalities such as acupuncture, massage, transcutaneous electrical stimulation, and interferential current therapy may offer relief to some patients with MPS. Additional studies are warranted to get a better understanding of managing myofascial pain. How Gabapentin Works in Treating Myofascial Pain Syndrome. Gabapentin is a medication that is commonly used to treat myofascial pain syndrome. It is a type of drug called an anticonvulsant, which means it is primarily used to treat epilepsy. However, it has also been found to be effective in relieving the symptoms of myofascial pain syndrome. This is a phase IV clinical study of how effective Gabapentin (gabapentin) is for Myofascial pain syndrome and for what kind of people. The study is created by eHealthMe from 452 Gabapentin users and is updated continuously. Gabapentin and pregabalin are first-line agents for the treatment of neuropathic pain but have also demonstrated some effectiveness in conditions characterized by muscle pathology. Studies showed varying effectiveness of muscle relaxants compared to other medications.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/fibromyalgia-myofascial-pain-syndrome-716183_color-d5762d991873409490990230d00c4e79.gif) |  |
 |  |