Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
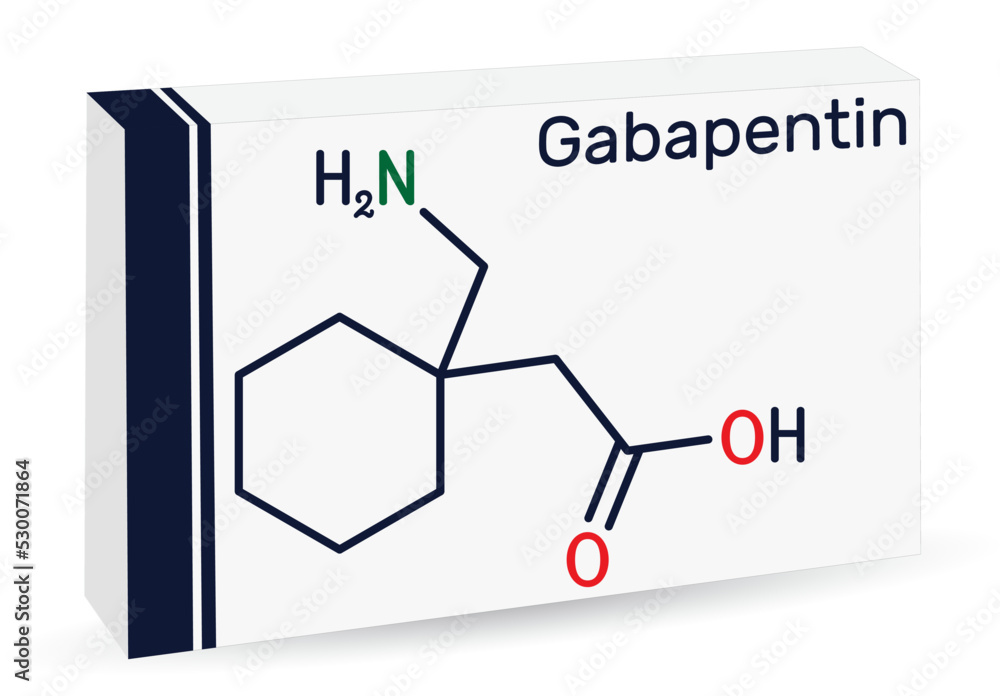
Gabapentin is also used as an adjunct to more potent anticonvulsants and for the management of certain types of neural pain. Definition and uses of gabapentin. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat seizures and nerve pain. Titrate dose as needed for pain relief; Maintenance dose: 900 to 1800 mg/day orally in 3 divided doses Maximum dose: 1800 mg per day Extended-release: Gralise (gabapentin) 24-hour extended-release tablets: Initial dose: Day 1: 300 mg orally with the evening meal Day 2: 600 mg orally with the evening meal That’s the situation for millions of people who suffer from idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy. The term “idiopathic” means that no cause can be identified; “sensory” refers to the type of nerve, in this case those carrying nerve signals such as pain or temperature; “poly” means “many” and “neuropathy” means nerve disease. Gabapentin has been shown to be beneficial in treating several types of neuropathic pain; however, the mechanism of action by which gabapentin exerts its analgesic effect is still unknown.¹ It is suggested that gabapentin may block the calcium channel alpha(2)delta (a2d)-1 receptor in the brain. Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. Gabapentin can reduce nerve pain in some people with shingles or diabetes, but it may not work for everyone and can cause side effects. Learn how gabapentin works, how to take it, and what to do if you stop taking it. Doctors soon realized that gabapentin also had benefits for treating nerve pain. It has since become a first-line medication for conditions like postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, fibromyalgia, and other types of chronic nerve pain. Gabapentin helps reduce sensations of burning, numbness, and tingling associated with nerve pain. One, from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom, includes the use of gabapentin as a first-tier treatment for all neuropathic pain. 14 Similarly, the European Pregabalin is Gabapentin alternatives for epilepsy, nerve pain, and anxiety. Other drugs for nerve pain include topiramate, baclofen, tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline and Dosulepin, and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors such as duloxetine. What Are Natural Alternatives for Nerve Pain? Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication used in the management of peripheral neuropathic pains, postherpetic neuralgia, and partial-onset seizures. Brand Names Gabarone, Gralise, Neurontin Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat seizures and nerve pain, especially after shingles. Learn about its dosage forms, common and serious side effects, interactions, and precautions. Gabapentin (Neurontin) is an antiseizure medication. It’s also used for nerve pain from shingles. Other long-acting forms called Gralise and Horizant are also available. For adults, your gabapentin dosage varies depending on your medical conditions and which form you’re taking. The maximum dosage is 3,600 mg per day. Gabapentin is a prescription drug used to treat nerve pain caused by damage or illness. Learn how long it takes to work, how much to take, and what to watch out for. Gabapentin is a medication that treats nerve pain by calming overactive nerves in your body. It may also prevent and control seizures in people with epilepsy. Learn about its common brand names, interactions, side effects, and precautions. For people with neuropathic pain. Gabapentin at a dose of 1800 to 3600 mg daily (1200 to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. Gabapentin is a prescription medication that can prevent and control partial seizures, relieve nerve pain after shingles and treat restless legs syndrome. Learn how to take gabapentin, what side effects to watch for, and what drugs to avoid while taking it. Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. The outcome of at least 50% pai Gabapentin is a medicine used to treat seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Learn about its dosage, side effects, interactions and warnings before taking it. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant that may relieve nerve pain and lower the risk of seizures. Learn about its different forms, dosing, side effects, interactions, and tips for safe use. Learn why gabapentin is among the most commonly used anticonvulsants for neuropathic pain and how to optimize its therapeutic dosing. Find out the pharmacology, bioavailability, side effects, and abuse potential of gabapentin.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |