Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-neuroscience-of-itch-2488868_color1-d501f506ed1040ba8f5a0ecef336669d.jpg) |
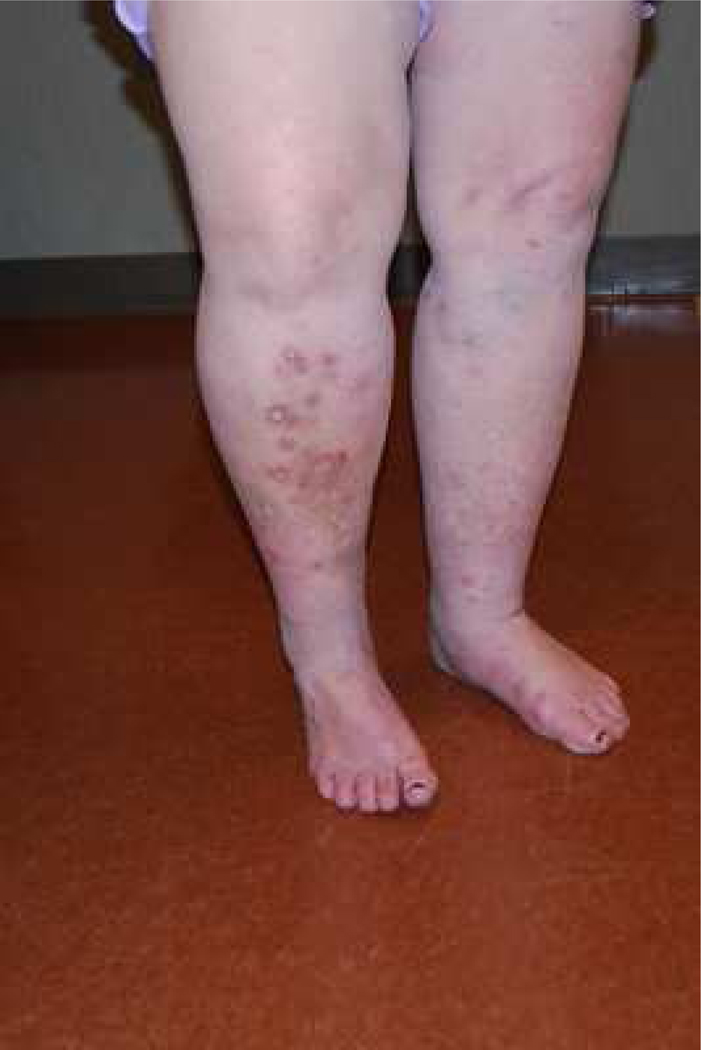
They are found to be promising alternative treatments for the relief of several forms of chronic pruritus, particularly uremic pruritus and neuropathic or neurogenic itch, in patients who fail conservative therapies. Keywords: gabapentin; itch; neurogenic itch; neuropathic itch; pregabalin; pruritus; uremic pruritus. A neuropathic itch is an itch that results from nervous system damage rather than issues with the skin. There are many causes of neuropathic itch, including stroke, diabetes, and shingles. the use of gabapentin and pregabalin as antipruritic agents are explored. They are found to be promising alternative treatments for the relief of several forms of chronic pruritus, particularly uremic pruritus and neuropathic or neurogenic itch, in patients who fail conservative therapies. (J Am Acad Dermatol 2016;75:619-25.) There is currently no standardized algorithm for the treatment of chronic pruritus (CP), or itch lasting more than 6 weeks, in adults aged ≥ 65 years. The antiepileptic agents gabapentin and pregabalin, however, are gaining popularity in the dermatologic community for their efficacy in treating CP of neuropathic origin. Yet the lack of literature specifically looking at the safety and As such, Dr. Elmariah says, gabapentin has been used extensively off-label for neuropathic pain and itch. “And there’s been efficacy reported for the treatment of neuropathic, brachioradialis, post-burn, uremic, cholestatic and postherpetic itch,” she says. Topical ketamine, often compounded with topical amitriptyline and/or topical lidocaine, has been used for intractable itch 3 and neuropathic itch with significant itch reduction 4. Systemic agents: Dermatologist have borrowed medications used for other diseases, and in other fields of medicine, to treat itch. Gabapentin is approved by the UD Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of seizures and PHN, 52 and is effective in the treatment of neuropathic forms of itch, such as brachioradial pruritus, prurigo nodularis, and notalgia paresthetica. 53 There are promising case reports regarding the use of gabapentin in scalp dysesthesia, 20 Gabapentin is a well-established treatment option for itch with a reassuring safety profile that does not require continued lab monitoring. Generalized itching is a common cause of visits to the dermatologist and can be difficult to treat, leading to sleepless nights and inability to function. The use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain/pruritus is recommended only in patients over 18 years of age. The starting dose is 900mg/day (given as 300mg 3 times daily) and increased if necessary based on response. In the present study, the use of oral gabapentin 300 mg a day for the treatment of itching caused by NP showed to be efficient and led to a significant improvement in rates of itching intensity as assessed by the VAS. A neurological itch (also called neuropathic itch) is caused by injury to nerve fibers in the brain, spinal cord, skin, or other parts of the body. Unlike many other types of itch, neuropathic itches often involve nerve pain and often get more intense the more you scratch. Gabapentin and pregabalin were initially developed as antiepileptics, but are now also used for treating neuropathic pain such as that caused by diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. 17, 18 Among the array of agents that can be used for these indications, gabapentin is favored because of its low adverse-effect profile, broad therapeutic index, absence of drug-drug interactions Much like neuropathic pain, neuropathic itch is a result of neuropathy due to damage to the nervous system (36 – 38), including damage to peripheral nerves, the spinal cord, and the brain. Neuropathic itch could be more common than generally appreciated because most neuropathic pain conditions may have a neuropathic itch component . Neuropathic pruritus may also present as a generalized process due to the phenomenon of central sensitization, in which limited nerve damage leads to heightened neurotransmitter release and hyperexcitable spinal neurons 10,11. Neuropathic itch has a significant impact on the sleep and quality of life of patients, even when it is localized 12. In this review we discuss the safety and efficacy of the gabapentinoids, and advocate for their use not just in neuropathic, but also in multifactorial, itch. Second-line therapies for generalized or severe neuropathic itch include gabapentin, pregabalin, amitriptyline, carbamazepine, or oxcarbazepine. They should be started at lower doses and increased as needed while monitoring for adverse effects. Gabapentin, even at low doses, is often used by HMGS Dermatology providers to treat neuropathic pruritus when standard therapy is ineffective. This drug has been used safely for years to treat pain after shingles (postherpetic neuralgia). Neuropathic itch is characterized by a persistent itch. It can be relentless and difficult to relieve. Anticonvulsants and pain modulators, such as gabapentin and carbamazepine, which are inhibitors of the neuropathic afferent pathway, are used for neuropathic pain and also have antipruritic effects . The antipruritic mechanism is still unknown, but it has been speculated to involve in both central and peripheral pathways. itch, as well as small fiber neuropathies such as postherpetic neu-ralgia.6 Patients with other itchy conditions such as prurigo nod-ularis, aquagenic pruritus, and uremic pruritus have also reported relief of itch with capsaicin.11,12 Additionally, a more potent 8% capsaicin patch can provide prolonged relief in neuropathic itch Neuropathic itch is the result of excess peripheral firing or dampened central inhibition of itch pathway neurons and a symptom of the same central and peripheral nervous system disorders that cause neuropathic pain, such as sensory polyneuropathy, radiculopathy, herpes zoster, stroke, or multiple sclerosis, according to Martin Steinhoff, M.D
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/the-neuroscience-of-itch-2488868_color1-d501f506ed1040ba8f5a0ecef336669d.jpg) |