Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
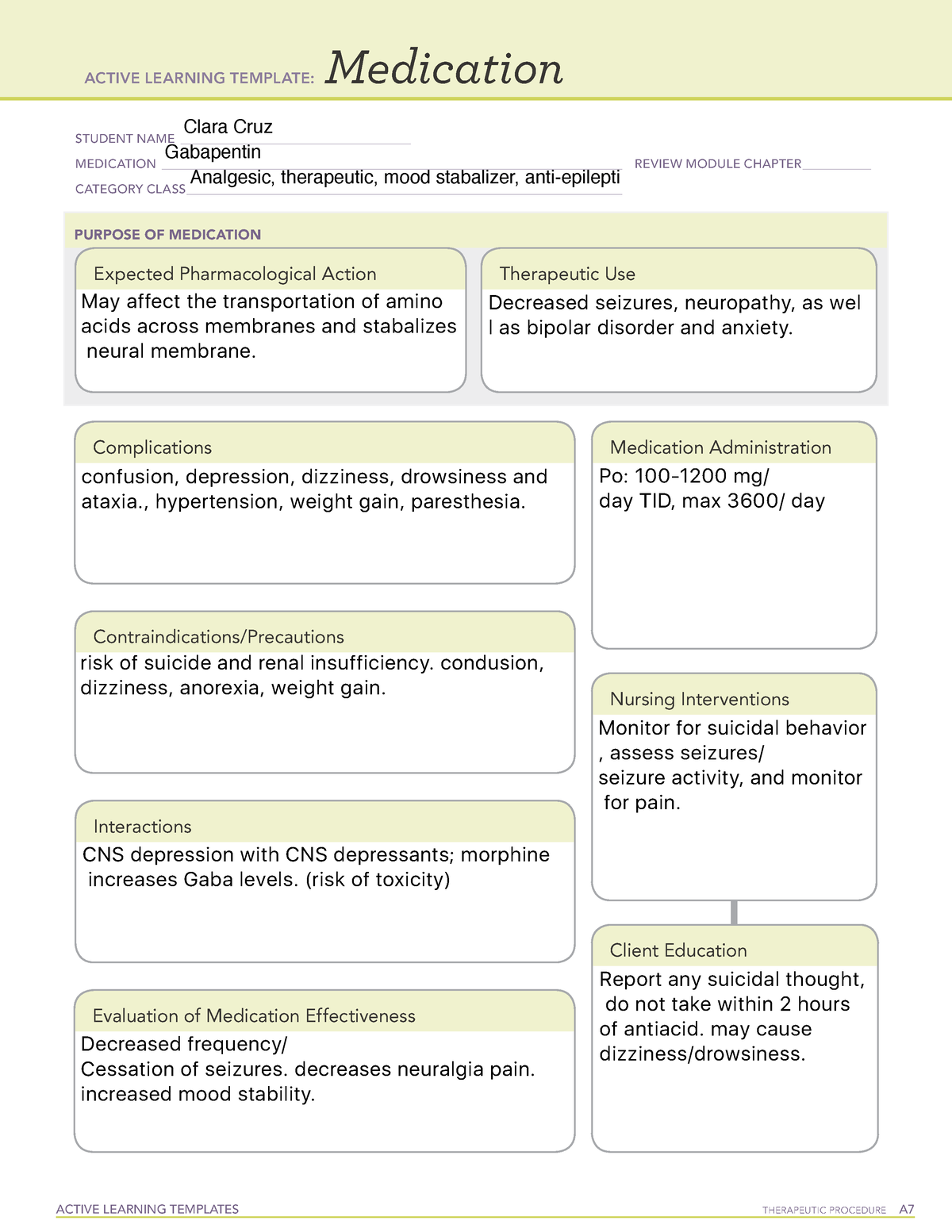
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant medication commonly prescribed for epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and various off-label uses. Understanding proper nursing considerations is crucial for safe and effective patient care. The oral solution contains 250 millgrams of gabapentin per 5 milliliter (50 mg per mL) Neurontin or generic gabapentin. Gabapentin capsules. It’s available as 100-, 300- or 400-milligram gelatin capsules (Neurontin or generic gabapentin). We use Gabapentin for the prevention of seizures for peripheral neuropathy, for neuropathic pain and for the prevention of migraines. So some of the side effects that we see with Gabapentin are things like drowsiness, facial edema, hypertension, and confusion. In this article, you’ll learn about Gabapentin (Neurontin) nursing implications and patient teachings. Also, its dosage, indication, contraindications, interactions, side effects, nursing assessment, and nursing interventions. Gabapentin is one of the top 100 drugs prescribed in the US, so there’s a very good chance it will show up on NCLEX or your nursing school exams. Let’s go through the key things you need to know about this medication using the Straight A Nursing DRRUGS framework. Mechanism of action: Gabapentin helps to stabilize cell membranes by changing cation (sodium, calcium, and potassium) transport, reducing excitability, and suppressing seizure focus or discharge. Indications for use: Adjunctive treatment for seizure control, postherpetic neuralgia, moderate to severe primary restless legs syndrome. Generic Name: gabapentin. Brand Name: Apo-Gabapentin (CAN), Gen-Gabapentin (CAN), Neurontin. Classification: Antiepileptic. Pregnancy Category C. Dosage & Route. Available forms : Capsules—100, 300, 400 mg; tablets—100, 300, 400, 600, 800 mg; oral solution—250 mg/5 mL. ADULTS. Epilepsy: Starting dose is 300 mg PO tid, then titrated up as Find information on Gabapentin (Gralise, Horizant) in Davis’s Drug Guide including dosage, side effects, interactions, nursing implications, mechanism of action, half life, administration, and more. Davis Drug Guide PDF. gabapentin Administer first dose at bedtime to decrease dizziness and drowsiness Monitor for worsening depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior Advise patient not to take gabapentin within 2 hr of an antacid. Gabapentin may cause dizziness and drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid driving or activities requiring alertness until response to medication is known. Seizure patients should not resume driving until physician gives clearance based on control of seizure disorder. It is important to consult with a veterinarian before using gabapentin in pregnant or nursing dogs. 7. How quickly does gabapentin work in dogs? Gabapentin typically starts to take effect within 1-2 hours of administration in dogs. However, the full effects may not be seen for several days to weeks, depending on the condition being treated. 8. Generic Name Gabapentin DrugBank Accession Number DB00996 Background. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid that was first approved for use in the United States in 1993. 16 It was originally developed as a novel anti-epileptic for the treatment of certain types of seizures 14,5 - today it is also widely used to treat neuropathic pain. 8 Three infants who were 2 to 3 weeks of age and one who was 14 weeks of age were breastfed during maternal use of gabapentin in an average daily dosages of 1575 mg (range 600 mg to 2.1 grams daily). Serum levels were measured after the morning nursing before the mothers' morning dose of gabapentin (10 to 15 hours after the prior evening's dose). Gabapentin is available in 2 forms—gabapentin immediate release and the prodrug gabapentin enacarbil. Gabapentin is available in tablet form with strengths of 600 mg and 800 mg, capsules in strengths of 100 mg, 300 mg, and 400 mg, as well as an oral solution of 250 mg/5mL. Gabapentin enacarbil is available in 300 mg extended-release tablets. Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. What is this drug used for? It is used to treat painful nerve diseases. It is used to help control certain kinds of seizures. It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor. What do I need to tell my doctor BEFORE I take this drug? If you are allergic to this drug; any part of this drug; or any other drugs, foods, or substances. ANTIEPILEPTICS, PART 2: DRUG NAME: vigabatrin (Sabril) gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise) CLASS: GABA inhibitors: GABA analogues: MECHANISM OF ACTION: Prevent GABA reuptake into presynaptic neurons; ↑ GABA concentration in synapse; ↓ seizure activity Read this chapter of Davis's Drug Guide for Rehabilitation Professionals online now, exclusively on F.A. Davis PT Collection. F.A. Davis PT Collection is a subscription-based resource from McGraw Hill that features trusted content from the best minds in PT. Nursing Considerations for Gabapentin. When administering or caring for patients taking gabapentin, nurses should consider several important factors. Nursing Assessment. 1. Assess the patient’s medical history, including any known allergies, previous adverse reactions to gabapentin or similar medications, and relevant medical conditions. Here are other nursing pharmacology study guides: Nursing Pharmacology – Study Guide for Nurses Our collection of topics related to nursing pharmacology; Pharmacology Nursing Mnemonics & Tips These nursing mnemonics aim to simplify the concepts of pharmacology through the use of a simple, concise guide. Generic Drug Name Stems Cheat Sheet
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |