Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
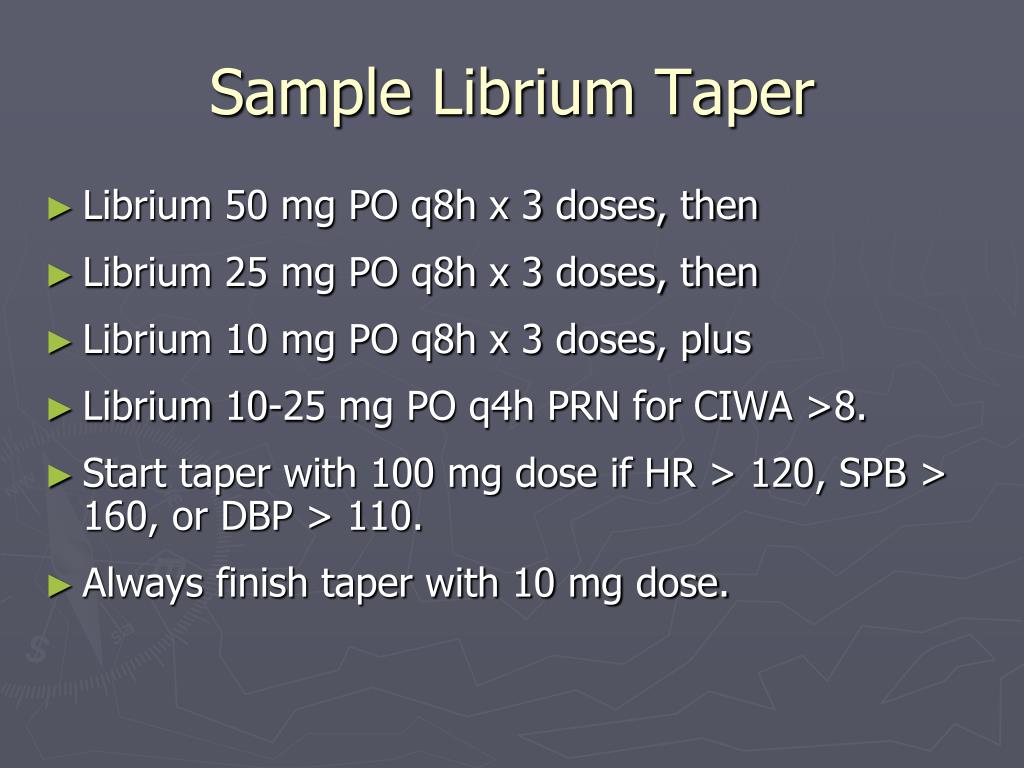
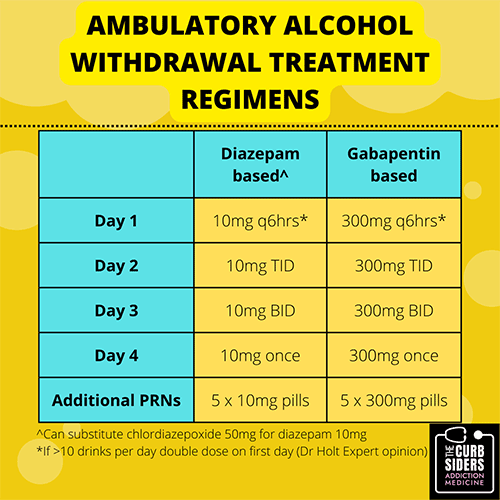
Population People with alcohol dependence commencing treatment for alcohol withdrawal in an outpatient setting Intervention Any treatment for alcohol withdrawal Comparator Not applicable Outcomes Recommendations regarding the treatment of alcohol withdrawal (e.g., which treatments are recommended, guidance for specific population groups) s can be treated with carbamazepine or gabapentin. Benzodiazepines are first-line therapy for moderate to severe symptoms, with carbamazepine and gabapenti. In ambulatory veterans with symptoms of alcohol withdrawal, gabapentin treatment resulted in significantly greater reduction in sedation (ESS) and a trend to reduced alcohol craving (PACS) by the end of treatment compared to chlordiazepoxide treatment. Although limited by the small sample size, the Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Find out what you need to know about gabapentin for alcohol withdrawal and discover the pros, cons, risks, and benefits, and how it may affect health. The National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism states that alcohol is the most widely used substance in the US. Over 75% of individuals aged 12 and older have reported drinking alcohol at some point in their lives, and nearly 30% of those aged 18 and older engage in binge drinking. 1 Binge drinking is defined as consuming 5 or more drinks on a single occasion for men and 4 or more UpToDate For instance, studies have highlighted the efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal symptoms (Mariani et al. 2006; Myrick et al. 2009). Additional trials found a benefit of combining gabapentin with naltrexone (Anton et al. 2011) and with flumazenil (Anton et al. 2009; Schacht et al. 2011). These studies consistently Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of gabapentin as a benzodiazepine-sparing agent in patients undergoing alcohol withdrawal treatment in all the hospitals of a large tertiary healthcare system. Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. outpatient alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol • MLDA is 21, 1984, regulated • >200 diseases and injury-related health conditions, ~95K US and 3M Gabapentin * 5-7 hours. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse. ↑ Muncie HL et al. Outpatient Management of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 2013 Nov 1;88(9):589-595. ↑ Leung JG, Hall-Flavin D, Nelson S, et al. The role of gabapentin in the management of alcohol withdrawal and dependence. Ann Pharmacother. 2015; 49(8):897-906. ↑ Myrick, H et al. A double blind trial of gaba pentin vs Gabapentin is an evidence-based alternative to benzodiazepines in the outpatient setting, but there is limited data for hospitalized patients with AWS. This study compared fixed-dose gabapentin to CIWA-directed benzodiazepines for AWS in the hospital setting. A randomized trial (n = 164) comparing outpatient and inpatient treatment of male veterans with mild to moderate withdrawal symptoms found the duration of therapy was shorter for outpatients. 13 ⦁ Gabapentin is advantageous for withdrawal because (unlike benzos) it can be continued for long-term treatment to prevent future alcohol relapse Moderate Outpatient Withdrawal With Benzodiazepines Clonazepam (Klonopin) is usually the first-choice benzodiazepine for outpatient withdrawal due to a lower likelihood of causing euphoria. Research on alternative pharmacologic agents to facilitate safe alcohol withdrawal is scant. Gabapentin is one medication shown in small studies to reduce the need for benzodiazepines in the setting of alcohol withdrawal. While gabapentin is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for alcoholism, a number of studies support the its use withdrawal and cravings: In a 12-day study detoxifying with either gabapentin or lorazepam (a benzodiazepine prescribed with the brand name Ativan), the former was less likely to drink – and had less craving, anxiety, and sedation.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |