Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
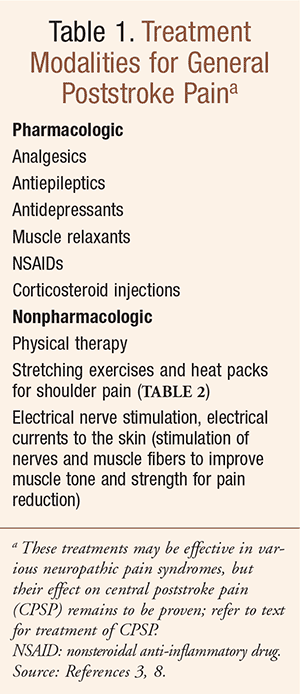
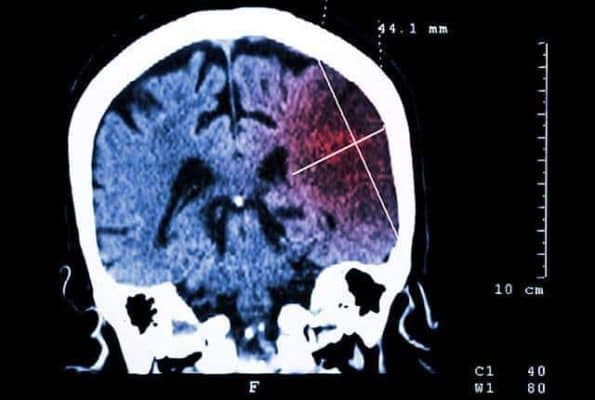
New research in mice led by Andrea Tedeschi, PhD, assistant professor of Neuroscience at The Ohio State University College of Medicine shows the drug gabapentin currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke. There was no significant difference in Pain Disability Index scores between groups. Serpell et al. (2002) randomized 307 patients with a wide range of neuropathic pain syndromes (9 with post stroke pain) to receive either gabapentin or placebo for 8-weeks. Gabapentin was given in three divided doses to a maximum of 2400 mg/day. Pain after stroke is a common symptom that is poorly understood by many practitioners. It can be easily overlooked due to its variable characteristics, concurrent comorbid medical issues, or impairments in cognition or communication. Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) are two anticonvulsants that doctors may prescribe for pain after a stroke. These drugs are calcium channel modulators. Gabapentin's role in stroke recovery. Gabapentin is a drug that has been approved for the treatment of seizures and nerve pain. It has been found to be effective in reducing pain and improving recovery after a stroke. Efficacy in pain reduction. Central post-stroke pain (CPSP) is a type of neuropathic pain that occurs after a stroke, affecting The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests. Experiencing pain after a stroke is common, and this can manifest in many ways, including leg pain. Post-stroke pain can range from irritating headaches to severe joint pain. It can compromise the quality of life for patients and caregivers, impacting their ability to sleep, their overall sense of well-being, and their participation in therapy. Thalamic pain syndrome, a type of central post-stroke pain (CPSP), may develops after a hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke and results in impairment of the thalamus. There is limited experience about gabapentin in treatment of central pains like CPSP. The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up Another study conducted by Mesgari et al. (2017) showed the ability of gabapentin to prevent CSD-induced disinhibition by increasing the amplitude of inhibitory postsynaptic potentials and inhibiting the induction of long-term potentiation after CSD. Further studies are required to investigate the effects of gabapentin on CSD. Pain after stroke Gabapentin has been found to enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signalling work of lost cells. In mice, daily gabapentin treatment for six weeks after a stroke restored fine motor functions in the animals' upper extremities. Stroke Pain. A stroke keeps blood from reaching the brain and leads to brain tissue damage. About 10% of people who experience a stroke eventually develop severe pain that is called post-stroke pain, central pain, or thalamic pain (after the part of the brain typically affected). The onset and character of this pain is highly variable. People after stroke who cannot or find it difficult to follow a mouth care regimen should receive mouth care from appropriately trained staff, family member or carer. Pain — neuropathic (central post-stroke pain) Treat people with central post-stroke pain with amitriptyline, gabapentin, or pregabalin. We systematically summarize the preclinical and clinical research on gabapentinoids in stroke, including ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, seizures after stroke, cortical spreading depolarization after stroke, pain after stroke, and nerve regeneration after stroke. Objective: This small clinical trial describes the efficacy of gabapentin therapy in patients with neuropathic pain syndromes after stroke. Background The problem of rehabilitation in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke remains one of the most actual in neurology. 80 % patients after stroke become disabled. The drug gabapentin, currently prescribed to control seizures and reduce nerve pain, may enhance recovery of movement after a stroke by helping neurons on the undamaged side of the brain take up the signaling work of lost cells, new research in mice suggests.The experiments mimicked ischemic stroke in humans, which occurs when a clot blocks bloo Pain is a frequent problem after stroke. It can occur soon after a stroke, but can also develop sometime later. This page looks at different types of post-stroke pain including muscle and joint pain such as spasticity and shoulder pain, headaches and central post-stroke pain. If you are in pain after a stroke, try speaking to your GP or stroke Gabapentin is often prescribed to stroke patients to alleviate post-stroke pain and improve recovery. Learn about its benefits, dosage guidelines, and potential side effects. In a rat model, gabapentin promoted recovery after stroke, unleashing plasticity in the corticospinal tract to improve motor function. Independent experts said the finding is promising for potential clinical applications in the future. Gabapentin has also been found to be effective in treating post-stroke pain, also known as central post-stroke pain (CPSP), which occurs in 8%-14% of patients with stroke. CPSP is a central neuropathic pain condition occurring after a stroke, characterised by pain and sensory abnormalities.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |