Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
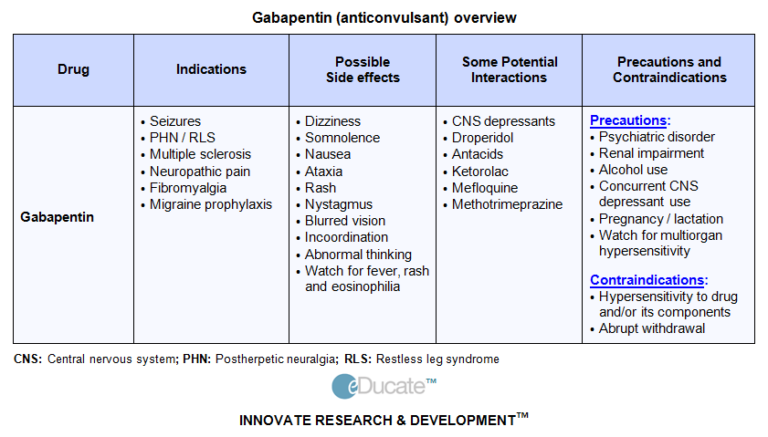
Hauer, J.M. and J.C. Solodiuk, Gabapentin for Management of Recurrent Pain in 22 Nonverbal Children with Severe Neurological Impairment: A Retrospective Analysis. Journal of palliative Context: Gabapentin has shown benefits for a variety of pain etiologies in adult patients, with off-label use as an adjunctive agent in pediatric patients occurring more frequently. Objectives: To summarize the studies which evaluate safety and efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of pediatric pain. Off-label drug use is common in the treatment of paediatric pain. The project investigates the efficacy and safety profile of gabapentin for use in children. There was no high quality evidence to support the use of anti-convulsant drugs in children and young people with chronic pain. One RCT compared the effectiveness of amitriptyline with gabapentin in the treatment of neuropathic pain in children . This was a well-designed study, but only limited conclusions could be drawn in view of the small Brown S, Johnston B, Amaria K, Watkins J, Campbell F, Pehora C, et al. A randomized controlled trial of amitriptyline versus gabapentin for complex regional pain syndrome type I and neuropathic pain in children. Scand J Pain. 2016. October;13:156–63. [Google Scholar] 49. Orellana Silva M, Yanez V, Hidalgo G, Valenzuela F, Saavedra R. 5% Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog that has been used in multiple disease states in children, including neuropathic pain, irritability, visceral hyperalgesia, neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rescue sedation and feeding intolerance. 1–7 Despite the increased utilization of gabapentin in neonates, 1 there remains a gap in the pedia Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® Why is it important for my child to take this medicine? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is gabapentin available as? • Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg • Capsules: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg; these contain small amounts of lactose • Liquid medicine: 50 mg in 1 mL; these may contain Gabapentin has shown benefits for a variety of pain etiologies in adult patients, with off-label use as an adjunctive agent in pediatric patients occurring more frequently. To summarize the studies which evaluate safety and efficacy of gabapentin for the treatment of pediatric pain. Child 12–17 years Initially 300 mg once daily on day 1, then 300 mg twice daily on day 2, then 300 mg 3 times a day on day 3, alternatively initially 300 mg 3 times a day on day 1, then increased in steps of 300 mg every 2–3 days in 3 divided doses, adjusted according to response; usual dose 0.9–3.6 g daily in 3 divided doses (max. per dose 1.6 g 3 times a day), some children may not On a few studies, gabapentin was used on children with neuropathic pain developed after thoracotomy, complex regional pain syndrome, or cerebral palsy, and it was found highly effective [5, 13, 14]. Gabapentin was used for multimodal analgesia in paediatric patients having neuropathic pain due to cancer. line, Scopus, and Web of Science up until November 2017, for randomized controlled trials that investigated the analgesic effects of gabapentin or pregabalin in children and adolescents <18 years of age. A total of 7 publications were identified, 5 regarding gabapentin as prophylactic postsurgical pain relief for either adenotonsillectomy (n = 3) or scoliosis surgery (n = 2), and 1 for Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog that has been used in multiple disease states in children, including neuropathic pain, irritability, visceral hyperalgesia, neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rescue sedation and feeding intolerance. 1 – 7 Despite the increased utilization of gabapentin in neonates, 1 there remains a gap in the Gabapentin is safe to use as a multimodal analgesic agent in various pediatric patient populations, but its efficacy likely depends on the cause of pain, according to study results published in In a study published over a decade ago, Hauer et al first identified the potential benefits of gabapentin in nine children with SNI 4 and a follow-up study by the same author identified an improvement in pain behaviours in over 90% of 22 children treated with gabapentin. 5 We performed a retrospective study in 42 patients, to see if the management of neuropathic pain in children and adults. It is generally well tolerated and offers several advantages over older anticonvulsants, with a milder adverse effect profile and few drug interactions.1-3 This article will review the use of gabapentin in children, both as an anticonvulsant and as an analgesic. Mechanism of Action Gabapentin Brand name: Neurontin® Why is it important for my child to take this medicine? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. What is gabapentin available as? • Tablets: 600 mg, 800 mg • Capsules: 100 mg, 300 mg, 400 mg; these contain small amounts of lactose • Liquid medicine: 50 mg in 1 mL; these may contain This leaflet is about the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). Why is it important for my child to take Gabapentin? Gabapentin will help your child to feel less pain. Detailed Gabapentin dosage information for adults and children. Includes dosages for Restless Legs Syndrome, Epilepsy and Postherpetic Neuralgia; plus renal, liver and dialysis adjustments. Pain is a frequent and significant problem for children with impairment of the central nervous system, with the highest frequency and severity occurring in children with the greatest impairment. Despite the significance of the problem, this population remains vulnerable to underrecognition and undertreatment of pain. Barriers to treatment may include uncertainty in identifying pain along with We performed a retrospective study to explore the use of gabapentinoid medications for symptom control in children with SNI. Patients attending the palliative care or gastroenterology department being treated with gabapentin for irritability, vomiting or pain of unknown origin were included.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |