Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
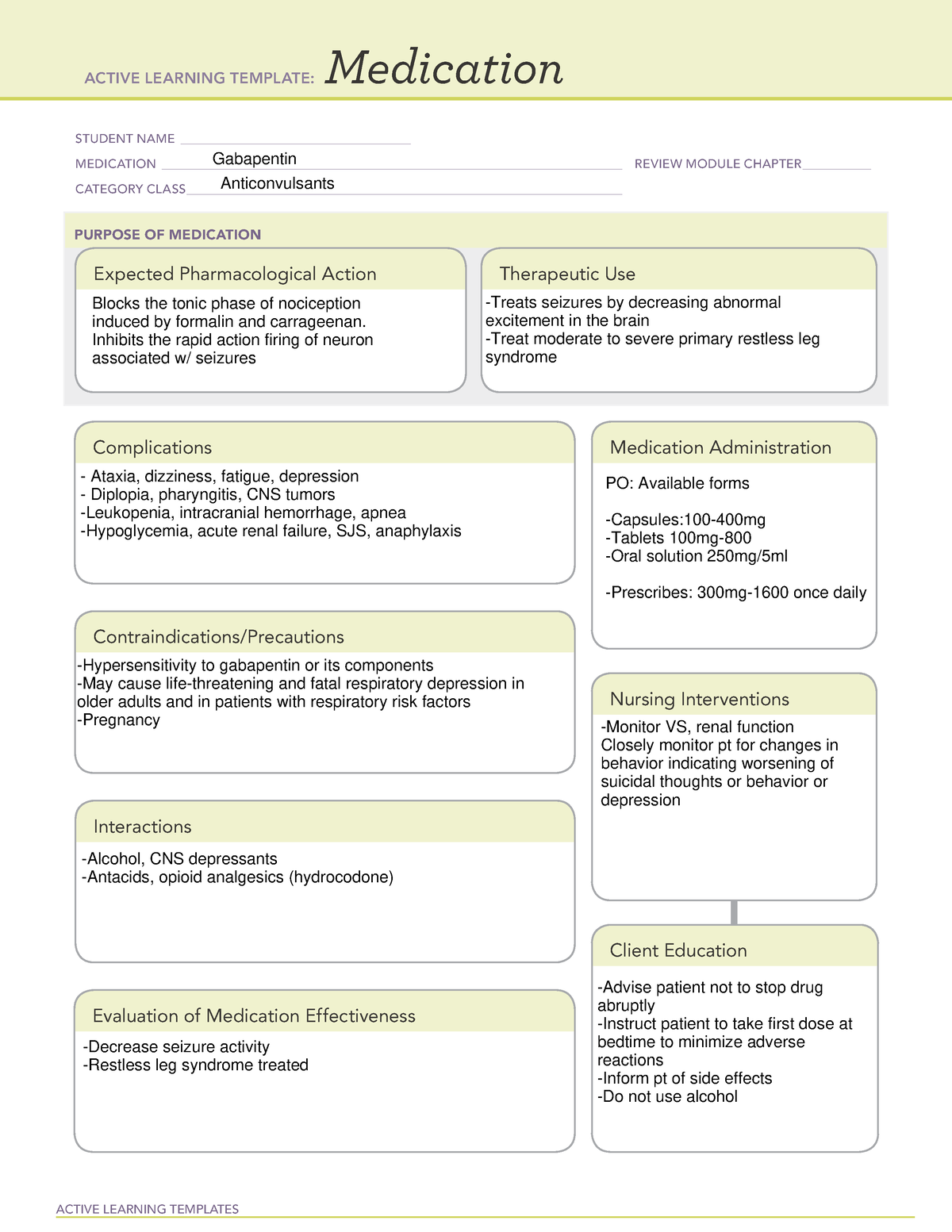
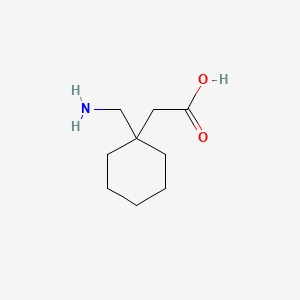
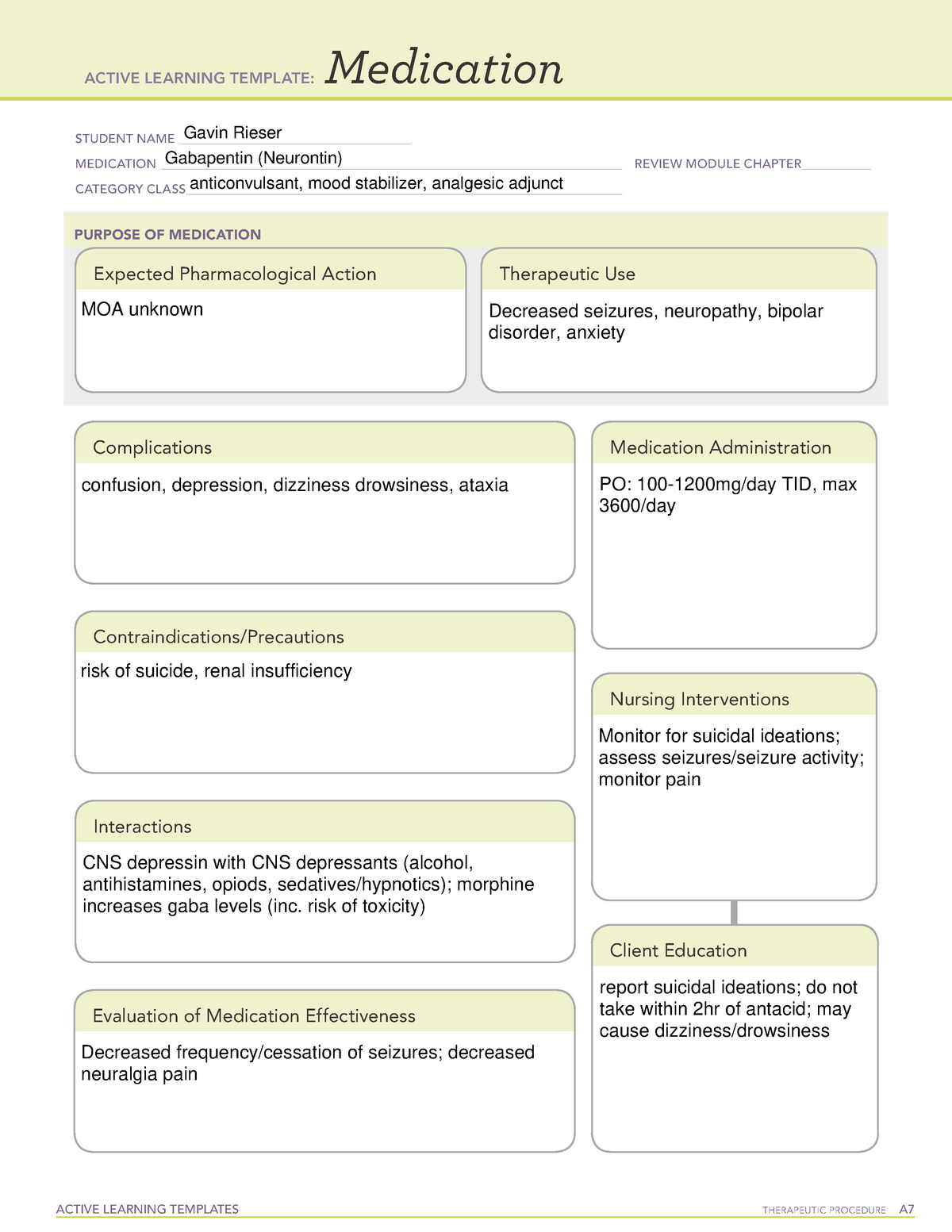
Gabapentin is used to treat and prevent some types of pain and seizures. It is also sometimes used for other conditions. Before you start. Tell your doctor if you have kidney problems. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding. How should you take it? Take gabapentin regularly as directed with a glass Gabapentin is used to treat some types of nerve pain and epilepsy and prevent migraine headaches. Find out how to take it safely and possible side effects. Gabapentin is also called Neurontin or Nupentin. Gabapentinoids are an effective treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy; there is increasing evidence that they are not effective for people with sciatica or non-specific low back pain. There is also growing concern of a rise in gabapentinoid misuse and dependence. What are gabapentinoids? For further information on other high-risk medicines visit our website at: www.saferx.co.nz No: 0182-01-109, Issued March 2017, Review March 2020 treat neuropathic pain, a type of pain caused by damage to the nerves. This medicine belongs to a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. How Gabapentin Medsurge works This medicine is thought to work by controlling brain chemicals which send signals to nerves to help control seizures or neuropathic pain. Gabapentin Medsurge also has pain NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME NEURONTIN 100 mg, 300 mg and 400 mg capsules NEURONTIN 600 mg and 800 mg film coated tablets 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each 100 mg capsule contains 100 mg of gabapentin. Each 300 mg capsule contains 300 mg of gabapentin. Each 400 mg capsule contains 400 mg of gabapentin. How effective is gabapentin for chronic neuropathic pain in adults? Gabapentin at doses of 1800–3600mg/day provided good levels of pain relief (at least 50% reduction over baseline) to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain was very limited. Gabapentin also has pain relieving effects. Your doctor may have prescribed gabapentin in addition to other medicines that you may be taking. This may be necessary if your current treatment is no longer working as well. Gabapentinoids are an efective treatment for post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy; there is increasing evidence that they are not efective for people with sciatica or non-specific low back pain. There is also growing concern of a rise in gabapentinoid misuse and dependence. What are gabapentinoids? neuropathic pain, focusing on the use of gabapentin and pregabalin, as subsidy changes will come into effect for these medicines in mid-2018. For further information on the diagnosis and full range of treatments for neuropathic pain, see: “Managing patients with neuropathic pain” bpac.org.nz/ BPJ/2016/May/pain.aspx Does gabapentin help treat nerve pain? How does gabapentin come? There are several brand names of gabapentin including Gralise, Horizant, and Neurontin. Use only the brand and form of gabapentin your doctor has prescribed. Gralise (gabapentin) is indicated for the management of postherpetic neuralgia only. It is not used for epilepsy. Gabapentin is indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain (see section 4.2). Adults and Children Older than 12 Years of Age Initiation of treatment should be as add-on therapy. Gabapentin can be given orally with or without food. Gabapentinoids are most effective for post-herpetic neuralgia and painful diabetic neuropathy. Before reading this article were you aware of the limited efficacy outside of neuropathic pain? Do you prescribe gabapentinoids for unapproved indications, and if so, what for and why? Pain (external link) New Zealand Formulary, NZ; Analgesics (external link) New Zealand Formulary, NZ; The principles of managing acute pain in primary care (external link) BPAC,NZ, 2018; Prescribing gabapentin and pregabalin: upcoming subsidy changes (external link) BPAC, NZ, 2018; Managing patients with neuropathic pain (external link) BPAC Gabapentin and pregabalin are indicated for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Use of gabapentinoids for other types of pain (eg, chronic or musculoskeletal pain) is unapproved and is not supported by clinical evidence. Discontinuation symptoms reported include insomnia, nausea, anxiety, pain, and sweating.4 Determining dose equivalence between gabapentin and pregabalin is complicated by gabapentin’s nonlinear bioavailability, in contrast to pregabalin’s linear bioavailability.6 Gabapentin’s bioavailability ranges from 80% with 100mg tds6 to 35% with 1 Information for parents and carers about the use of gabapentin for neuropathic pain (pain caused by nerve damage). For free medical advice call Healthline 0800 611 116. Healthline provides a 24 hour, 7 days a week, over-the-phone health service. For emergencies call 111. As pregabalin has not previously been subsidised in New Zealand, it may be a new medicine for some prescribers. Like gabapentin, pregabalin was designed with the original therapeutic intent of managing seizures in patients with epilepsy, however, in clinical practice it is primarily used for managing neuropathic pain. The New Zealand Formulary. The NZF is an independent resource providing healthcare professionals with clinically validated medicines information and guidance on best practice, enabling healthcare professionals to select safe and effective medicines for individual patients. qualities.1 The pain may be constant, in response to triggers, or occur intermittently with no obvious cause. Long-term neuropathic pain can cause central sensitisation, resulting in an exaggerated pain in response to mildly painful stimuli (hyperalgesia) or pain in response to innocuous stimuli (allodynia).
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |