Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
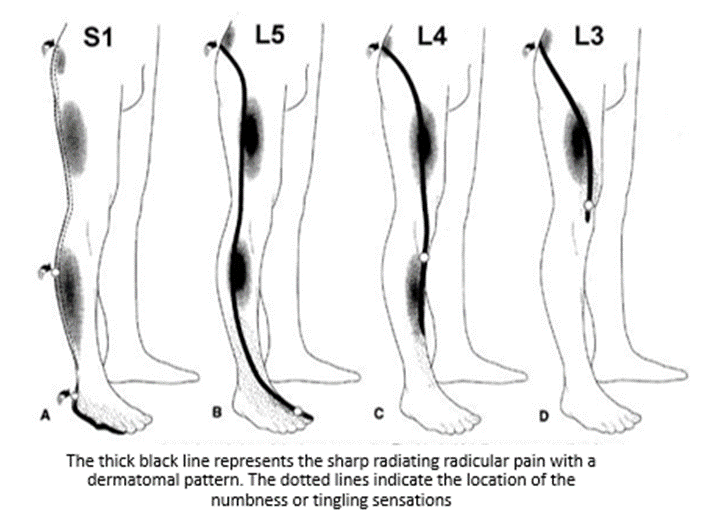 |  |
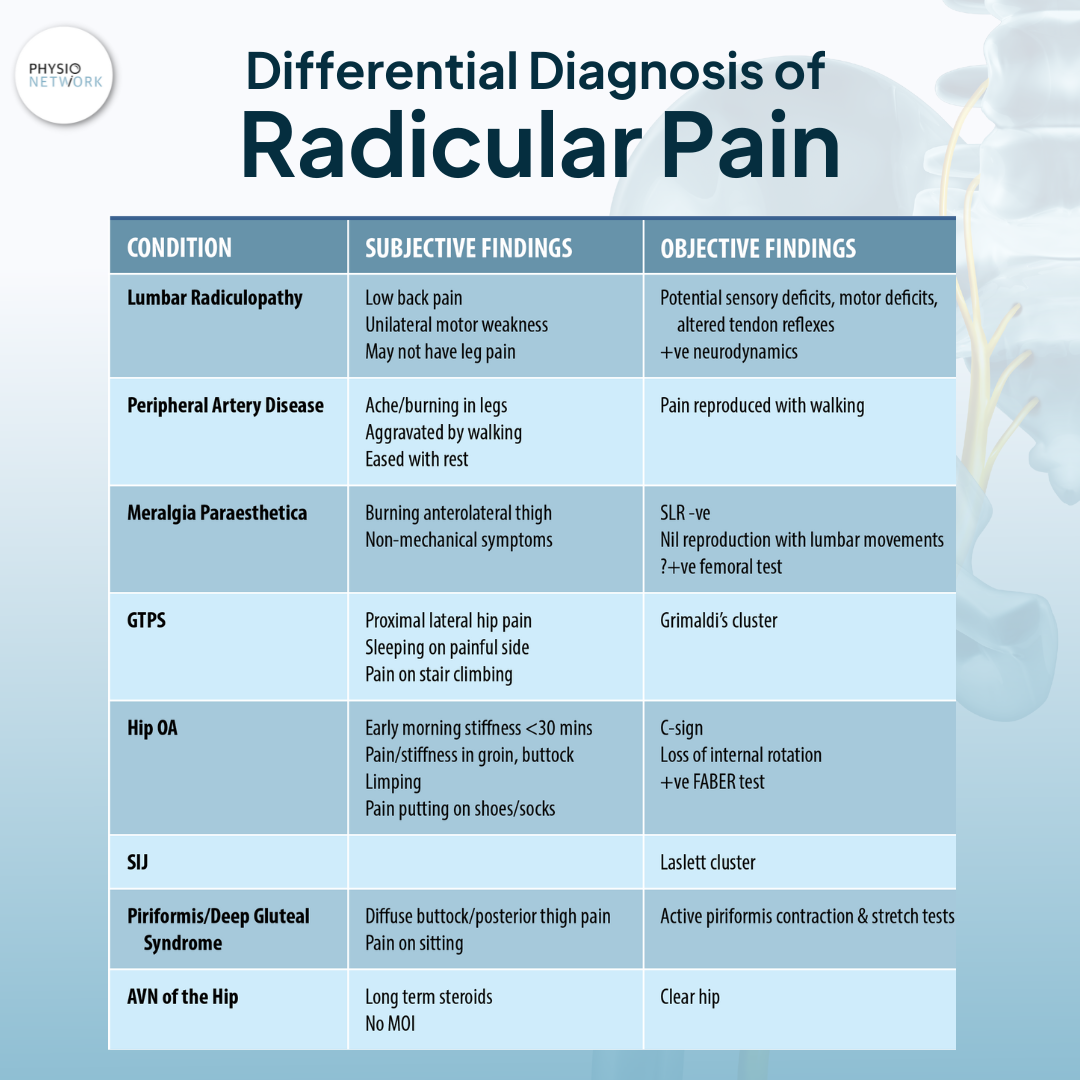
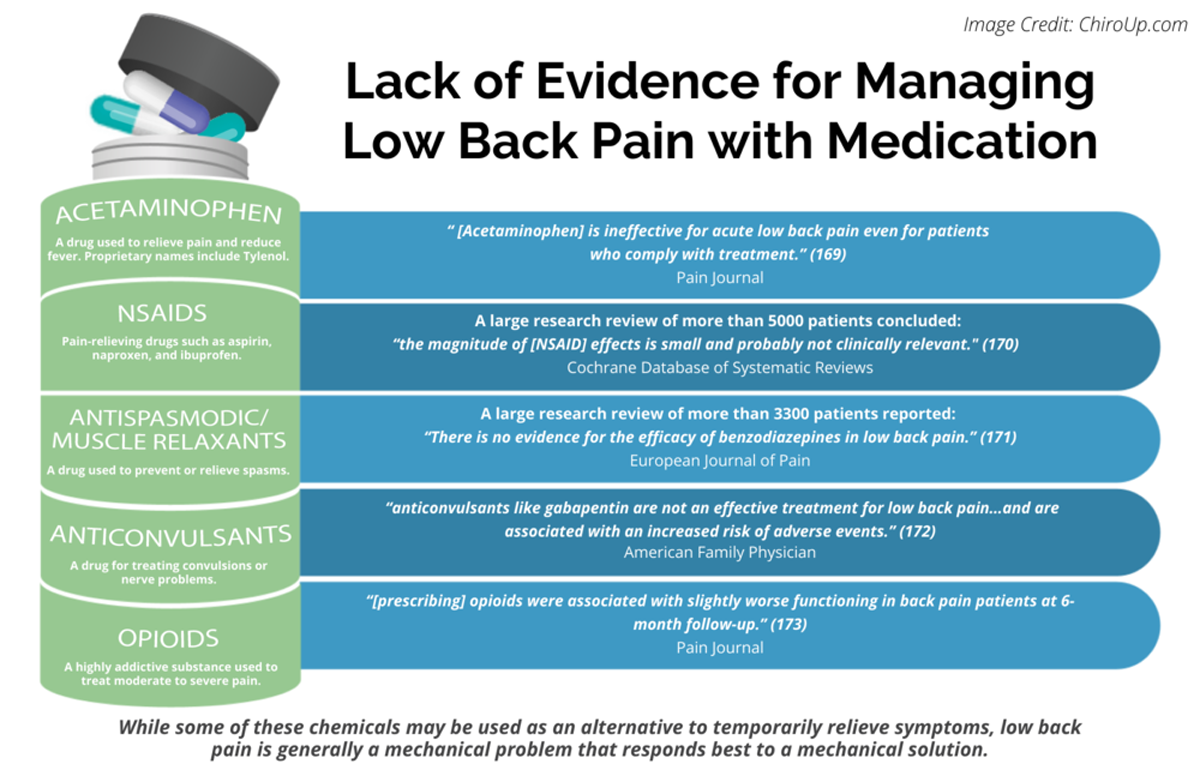
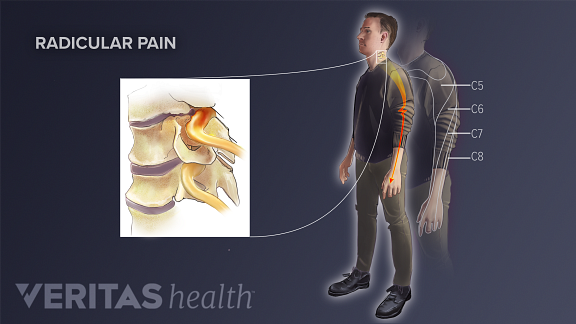
Gabapentin for other types of nerve pain. Gabapentin can also treat nerve pain from PHN, which is the most common complication of shingles. It’s also used off-label to treat diabetes-related nerve pain. If you have nerve pain from other causes — like back injury, nerve injury, or after surgery — it still may help. Exclusion criteria: Axial pain greater than radicular pain, motor deficits, bowel and/or bladder dysfunction, workmen's compensation or disability issues, depression or the use of anti-depressants, current use of strong narcotics, history of addiction, current or prior gabapentin or pregabalin use, known neuropathy such as diabetic neuropathy Gabapentin could be an option in the conservative management of acute or chronic radicular pain. The efficacy of gabapentin monotherapy was investigated against both acute or chronic radicular pain caused by lumbar disk hernia (LDH) or lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS). sacral radicular pain may occur with other radicular irritation symptoms (12). Radicular pain distinguishes itself from somatic referred pain (13). The physiological basis of radicular pain stems from “ectopic discharges emanating from a dorsal root or its ganglion” (13). It is held that disc herniation is the most common cause of radicular Efficacy of anticonvulsants for lumbar radicular pain. Four studies investigated the efficacy of gabapentinoids (pregabalin or gabapentin) versus placebo in patients with lumbar radicular pain, 27, 29, 30, 34 in which 3 studies provided data for inclusion in the forest plot 29, 30, 34 . Gabapentin is prescribed frequently for chronic back pain syndromes in both primary care and specialty pain clinics, particularly when there is a ‘radicular’ or neuropathic component with pain radiating into the upper or lower legs . Is an epidural steroid injection or gabapentin (Neurontin) more effective for pain relief in patients with lumbosacral radicular pain due to a herniated disk or spinal stenosis? Interpretation: There is moderate- to high-quality evidence that anticonvulsants are ineffective for treatment of low back pain or lumbar radicular pain. There is high-quality evidence that gabapentinoids have a higher risk for adverse events. Protocol registration: PROSPERO-CRD42016046363. © 2018 Joule Inc. or its licensors. Methods: Thirty-five patients with radicular pain and diagnosed as L4, L5 or S1 radiculopathy were treated with oral gabapentin from a total of 300 mg per day once up to a total of 1800 mg per day divided in 3 doses for eight-week trial period. Participants: 145 people with lumbosacral radicular pain secondary to herniated disc or spinal stenosis for less than four years in duration and in whom leg pain is as severe or more severe than back pain. Interventions: Participants received either epidural steroid injection plus placebo pills or sham injection plus gabapentin. Background: The health and efficacy profiles of Gralise® in the treatment of pain from spinal stenosis and radicular symptomatology have not been measured. A review of the current literature indicates that no studies exist that evaluate the safety and efficacy profiles of Gralise® in the treatment of pain from spinal stenosis and radicular symptomatology. Gabapentin is not effective for the treatment of radicular low back pain and is associated with adverse effects. (Strength of Recommendation: B, based on a systematic review of A common assumption is of leg pain indicating NP. However, in most cases leg pain is nonspecific and inconsistent with radicular pain, and only a painful radiculopathy with sensory signs would fulfill the diagnosis of definite NP . Even if one considers that gabapentinoids are effective against NP related to CLBP, contrasting evidences are This review finds good evidence that these drugs are not an effective treatment for low back pain with or without radiculopathy, and are associated with an increased risk of adverse events. Gabapentinoids are not approved for treatment of fibromyalgia in Australia, but are commonly used. 24 A 2017 systematic review of gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain found only one trial that compared gabapentin with placebo for self-reported pain, and there was no good evidence to support its use. 24 A 2022 meta-analysis of 44 RCTs reported that Gabapentinoids are commonly prescribed to control neuropathic pain of lumbar radiculopathy. Few trials have compared the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) and pregabalin (PGB). Therefore, the authors conducted a meta-analysis to compare the difference in effect between GBP and PGB in lumbar radiculopathy patients. A randomized controlled trial of gabapentin for chronic low back pain with and without a radiating component. Pain Transcutaneous neurostimulation parameters for neuropathic radicular pain: Gabapentin and epidural steroid injections used to treat lumbosacral radicular pain both resulted in modest improvements in pain and function, which persisted through three months. Although some differences favored epidural steroid injections, these tended to be small and transient. Lumbar radiculopathy can be presented as low back pain and radiating pain. Transforaminal epidural steroid injection (TFESI) has been used to treat radicular pain, and after the injection, additional medications such as gabapentinoids including pregabalin (PGB) and gabapentin (GBP) can be administered to relieve remnant pain. Neuropathic Pain. 600mg PO load in ED; Discharge with 300mg → 900mg per day divided tid (as in post-herpetic neuralgia regimen) Discharge with pain specialist follow-up; Max dosage 3600mg if patient already on gabapentin; Taper dose > 7 days to discontinue; Pediatric Dosing Partial seizures
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |