Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
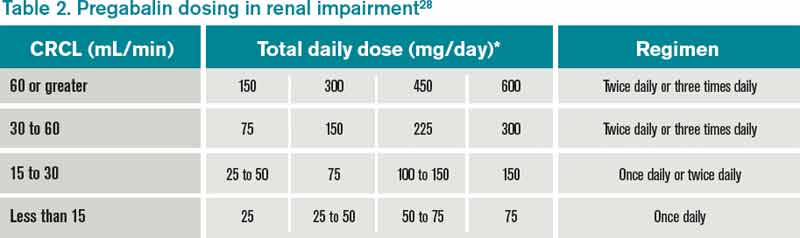
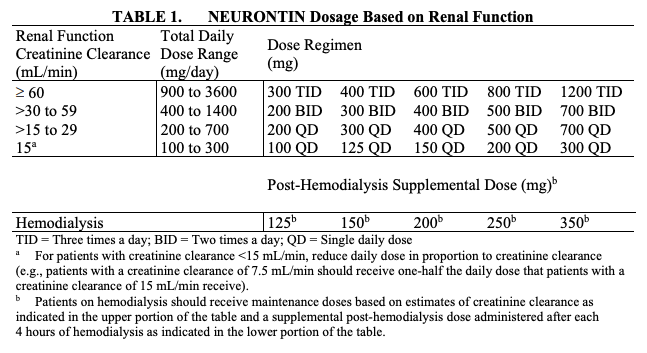
In patients with normal renal function, the maximum dose of gabapentin is 3600mg daily in divided doses. However, gabapentin is renally cleared and so the dose needs to be adjusted according to the GFR. Pain is one of the most common and distressing symptoms among patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) . The prevalence of pain has been associated with substantially lower health-related quality of life and greater psychosocial distress, insomnia, and depressive symptoms [ 2-9 ]. The short answer is: yes, gabapentin can be problematic for individuals with kidney failure and chronic kidney disease (CKD). While gabapentin is often prescribed for pain management, particularly nerve pain, and sometimes for seizures, its primary elimination pathway is through the kidneys. Loading dose of 300–400 mg in patients who have never received gabapentin. Maintenance dose of 200–300 mg after each HD : session and increase according to tolerability. Majority drugs, including Gabapentin, are eliminated by the kidneys and will accumulate to a toxic level in renally compromised patients as in this case. Per Lexicomp, Gabapentin’s recommended dose in patients with renal impairment is as follows: CrCl >15 to 29 mL/minute: 200 to 700 mg once daily. CrCl 15 mL/minute: 100 to 300 mg once daily Usual initial gabapentin dose: 300mg q8h. Usual maintenance dose: 300-600mg q8h. Maximum dosage/day: 3600 mg. [15-29]: Dosage range: 200-700mg/day. [<15]: 100-300 mg/day. Use lower end of this range for CRCL <7.5 ml/min. TABLE 1. Gabapentin Dosage Based on Renal Function. TID = Three times a day; BID = Two times a day; QD = Single daily dose. a. For adults with normal kidneys: Pain Relief: Start with 300 mg three times a day. The doctor might increase the dose to up to 3600 mg per day, taken in divided doses. Seizures: Start with 300 mg once a day, then increase to 900 mg per day, taken in three doses. 4. Renal Dosing Recommendations. Dose Adjustment: 900 - 3600 mg / TID. The 20 mg/kg stress-reduction dose of gabapentin may be beneficial to facilitate preventive veterinary care in younger, healthy cats, but this dose may be inappropriate for elderly cats, specifically those with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Gabapentin is not metabolized or protein bound, and is cleared only by renal excretion in humans; it is Gabapentin and pregabalin are commonly used for neuropathic pain in CKD patients but are not fully understood as this population remains excluded from efficacy and safety trials. Renal adjustments for the gabapentinoids are prodigiously recommended in the literature. Patients with chronic kidney disease often receive inappropriately high gabapentin dosage for their kidney function, occasioning overt toxicity; advanced age and comorbidity predispose these patients for toxicity. Gabapentin Dosage Guidelines in Adults, Adolescents 12 Years of Age and Older with Renal Impairment 1-5. Gabapentin is widely used in the management of pain. It is entirely excreted through the renal system so this needs to be considered in any patient becoming acutely ill and developing renal failure. We describe a patient who developed significant deterioration in her conscious level due to iatrogenic gabapentin overdose. Conclusion. Gabapentinoids are eliminated from the body solely by the kidney, and pharmacokinetic studies show a stepwise prolongation in the elimination half-life of gabapentin and pregabalin as kidney function declines. 9, 10 Gabapentinoids should therefore be started at lower doses in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD; guidelines are summarized Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its favorable pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Existing literature on such risk is lacking. 3 days. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 3 to 4 years of age is 40 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. The recommended maintenance dose of NEURONTIN in patients 5 to 11 years of age is 25 mg/kg/day to 35 mg/kg/day, given in three divided doses. NEURONTIN may be administered as the oral solution, capsule, or tablet, or Use: For the treatment of moderate-to-severe primary RLS in adults. Maximum dose: 2400 to 3600 mg/day; doses up to 2400 mg/day have been well tolerated in long-term studies; doses of 3600 mg/day have be used in a small number of patients for a relatively short duration and have been well tolerated. Gabapentin is frequently used as an analgesic in patients with chronic kidney disease. Although gabapentin is well known for its well recieved pharmacokinetics, it is exclusively eliminated renally, and patients with chronic kidney disease are at risk for toxicity. Renal impairment: Gabapentin dose reduction may be required, depending on renal function. Next: Interactions. Interaction Checker. Enter a drug name to check for any View gabapentin information, including dose, uses, side-effects, renal impairment, pregnancy, breast feeding, monitoring requirements and important safety information.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |