Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
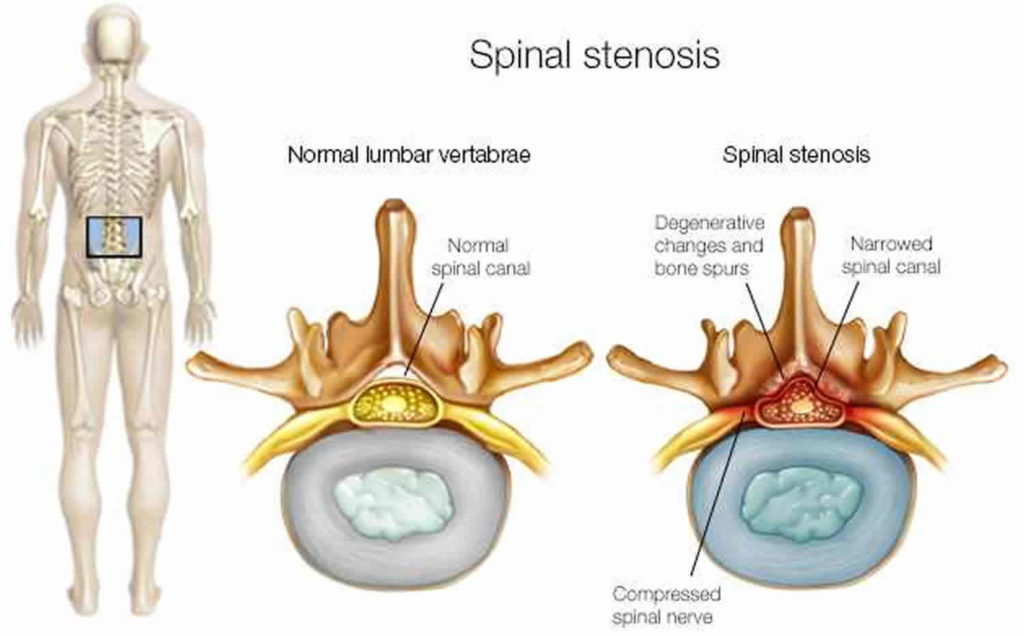 |  |
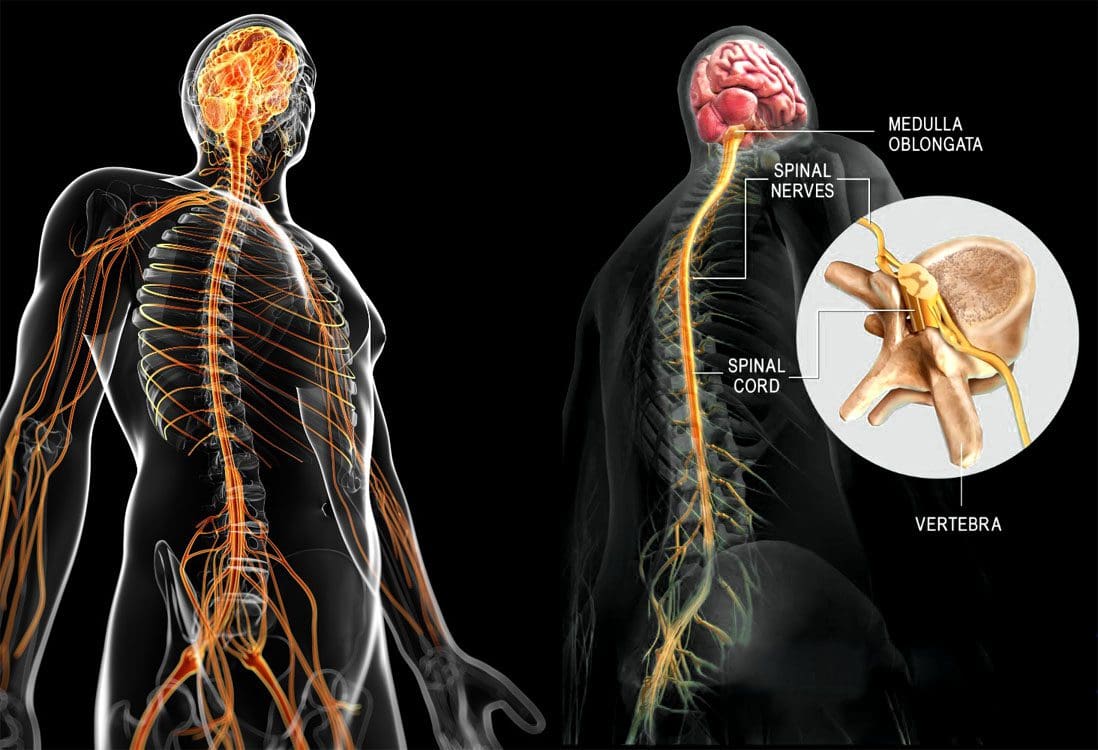
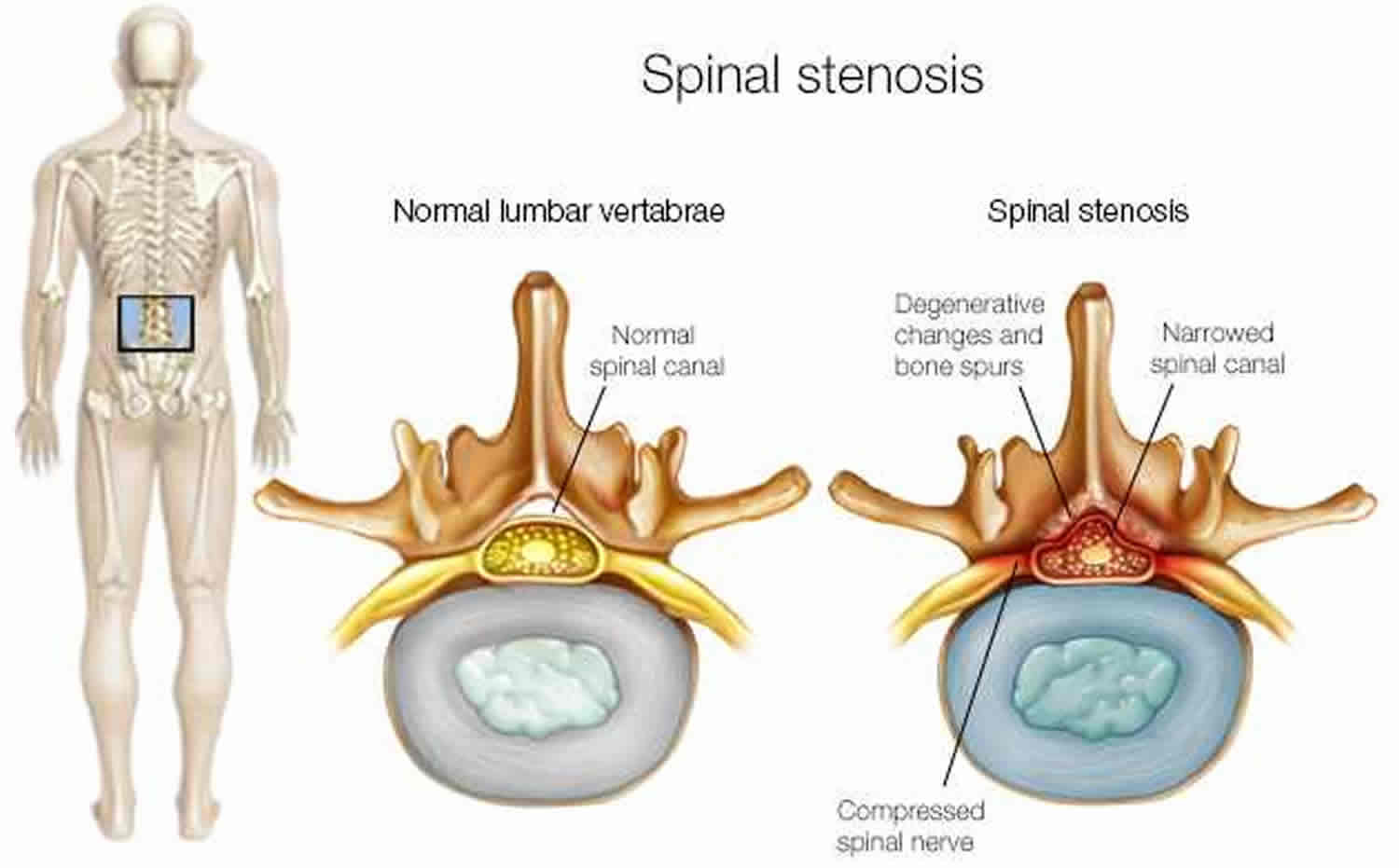
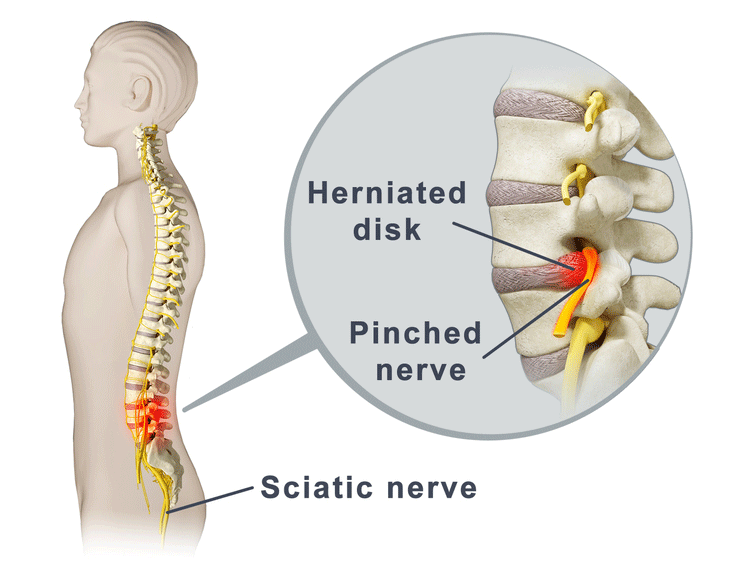
Oral steroids are powerful anti-inflammatory medications that may be an effective treatment for low back pain from degenerative disc disease. Typically, oral steroids are prescribed in a Medrol Dose Pack, starting with a high dose to provide initial low back pain relief, then tapering down to a lower dose over 5 or 6 days. Nerve pain medication: Gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica) may help reduce neck and back nerve pain, especially sciatica. Begin with low doses to avoid daytime drowsiness and fall risk. Muscle relaxants. Tizanidine (Zanaflex) and baclofen (Lioresal) may reduce pain from muscle spasms. Providers sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label for spinal stenosis. But there’s not much evidence that it provides long-term pain relief. A recent clinical practice guideline did not recommend gabapentin for spinal stenosis treatment. Severe spinal stenosis often needs surgery. However, it's best to take it at night, as one of the most frequent side effects of gabapentin is drowsiness. Most people will end up taking gabapentin three times daily. However, to ensure a consistent level of gabapentin throughout the day, it's recommended to take the medication at even intervals, approximately every eight hours. Lower Back Pain Medication. Lower back pain medication for severe spinal stenosis pain may include NSAIDs, antidepressants, anti-seizure medication, or corticosteroid shots. Medication can provide near-immediate relief from severe spinal stenosis pain, but may carry the risk of side effects and complications. NSAIDs Despite its many uses, Gabapentin is particularly effective at treating neuropathic (nerve-related) pain. According to research, Gabapentin can often alleviate back problems caused by a herniated disc or spinal stenosis. Spinal herniation occurs when a disc between adjacent spinal vertebrae slips out of place and pinches a nerve. I have been taking Gabapentin for years. I have DJD, had spinal stenosis in my neck but had surgery to correct that, and Osteoarthritis and peripheral neuropathy. The Gabapentin really helps with my peripheral neuropathy leg pain. I basically have NO pain due to this wonder drug. I have been reading about a lot of side effects, but I have not Gabapentin can be very effective in treating various types of back pains, including: Sciatica; Spinal Stenosis; Nerve Pain from Various Causes; Post-Surgery Back Pain; Arthritis-related back pain; Fibromyalgia; Is Gabapentin a Long-Term Solution for Back Pain? Spinal stenosis is a nerve compression disorder that causes low back pain and neck pain. Lumbar or cervical spinal stenosis pain often can be treated without spine surgery using medications and Gabapentin for Sciatica: Sciatica, marked by sciatic nerve compression, presents as lower back pain radiating down one or both legs. While exercise, physical therapy, and NSAIDs prove effective, a study with 747 participants found gabapentin to be less impactful for sciatica. Gabapentin changes the way the brain and body exchange messages. It calms the nerves by blocking pain-causing neurotransmitters, making gabapentin an effective treatment for sciatica and Treatment for spinal stenosis depends on how severe your symptoms are. such as gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise), are used to reduce pain caused by damaged nerves About 5% to 10% of people with low back pain have sciatica, 2 in which the leg pain follows the sciatic nerve and can be accompanied by strength, sensory and reflex changes in the leg. 3 A smaller proportion of people have neurogenic claudication, in which the leg pain is associated with spinal stenosis and symptoms are exacerbated with Gabapentin is commonly prescribed for sciatica. But the evidence supporting its use for sciatic nerve pain is weak. Sciatica is a very common condition that’s also known as lumbosacral radiculopathy. Up to 40% of people will have sciatica within their lifetime. Exclusion criteria: Known or suspected serious spinal pathology (e.g. cauda equina syndrome, spinal fracture, pregnancy, breastfeeding, planning conception tion (men [with their partners] and women) during the first 8 weeks of the trial; planned spinal surgery or other interventional procedures (e.g., a glucocorticoid injection) for sciatica Gabapentin, which has been used in the treatment of neuropathic pain, may be effective in the treatment of symptoms associated with LSS. Methods: Fifty-five patients with LSS, who had NIC as the primary complaint, were randomized into 2 groups. Several conventional treatments have been suggested for lumbar radiating pain, such as pain relief medications (acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, anti-epileptic drugs [gabapentin and pregabalin], membrane stabilizing agents, and narcotics), spinal manipulation, 1) physical therapy, massage, activity as Gabapentin is most effective in relieving neuropathic pain conditions caused by disk herniation, spinal stenosis, diabetic neuropathy, and postherpetic neuralgia. It provides limited sciatica and fibromyalgia relief, and is ineffective for reducing arthritis-related chronic low back pain. Gabapentin is prescribed for analgesia in chronic low back pain, yet there are no controlled trials supporting this practice. This randomized, two-arm, 12-week, parallel group study compared gabapentin (forced titration up to 3600 mg daily) to inert placebo. Despite the specific indications of gabapentinoids, there is a notable increase in the off-label prescription of, which has raised the concern about the misuse of these drugs since the benefits remain unclear. 17, 18, 19 To our knowledge regarding their use on sciatica, pain relief only has been reported in one trial comparing gabapentin with placebo 20 and in no one of those investigating
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |