Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
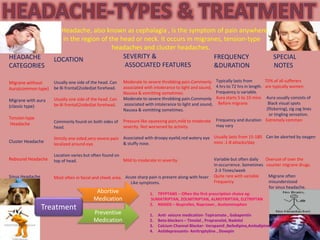 |  |
Gabapentin and Sinus headache - a phase IV clinical study of FDA data Summary: Sinus headache is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 50-59 old, have been taking the drug for < 1 month also take Cymbalta, and have Asthma. Gabapentin is used to control seizures, to treat nerve pain that can happen after having had shingles, and to treat a condition called restless legs syndrome. In addition to these FDA-approved uses, doctors sometimes prescribe gabapentin off-label. For nausea, the anti-emetic ondansetron (Zofran) is very effective, but one of the side effects is headache. You're better off using promethazine or prochlorperazine (Compazine), both of which treat nausea but also help ease headache pain, says Dr. Loder. Additionally, many anti-nausea drugs are available as rectal suppositories. Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study. You've consulted multiple specialists, and they found no issues, suggesting tension headaches. You're undergoing treatment with Gabapentin and physical therapy. There are online articles suggesting nerve-related causes for such pain. You recommend researching "chronic headaches after sinus surgery" for more information. Sinus pain is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 1 - 6 months also take Pantoprazole, and have Insomnia. A new review indicates that gabapentin may be an effective adjunct therapy for primary headache syndromes, but that there is not enough evidence to support its use as a primary Sinusitis is reported as a side effect among people who take Gabapentin (gabapentin), especially for people who are female, 60+ old, have been taking the drug for 1 - 6 months also take Acetaminophen, and have Immunodeficiency common variable. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Gabapentin is a drug that’s approved to help prevent seizures in people with epilepsy and treat nerve pain from shingles. It’s also sometimes used off-label for migraine prevention. I've had a sinus headache above my eyes. What can I take? Answer. You have many different options for a sinus headache. First off, you want to make sure you simply have a sinus headache due to congestion or inflamed nasal passages instead of a sinus infection. While sinus infections can heal on their own, often times antibiotic therapy is A viral or bacterial sinus infection causes a sinus headache and includes other symptoms, such as thick, discolored nasal discharge, facial pain and pressure, and fever. Ice-Pick Headache Ice-pick headache , or primary stabbing headache, is marked by intense, brief stabbing pain but no other symptoms. Discover the potential of gabapentin for preventing migraine attacks and headaches. While not a first-line treatment, it can be effective in combination with other options. The most common gabapentin (Neurontin) side effects are dizziness and drowsiness. This may affect your ability to drive or perform other activities. Other gabapentin side effects include edema (fluid buildup), weight gain, and eye problems, but these aren’t as common. Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Limit the use of any headache medications taken as needed to relieve headache pain to no more than two to three days per a week (or less than 10 days per month). Contact your doctor if you need to take headache medications more than two days per week. Contact your doctor if you have headache more than four days per month. of patients presenting with sinus headache is migraine di-rectedtherapy.Inahighlyselectgroupofpatients,directed nasal surgery addressing endonasal contact points may be an option. C 2013 ARS-AAOA, LLC. Key Words: headache; sinus headache; rhinogenic headache; migraine; contact points HowtoCitethisArticle: PatelZM, KennedyDW,SetzenM,PoetkerDM, Headache subtype Diagnostic criteria Nonpharmacologic treatment options Gabapentin (Neurontin) is minimally effective at high doses, and adverse effects are common. Gabapentin is in the drug class gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs. A total of 324 drugs are known to interact with Sinus Congestion & Pain. Sinus congestion & pain is in the drug class upper respiratory combinations. Sinus congestion & pain is used to treat Cough and Nasal Congestion. Patients with the episodic type remained headache-free at 3 months after discontinuation of therapy. Patients with chronic cluster were headache-free during the 4 months after initiation of treatment while taking this medication. The longest period of being continuously headache free on gabapentin was 18 months 6.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |