Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 | 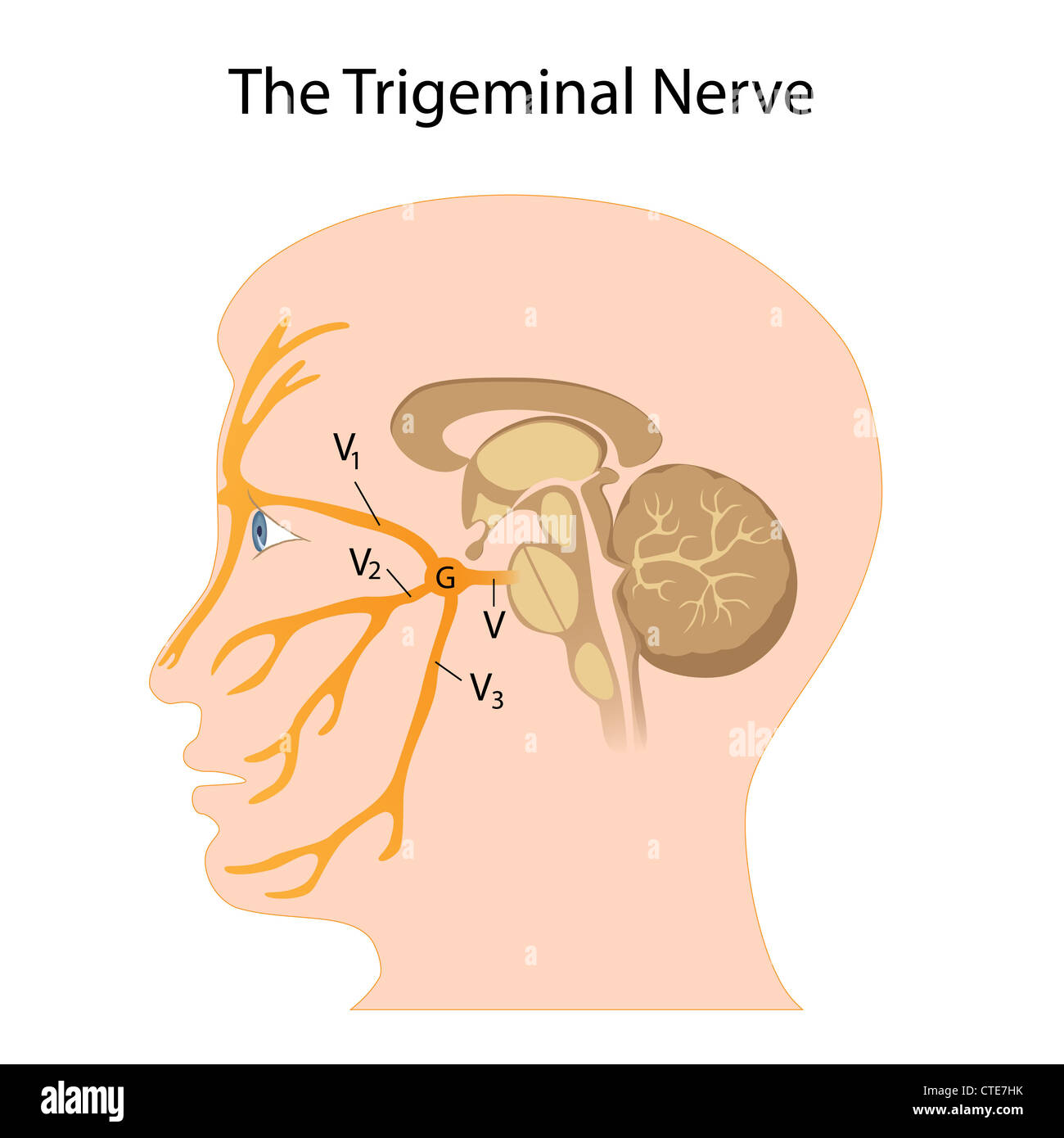 |
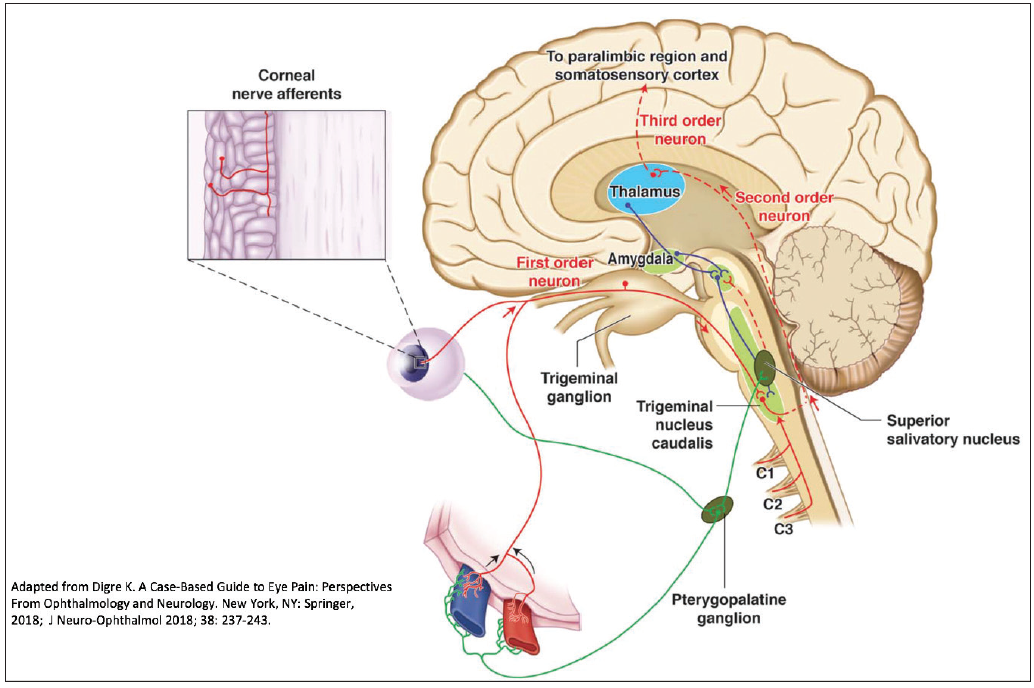
What are the effects of ongoing treatments in persons with trigeminal neuralgia? Gabapentin does have support for use in treating other neuropathic pain conditions, particularly multiple b During a relapse of trigeminal neuralgia and especially just after paroxysms of pain, there may be subtle transient unilateral sensory change in the area innervated by the trigeminal nerve. The presence of permanent sensory alterations and atypical features such as absent refractory period and no pain remission The aim of this systematic review was to determine the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) in the treatment of pain of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (TN). A comprehensive literature search was conducted using the Cumulative Index of Nursing and Allied Health Literature (EBSCO Industries), Emcare (Ovid), Research supports the use of the anticonvulsants gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant) and pregabalin (Lyrica) to help relieve pain caused by damaged nerves. Both gabapentin and pregabalin are particularly effective in the treatment of postherpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and pain caused by a spinal cord injury. Trigeminal neuralgia is an uncommon disorder characterized by recurrent attacks of lancinating pain in the trigeminal nerve distribution. Carbamazepine is the drug of choice for the initial The guidelines summarize the data for recommending pharmacotherapy with the best evidence for carbamazepine, but also includes the use of oxcarbazepine, lamotrigine, baclofen, gabapentin, and botulinum toxin. Today, trigeminal neuralgia is usually treated with drugs called anti-convulsants, which include carbamazepine (Tegretol®), phenytoin (Dilantin®), (Trileptal®) and gabapentin (Neurontin®). Phenytoin was first introduced in 1942, and in 1962 carbamazepine became the most commonly used drug. Carbamazepine has also been shown to potentiate gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors made up of alpha1, beta2, and gamma2 subunits. This may be relevant to its efficacy in neuropathic pain. 24 In newly diagnosed cases of TN, the usual starting dose is 100 to 200 mg twice daily. I am currently on 1800 mg/day of gabapentin, but am still having a fair amount of pain. On a scale of 1 to 10, the background level is about a 2 with occasional flares to a level of 5 or 6. Does anyone have luck with gabapentin, and if so, what dosages? Gabapentin is a prescription antiepileptic medication commonly used to treat postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain, and other neuropathic pain conditions. Learn more about how long it takes to treat nerve pain and what to expect when you're prescribed it. Gabapentin is licensed for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain such as painful diabetic neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia in adults [ABPI, 2020a].However, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommends gabapentin as a first-line treatment option for adults with all neuropathic pain (except trigeminal neuralgia) [NICE, 2019a]. Introduction. Trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a peculiar neuropathic facial pain condition characterized by paroxysmal pain in the distribution territory of one or more divisions of trigeminal nerve, evoked by tactile, innocuous stimulation of trigger zones. 1 Trigger zones and paroxysmal pain sensation may be dissociated, probably due to a phenomenon of cross-excitation between somatosensory Gabapentin for Trigeminal Neuralgia User Reviews Brand names: Neurontin, Gralise, Gabarone, Fanatrex. Gabapentin has an average rating of 7.5 out of 10 from a total of 35 reviews for the off-label treatment of Trigeminal Neuralgia. 71% of reviewers reported a positive experience, while 17% reported a negative experience. The preferred treatment for trigeminal neuralgia consists of antiepileptic drugs. Among them, gabapentin has shown promise in relieving some forms of neuropathic pain. This retrospective review examined 194 consecutive cases of trigeminal neuralgia, many of whom had paroxysmal facial pain resistant Lemos L, Flores S, Oliveira P, Almeida A. Gabapentin supplemented with ropivacain block of trigger points improves pain control and quality of life in trigeminal neuralgia patients when compared with gabapentin alone. The aim of this systematic review was to determine the efficacy of gabapentin (GBP) in the treatment of pain of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia (TN). ABSTRACT: Trigeminal neuralgia (TGN) is a sudden onset, short-duration, yet debilitating neuropathic pain arising from the compression of the fifth cranial nerve, precipitated by daily activities such as chewing and speaking. This chronic condition is most common in older females, affecting up to 27 per 100,000 individuals worldwide. Lemos L, Flores S, Oliveira P, Almeida A. Gabapentin supplemented with ropivacain block of trigger points improves pain control and quality of life in trigeminal neuralgia patients when compared with gabapentin alone. This retrospective study of 194 patients with trigeminal neuralgia found that gabapentin was effective in relieving or reducing paroxysmal pain in nearly half of the 92 patients who underwent a trial of therapy. Onset of pain relief in most cases occurred within 1 to 3 weeks. The efficacy of α2δ ligands, gabapentin and pregabalin, has been assessed in seven controlled or open-label studies. Despite the low quality of evidence, the favorable tolerability profile and the possible action on concomitant continuous pain make this drug category of interest for future trials in trigeminal neuralgia.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-GettyImages-1348724431-3f5c216541064d2a85f13ddc273fb650.jpg) |
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |