Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-AmeliaManley-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-df2874f5573a4f8f8924ae134c18ea84.jpg) |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-JulieBang-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-fdb75872865e4898bb04fa246b43963a.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
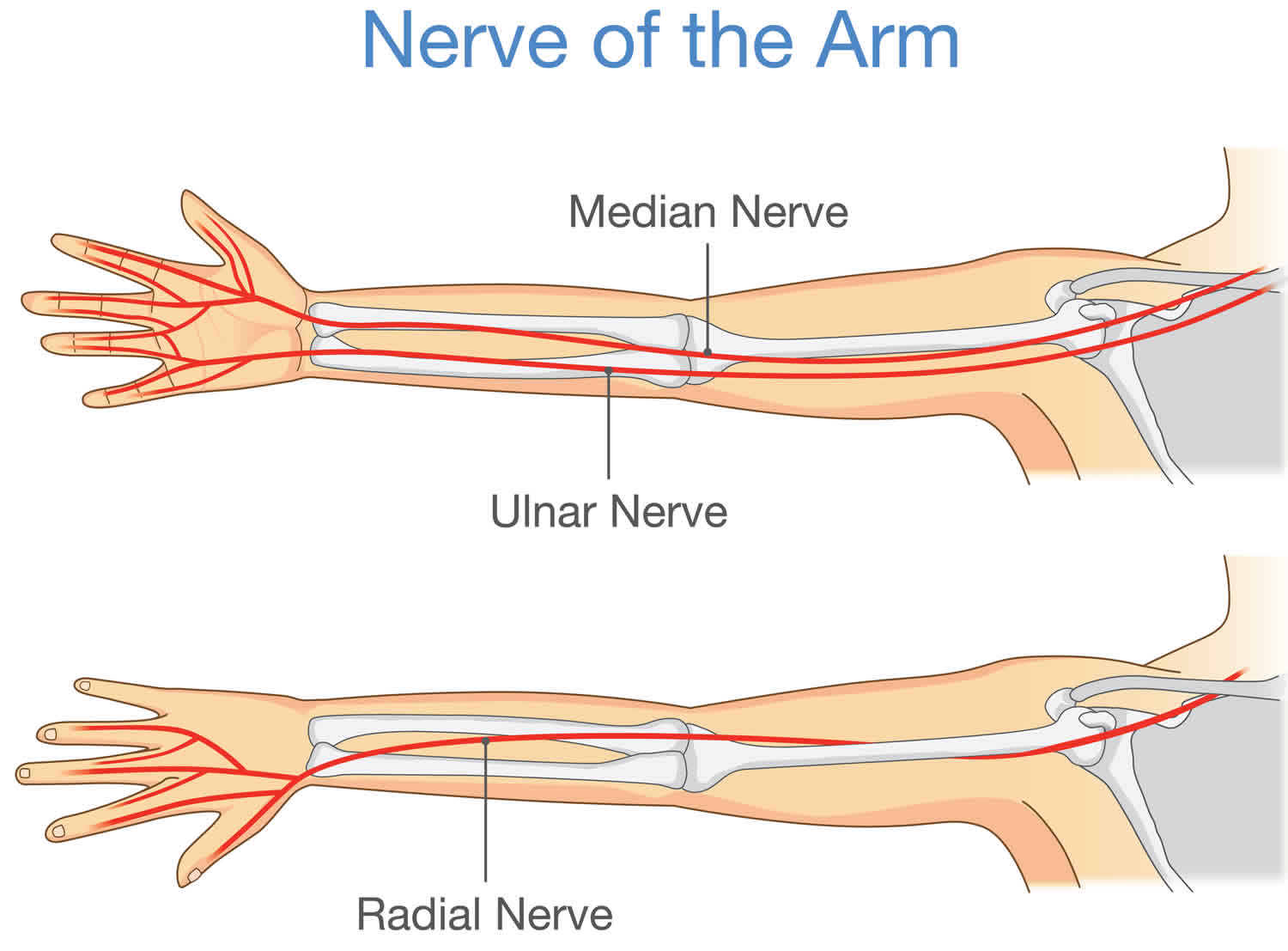 |
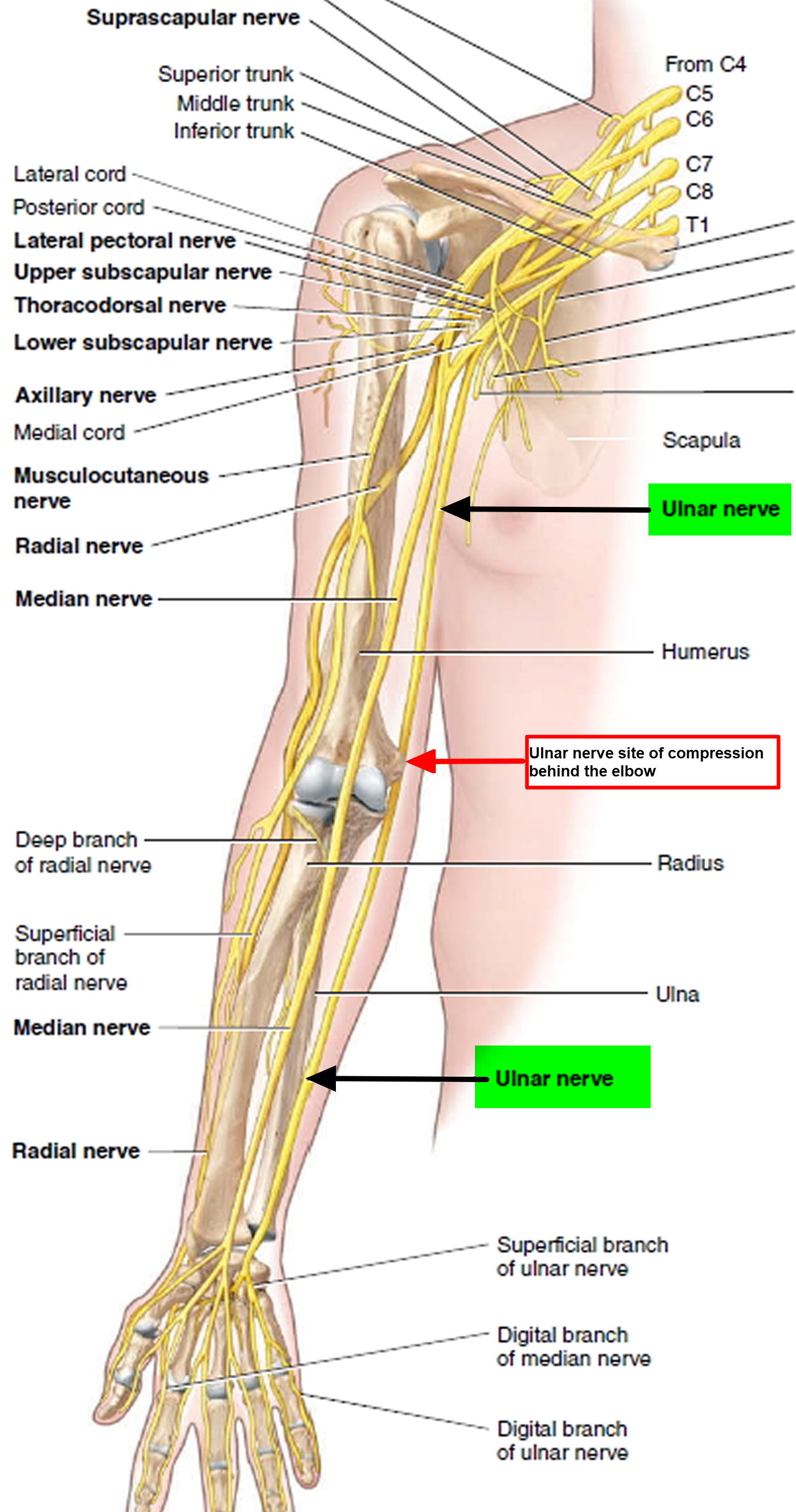
Gabapentin is approved to treat nerve pain (neuralgia) that results from nerve damage. Gabapentin may be used to treat: Nerve pain caused by a herpes zoster viral infection, also known as shingles. This pain is called post-herpetic neuralgia (PHN), and it can be severe and chronic. Pain, an unpleasant sensation and emotional experience that in our daily life, is an alert of tissue injury to prevent further or impending tissue damage . Acute pain is a useful biologic purpose and self-limiting in nature that arises in response to a specific injury. Chronic pain, in contrast, may be considered as a disease state. A steroid injection helps decrease pain and swelling. Surgery may be needed if your symptoms do not get better within 3 months. Surgery will take pressure off your ulnar nerve. Your surgeon may move your nerve to a different area to stop it from being stretched or pinched. He or she may remove part of your bone if it is pressing on your nerve. This review updates parts of two earlier Cochrane reviews investigating effects of gabapentin in chronic neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). Antiepileptic drugs are used to manage pain, predominantly for chronic neuropathic pain, especially when the pain is lancinating or burning. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when something irritates or puts pressure on your ulnar nerve that runs down your arm. Cubital tunnel syndrome affects your ulnar nerve in your elbow. It’s the most common type of ulnar nerve entrapment. Guyon’s canal syndrome, which affects the nerve in your wrist, is a rare peripheral neuropathy. If you've been prescribed gabapentin for nerve pain, you may begin to feel pain relief within one to two weeks of starting it, depending on your dosage. However, for some people, it can take longer to see benefits. Gabapentin is commonly used to treat neuropathic pain (pain due to nerve damage). This review updates a review published in 2014, and previous reviews published in 2011, 2005 and 2000. To assess the analgesic efficacy and adverse effects of Gabapentin alleviates affective pain after traumatic nerve injury. Neuroreport . 2015;26(9):522–527. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000382 (13) Khan J, Noboru N, Imamura Y, Eliav E. Effect of Pregabalin and Diclofenac on tactile allodynia, mechanical hyperalgesia and pro inflammatory cytokine levels (IL-6, IL-1β) induced by chronic constriction Usually advised by medical experts that you have to take 3 doses of Gabapentin every day to treat your nerve pain. The mg one has to consume depends on the extent of the pain. Initially, only a slighter dosage will be prescribed to check if Gabapentin suits your body and to ensure no resultant side effects are experienced. Gabapentin provides pain relief of a high level in about a third of people who take if for painful neuropathic pain. Adverse events are frequent, but mostly tolerable. More conservative estimates of efficacy resulted from using better definitions of efficacy outcome at higher, clinically important, This summary uses a Cochrane review, updated in 2014, to address the efficacy of gabapentin compared with placebo to palliate neuropathic pain. 3 The Cochrane review includes 37 trials enrolling The rehabilitation implications are that gabapentin can be offered to patients experiencing chronic neuropathic pain, but with the expectations that the therapy may need to be combined with or replaced with other nonpharmacologic interventions, such as physical therapy and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. 6. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. The purpose of this report is to review the clinical evidence on the efficacy, safety and guidelines for use of gabapentin in adults with neuropathic pain, and to examine evidence on the misuse or abuse of gabapentin and other drugs for neuropathic pain. Twenty-four systematic reviews or meta-analyses and one RCT met the inclusion criteria and provided data on efficacy and safety of gabapentin in patients with neuropathic pain. This Rapid Response Report, however, focused on four reports which provided either direct or indirect comparisons between gabapentin and active agents. Gabapentin seems to be effective in multiple painful neuropathic conditions. The variable prescribing patterns of the uncontrolled studies raise the suspicion that effectiveness may be reduced if one limits administration of the drug to very low doses, whereas rapid dose escalation may be associated The ulnar nerve is an extension of the medial cord of the brachial plexus. It is a mixed nerve that supplies innervation to muscles in the forearm and hand and provides sensation over the medial half of the fourth digit and the entire fifth digit (the ulnar aspect of the palm) and the ulnar portion of the posterior aspect of the hand (dorsal In the spine, the two most common locations are in the neck and the lower back. Compression of the nerves in the neck (cervical spine) can cause pain and tingling down the arms, while a pinched nerve in the lower back (lumbar spine) often leads to sciatic nerve pain, radiating down one leg. Other examples of pinched nerves in the body include: Pain intensity is referred as 0 to 10, in which 0 = no pain at all and 10 = the worst pain possible. Patients were asked to sign on the VAS scale that corresponded their pain. Grip strength was measured by a Lafayette hand dynamometer and pinch strength was determined by Lafayette Hydraulic Pinch Gauge (3700 Sagamore Parkway North, Lafayette In a case report, two patients (1 man and 1 woman) aged 18-58 years were described.Of whom, one patient developed drowsiness during treatment with gabapentin for ulnar neuropathic pain and the another patient exhibited treatment failure during treatment with gabapentin for ulnar neuropathic pain [routes, duration of treatment to reaction onset and outcome not stated; not all dosages stated].
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-AmeliaManley-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-df2874f5573a4f8f8924ae134c18ea84.jpg) |
 |  |
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH-JulieBang-UlnarNerveEntrapment-4000x2700-fdb75872865e4898bb04fa246b43963a.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |