Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
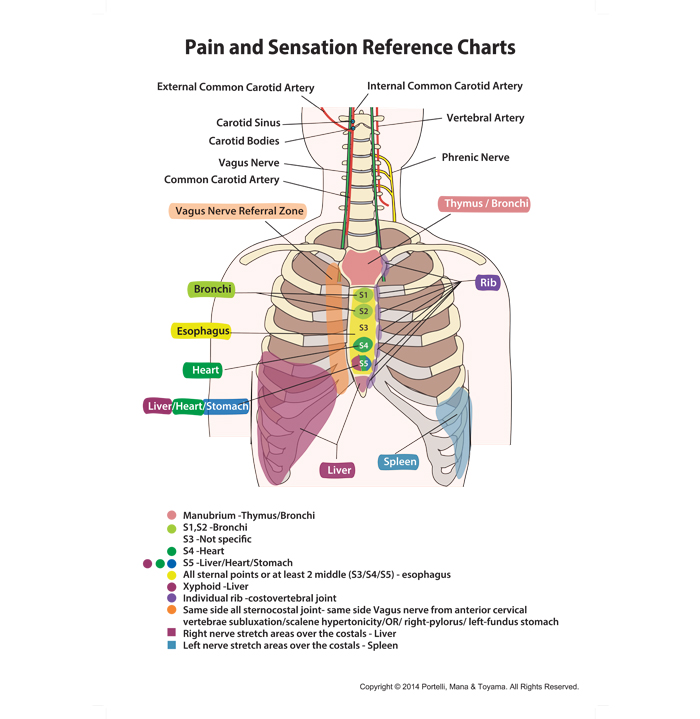
Drugs that effectively manage neuropathic pain disorders (gabapentin and pregabalin) reportedly improved global IBS symptoms and alleviated visceral pain, which requires further confirmation. Clonidine appears to be the only conventional pain-managing drug that benefits the general IBS population. Gabapentin, a 3-alkylated analogue of γ-amino butyric acid (GABA), has recently been used for the treatment of neuropathic pain with minimal side-effects. 7 Gbapentin has been shown to attenuate hyperalgesia and allodynia in animal models of neuropathic, inflammatory and surgical pain. 8–13 Although its mechanism of action remains unclear Visceral pain relates to pain in the organs of the body, so it could be the chest, or more likely, the abdomen or the pelvis. It is somewhat unlike other pain syndromes in a sense that visceral pain activates the autonomic nervous system, specifically the parasympathetic nervous system or the sympathetic nervous system or both, which is why a lot of patients who have visceral pain also have The use of gabapentin in this case was informed by emerging evidence supporting its efficacy in managing visceral hyperalgesia in neonates . Visceral hyperalgesia has been described as increased pain from GI stimulus. The origin is suspected to be neuropathic, and hence why gabapentin was studied as a possible resource in management [3,4 Gabapentin and pregabalin are increasingly being prescribed for chronic neuropathic pain conditions including peripheral neuropathies and, more recently, fibromyalgia. Their benefit for visceral or central pain syndromes is not established, although a few case reports have suggested benefit for visceral pain. Mu agonists, gabapentinoids, and GABAB agonists reduce pain by binding to central receptors and channels. Combinations of analgesics and adjuvants in animal models have supra-additive antinociception and should be considered in clinical trials. Abdominal pain can be categorized as visceral or somatic. Visceral pain arises internally and is characteristically diffuse, intermittent, and difficult to localize. It is caused by stretching of the viscera and deep inflammation or obstruction. Somatic pain is musculoskeletal, and is generally well localized. Barletta argues that while Gabapentin is excellent for chronic pain, it is not useful for acute, surgical, or postoperative pain. Dooley commented, “Gabapentin [for] that acute postoperative period is really not going to work as an analgesic the way a non-steroidal inflammatory drug [NSAID] is, an opioid, those sorts of things. Gabapentin has recently been used clinically as an antihyperalgesic agent to treat certain neuropathic pain states. The aim of this study is to test whether gabapentin is able to inhibit responses to peritoneal irritation-induced visceral pain and to examine the effect of gabapentin on spinal cord amino acid release. Gabapentin as an adjunctive drug could be more effective in reducing the severity of GI symptoms in patients with dyspepsia, especially neurological symptoms (such as pain, reflux, and indigestion). Keywords: Functional dyspepsia, gabapentin, gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterologists at Massachusetts General Hospital have begun prescribing low-dose gabapentin for patients with functional dyspepsia because it is thought to be capable of relieving visceral pain. Goals: We sought to determine the efficacy of gabapentin in the treatment of functional dyspepsia among an observational cohort of patients. Background: Gabapentin has an established role in the treatment of neuropathic pain, with evidence supporting a benefit in visceral hypersensitivity. Amitriptyline (Elavil) or nortriptyline (Pamelor) − antidepressants that help with pain ; Gabapentin (Neurontin) or Lyrica (pregabalin) − help with nerve pain ; Typical pain medicines do not help with this type of pain. Strong pain medications, like narcotics, are not used because they can slow down the digestive system and cause increased Gabapentin is a gamma-aminobutyric acid analog that has been used in multiple disease states in children, including neuropathic pain, irritability, visceral hyperalgesia, neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), rescue sedation and feeding intolerance. 1 – 7 Despite the increased utilization of gabapentin in neonates, 1 there remains a gap in the Gabapentin, a structural analogue of γ-aminobutyric acid, has antiepileptic and antinociceptive properties. 1 It targets multiple pathways involved in neuropathic pain and inflammation. 1 In adults, gabapentin is commonly used to help alleviate cancer and chemotherapy-related pain, spinal cord injury-related pain, and peripheral neuropathic pain Visceral hyperalgesia refers to increased pain sensation in response to gastrointestinal sensory stimulus. In neonates with neurological impairments, gabapentin has been successfully used as a treatment for visceral hyperalgesia in neonates. The authors describe a preterm infant with myelomeningocel The rationale for using gabapentin or pregabalin in these children with possible visceral hyperalgesia was based on its role in reducing neuropathic pain as well as its central effects. 6 Patients were not involved in the design or the conduction of this research. Visceral hyperalgesia refers to increased pain sensation in response to gastrointestinal sensory stimulus. In neonates with neurological impairments, gabapentin has been successfully used as a treatment for visceral hyperalgesia in neonates. Our report indicates that gabapentin can be considered in porphyria patients, especially when patients had seizures or acute abdomen, when morphine is not available or contraindicated, when abdomen pain transforms as chronic pattern, and when neuropathic pain occurs in extremities. Drugs that effectively manage neuropathic pain disorders (gabapentin and pregabalin) reportedly improved global IBS symptoms and alleviated visceral pain, which requires further confirmation. Clonidine appears to be the only conventional pain-managing drug that benefits the general IBS population.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |