Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | 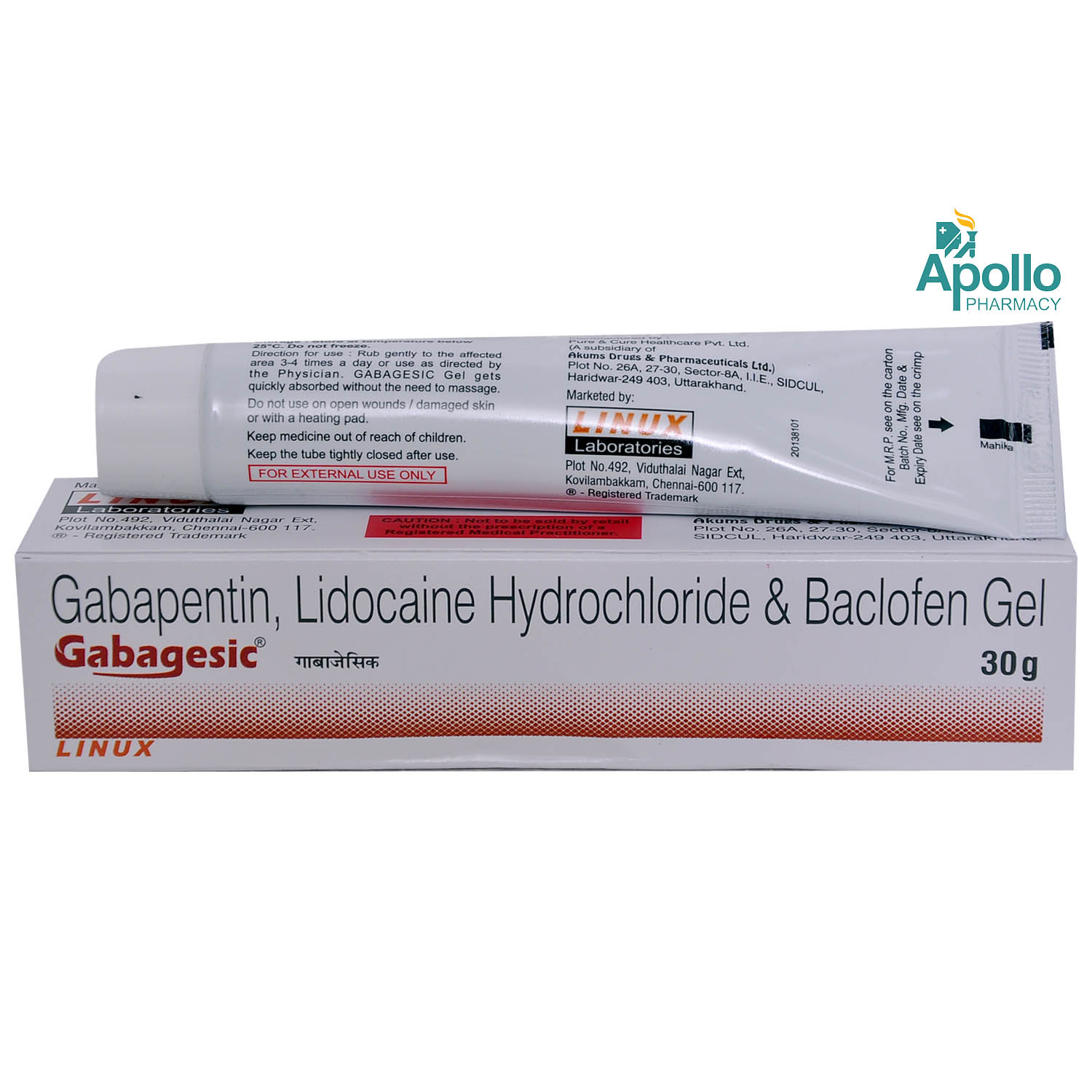 |
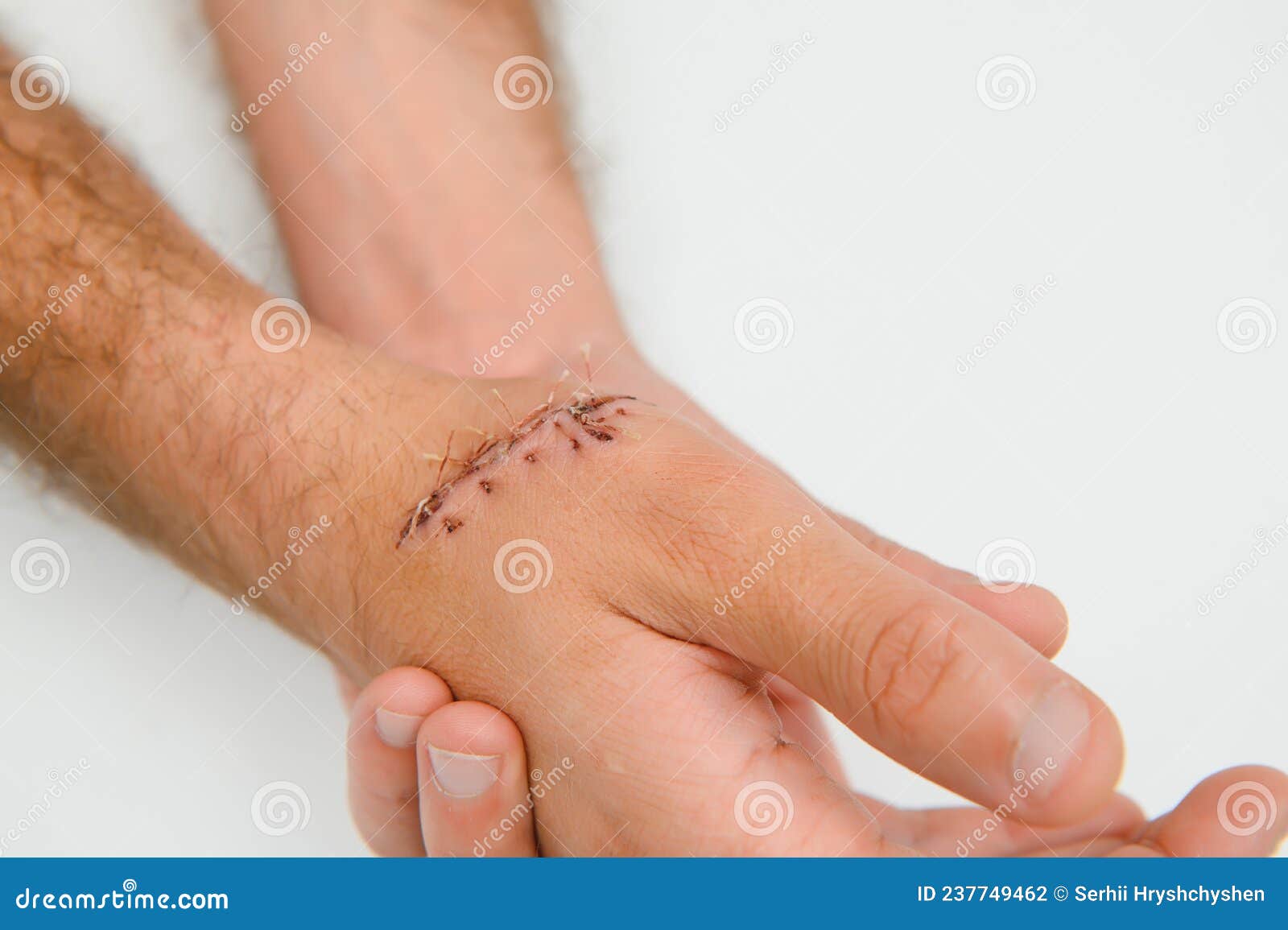
Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. Gabapentin and other anticonvulsant medications have been established as an effective treatment for chronic neuropathic pain and are commonly used for such conditions as herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy, and phantom limb pain following amputation. 4.3. Wound pain characteristics. In this meta‐analysis, we also aimed at describing a broad range of wound pain characteristics. However, we did not identify enough studies to synthesise any results regarding pain quality descriptors, temporal fluctuations, and pain interference with function. Gabapentin is a novel drug used for the treatment of postoperative pain with antihyperalgesic properties and a unique mechanism of action, which differentiates it from other commonly used drugs. Various studies have shown that perioperative use of gabapentin reduces postoperative pain. A patient with mycosis fungoides illustrates the problem of pain management during wound care and suggests the utility of a novel treatment, gabapentin. Skin lesions, be they induced through necrosis of tumor, therapy (e.g., radiotherapy), or by pressure ulceration, are often the cause of continuous pain or acute wound dressing pain. Gabapentinoids are effective adjunct drugs for reducing postoperative pain. However, the effects of gabapentinoids on wound healing have not been evaluated yet. In this study we evaluated their effects on wound healing. The search used the following subject headings and text terms: “gabapentin”, “Neurontin”, “postoperative care”, “postoperative period”, “perioperative care”, “surgery”, “pain treatment”, “analgesic” and “analgesia” . Bibliographies of included articles and published reviews were also searched. This review evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of peri-operative gabapentin administration to control acute post-operative pain. Peri-operative gabapentin administration was found to be effective in reducing pain scores, opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects in the first 24 hours after surgery. Preventing, minimizing, and managing pain in patients with chronic wounds: challenges and solutions Thomas E Serena,1 Raphael A Yaakov,1 Saima Aslam1,2 Rummana S Aslam2 1Clinical Research, SerenaGroup Wound and Hyperbaric Centers, Cambridge, MA, 2Center for Advanced Wound Care, Hackensack University Medical Center, Hackensack, NJ, USA Abstract: It is widely known that pain frequently Wound infiltration with local anaesthetics, systemic gabapentin and II-IH NB need further trials to assess their efficacy. Key words: Anaesthesia, caesarean section, post-caesarean analgesia. INTRODUCTION. Pain is ranked highest among undesirable clinical outcomes associated with caesarean section (CS). Adequate post-operative analgesia in the Gabapentinoid drugs—specifically gabapentin (Neurontin) and pregabalin (Lyrica)—are increasingly being prescribed for pain because physicians and patients seek alternatives to opioids in the Virtual reality as an adjunctive pain control during burn wound care in adolescent patients. Pain 2000;85(1–2):305–309. [Google Scholar] 111. Maani C, Hoffman HG, DeSocio PA et al. Pain control during wound care for combati-related burn injuries using custom, articulated arm-mounted virtual reality goggles. The pain may occur during wound cleansing or debridement (noncyclic pain), during repeated treatments such as daily dressing changes or repositioning (cyclic wound pain), or during quiet time without manipulation (persistent pain).1 The pain experience might even be one of anticipation; the anxiety of a painful event potentially is as disabling The authors found that 1200mg of gabapentin 2 hours prior to operative debridement of burn wounds led to a significant decrease in pain in the immediate 24-hour postoperative period, as measured by the visual analog score and by patient-requested morphine consumption. Poor pain and anxiety management can contribute to delayed wound healing . Burn pain is also among the most common causes of distress during the first year after discharge [ 2,3 ]. Inadequate burn pain management still exists during both the acute and rehabilitation phases of care [ 4,5 ]. Gabapentin appears safe and well tolerated when used for persistent post-operative and post-traumatic pain in thoracic surgery patients, although minor side effects do occur. Gabapentin may relieve refractory chest wall pain in some of these patients, particularly those with more severe pain. Furthe A patient with mycosis fungoides illustrates the problem of pain management during wound care and suggests the utility of a novel treatment, gabapentin. Skin lesions, be they induced through necrosis of tumor, therapy (e.g., radiotherapy), or by pressure ulceration, are often the cause of continuous pain or acute wound dressing pain. Optimizing the analgesic treatment in those patients is thus Purpose of Review Chronic wounds are increasing in prevalence and are often associated with significant pain, which can have a major impact on quality of life. Safe and effective pain management can be challenging, an unfortunate reality that is highlighted by the ongoing opioid crisis. This review aims to provide an evidence-based framework for pharmacologic and non-pharmacologic pain The World Health Organization (WHO) provided guidelines for the treatment of cancer pain in titrating the type and dose of analgesia to the level of pain.²⁴ These guidelines can be applied to wound pain.²⁵ The recommended steps for control of wound pain include 1) nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and local anesthesia, 2) addition of a We recommend being selective with regard to using gabapentinoids for acute postoperative pain management after careful consideration of the potential side effect profile based on patient comorbidities as well as the expected severity of postoperative pain.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |