Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
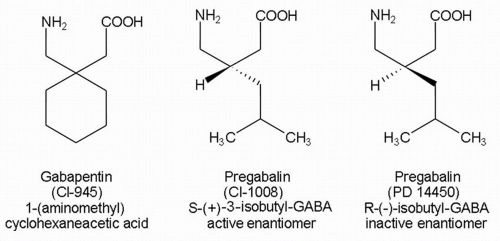
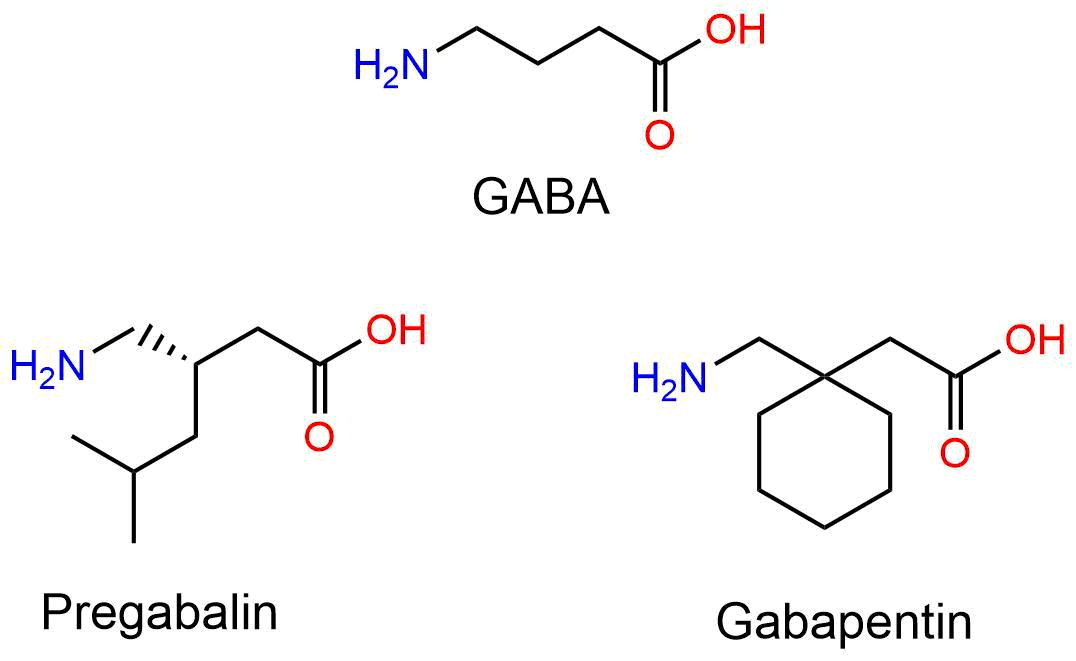
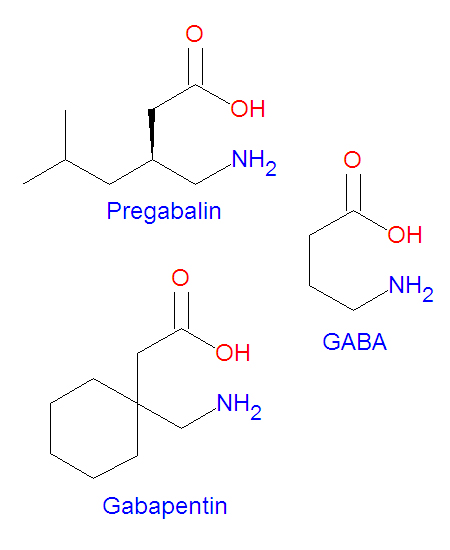
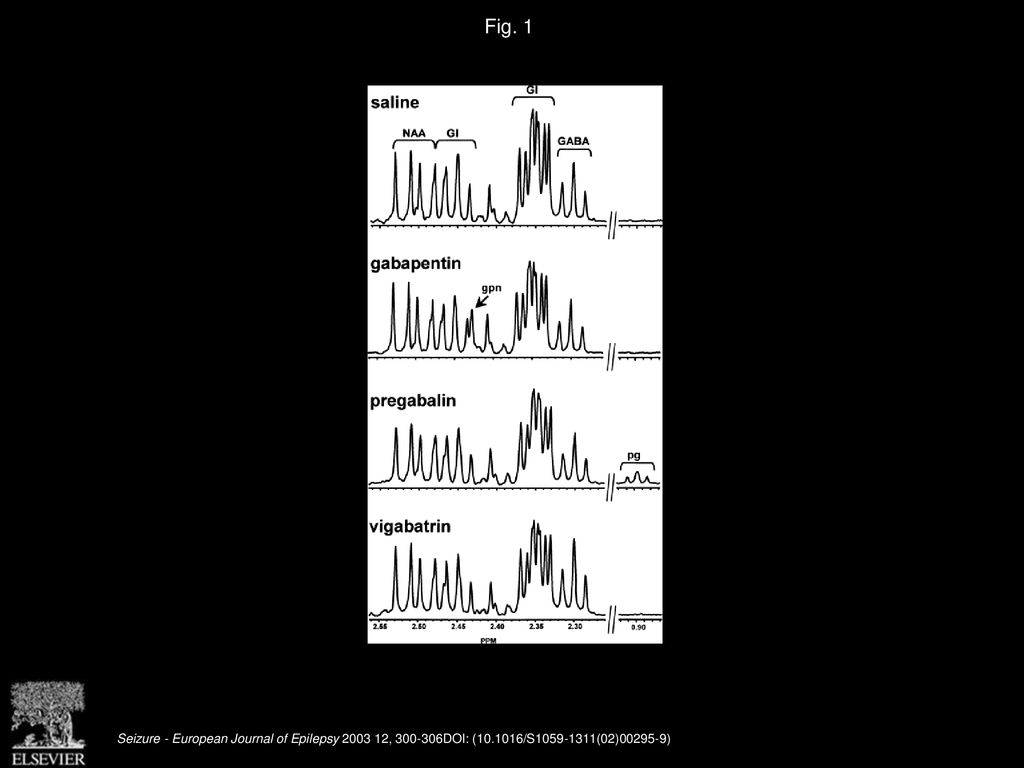
Although the mechanism of gabapentin therapeutic action is unclear, human subjects studies suggest that its administration leads to an overall increase in central GABA levels. In neocortical tissue extracted from individuals with intractable epilepsy, gabapentin administration resulted in 13% increase in cellular GABA concentrations ( Errante Gabapentin - Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug commonly used as adjunctive therapy to treat partial seizures. Therapeutic drug monitoring is useful to optimize dose and to avoid toxicity. Levels of GABA A receptor agonists are not increased by gabapentin. (a) A schematic diagram shows the experimental timeline. (b) Gabapentin does not change levels of GABA A receptor agonists in the brain and spinal cord. n = 8 and 6 for control and gabapentin, respectively; P > 0.1 for each agonist, unpaired Student t-test. Data are mean ± SEM. Research about the effects of gabapentin on gamma -aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurotransmitter levels has reported inconsistent results, i.e., increase in GABA levels based on human studies, 10 but no effects have been reported in in vitro studies. 11 Moreover, gabapentin affects GABA (A), but not GABA (B) receptor responses, based on in vitro stu GABA rose 48% at 6 hours with gabapentin but not with lamotrigine. With long-term dosing and once target doses were achieved at 4 weeks, significant elevations in GABA were observed compared with baseline for all three drugs (topiramate 46%, gabapentin 25%, lamotrigine 25%). Objective: Although gabapentin has demonstrated efficacy in mitigating alcohol withdrawal symptoms and preventing relapse drinking in individuals with alcohol use disorder (AUD), the neurobiological mechanisms of action underlying these therapeutic effects remain unknown. The present study evaluated changes in GABA and glutamate levels in the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) as To understand how gabapentin might influence dopamine levels, we first need to explore its primary mechanisms of action. Contrary to its name, gabapentin does not directly interact with GABA receptors or influence GABA levels in the brain. Instead, its primary mode of action involves modulating voltage-gated calcium channels. Gabapentin (Neurontin®) is an oral antiepileptic agent that is structurally related to the neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) but it does not interact with GABA receptors in the brain. Its mechanism of action is unknown but it has properties in common with other anticonvulsant medications. Levels of GABA A receptor agonists are not increased by gabapentin. (a) A schematic diagram shows the experimental timeline. (b) Gabapentin does not change levels of GABA A receptor agonists in the brain and spinal cord. n = 8 and 6 for control and gabapentin, respectively; P > 0.1 for each agonist, unpaired Student t-test. Data are mean ± SEM. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on GABA was elevated in patients taking gabapentin compared with 14 complex partial epilepsy patients, matched for antiepileptic drug treatment. Brain GABA levels appeared to be higher in patients taking high-dose gabapentin (3,300-3,600 mg/day) than in those taking standard doses (1,200-2,400 mg/day). Fig. 5 Levels of GABA A receptor agonists are not increased by gabapentin. (a) A schematic diagram shows the experimental timeline. (b) Gabapentin does not change levels of GABA A receptor agonists in the brain and spinal cord. n = 8 and 6 for control and gabapentin, respectively; P > 0.1 for each agonist, unpaired Student t-test. Data are mean Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug effective as add-on therapy in treating complex partial seizures and partial seizures with secondary generalization. Gabapentin does not bind to serum proteins and does not exhibit pharmacokinetic interactions with other antiepileptic drugs. Test sent to Mayo Clinic Laboratories. Rodent studies would suggest that gabapentin enhances GAD activity at clinically relevant drug levels, whereas much higher drug levels than are typically obtained in the clinical setting are Although designed as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) analogue, gabapentin does not bind to GABA receptors, nor does it affect the neuronal uptake or degradation of GABA. In fact, the precise mechanism by which it exerts its analgesic and anticonvulsant effects is unknown. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin is most often dosed based on the patients renal (kidney) function. The prescribing information for the medication does not even mention therapeutic blood levels to watch for. Over time however, certain blood levels have been determined. Therapeutic Concentration appears to be around 5.9-21 mcg/mL (34.5-123 µmol/L). Treatment of mice with gabapentin resulted in an increase in surface, but not total, expression in cerebellum and hippocampus. There was no change in expression of α1- or α5-subunits. Treatment of mice with gabapentin did not increase GABA, taurine, or alanine levels, or neurosteroids in the brain. Glutamine is the precursor of GABA. A dose of 2000 mg or more of glutamine a day when taken on an empty stomach with vitamin B6 (2mg or more), will increase your natural level of GABA and probably reduce your pain levels. Pure GABA is available as a tablet, capsule or in sublingual (under-the tongue) form in most health food stores or online.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |