Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |
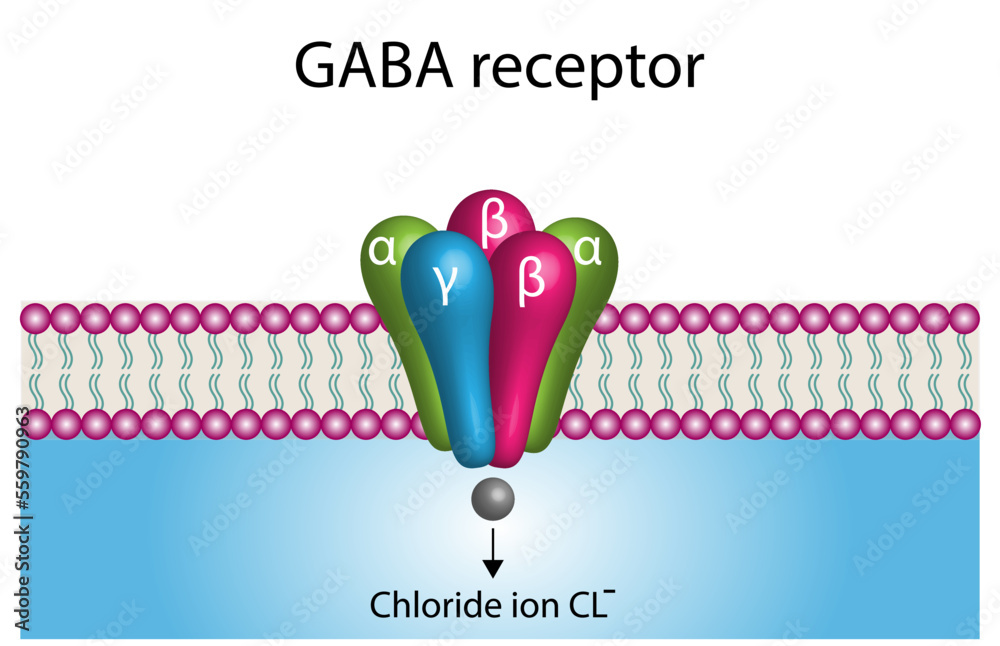 |  |
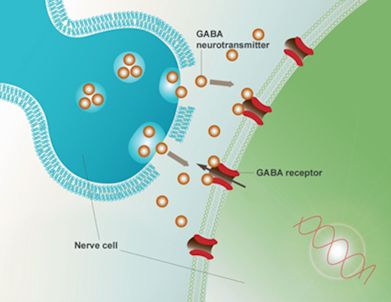
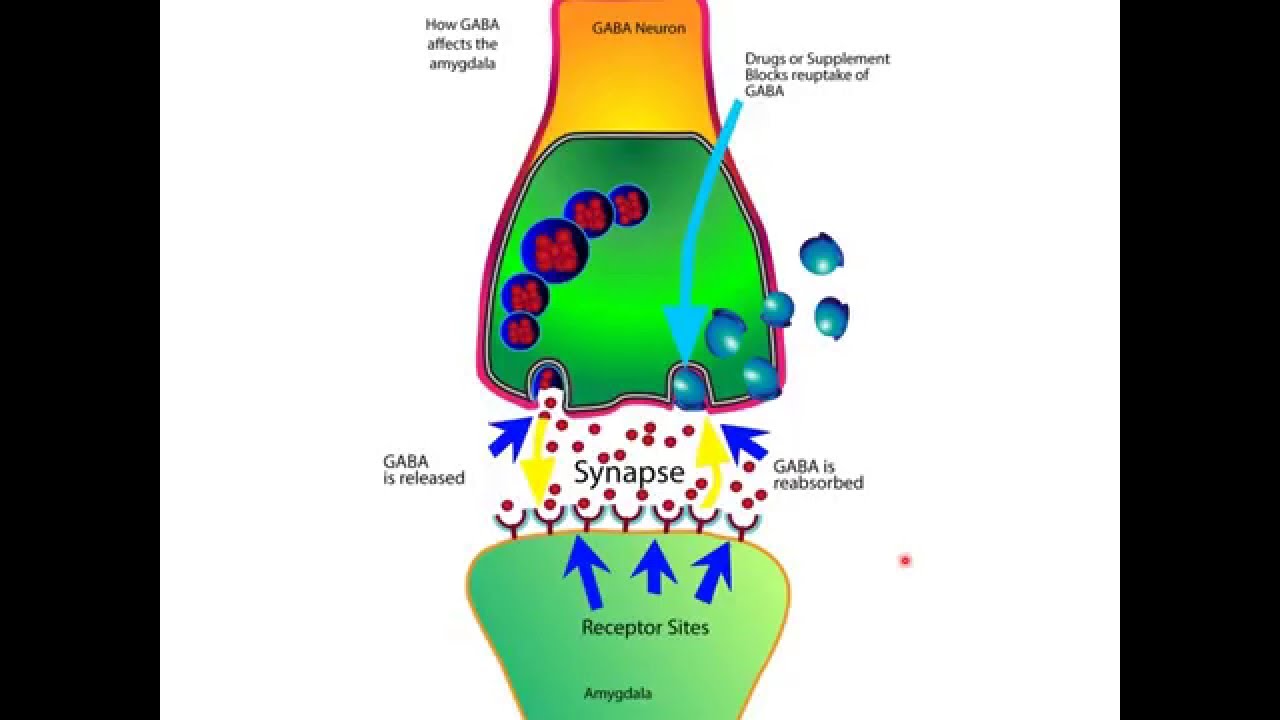
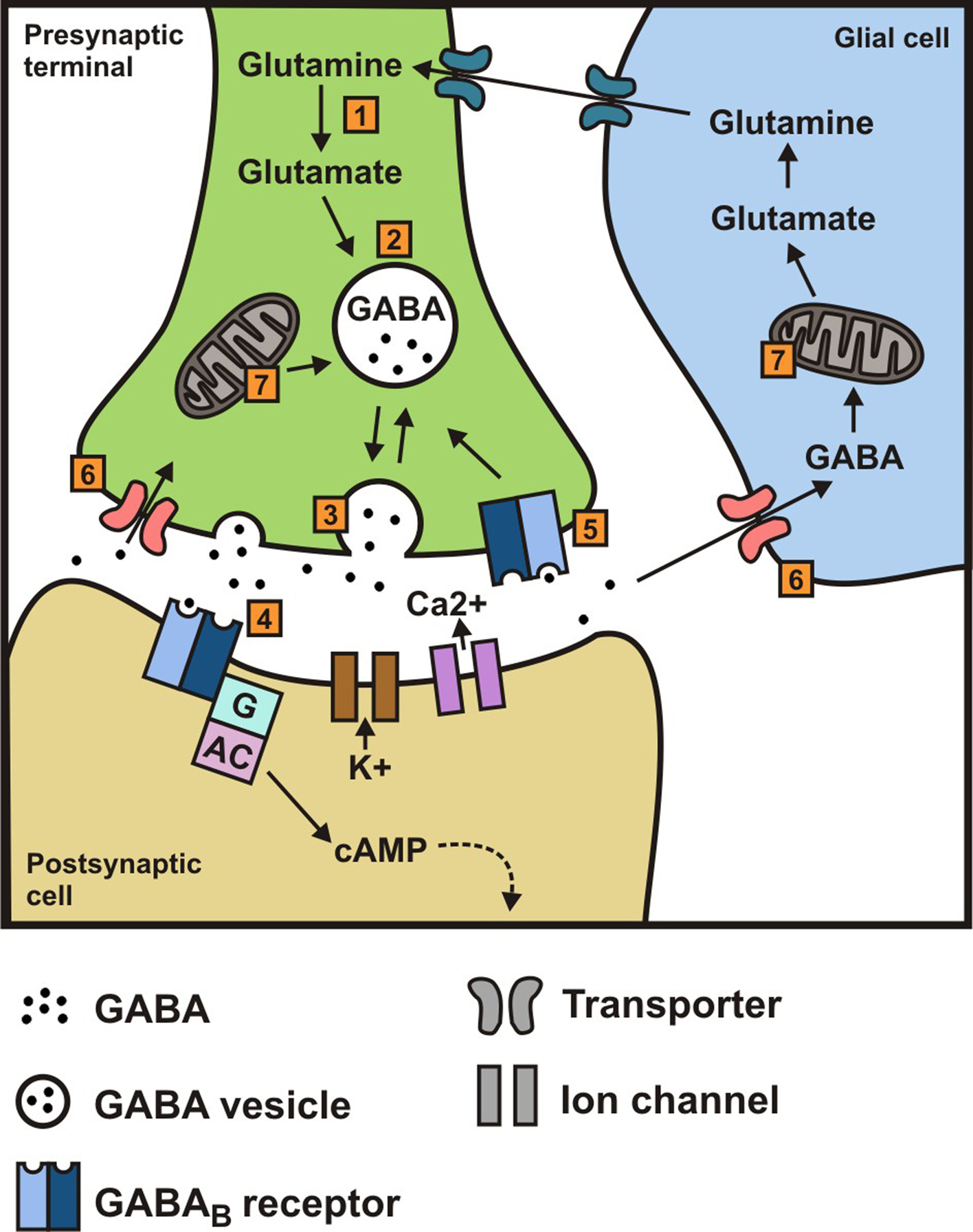
Gabapentin, first synthesized in the 1970s, was initially designed as an analogue of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. However, its mechanism of action turned out to be more complex than initially thought. Gabapentin is a gabapentinoid, which acts as an inhibitor of the α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs) that are linked to neurotransmitter release. Gabapentin binds with high affinity to the α 2 δ VDCCs [ 6 ], which is considered the primary target of the drug. GABA acts as a neurotransmitter and interacts with GABA receptors in the central nervous system, while gabapentin interacts with the α2δ subunit of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel. Both help reduce neuronal excitability, but the mechanisms are not fully understood. In vitro, gabapentin reduces the release of several mono-amine neurotransmitters. Gabapentin prevents pain responses in several animal models of hyperalgesia and prevents neuronal death in vitro and in vivo with models of the neurodegenerative disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Gabapentin is an anti-convulsant medication that inhibits the release of excitatory neurotransmitters, allowing for its use against pathologic neurotransmission such as that seen in neuropathic pain and seizure disorders. 16,19 It has a wide therapeutic index, with doses in excess of 8000 mg/kg failing to cause a fatal reaction in rats. 21 Both GABA and gabapentin are similar to each other but they have their differences. The first point of difference is their structural make-up. Gabapentin is a GABA analog, meaning that it looks very similar structurally but it is not completely the same. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the central nervous system (CNS) that Gabapentin prevents neuronal death in several models including those designed to mimic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). This may occur by inhibition of glutamate synthesis by branched-chain amino acid aminotransferase (BCAA-t). Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on glutamate are not known. Gabapentin's binding site is located on the α 2 δ subunit of voltage gated calcium channels. 6 In vitro, gabapentin can inhibit neuronal calcium currents by 35% and decrease neuronal tachykinin-mediated activity. 7,8 It has been suggested that mitigation of hypothalamic tachykinin neurotransmitter activity via a decrease in neuronal calcium GABA is an amino acid neurotransmitter. Gabapentin is a structural analogue of GABA. Function: GABA acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and analgesic drug. Medical Uses: GABA is not used as a medication. Gabapentin is used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and restless legs Similarly, gabapentin and dopamine interactions highlight how drugs designed to mimic GABA can have complex effects on other neurotransmitter systems. Potential therapeutic approaches targeting GABA-dopamine balance are an active area of research. The other, gabapentin, which you may also know as Neurontin, is a so-called analog of GABA, meaning that it was designed to mimic certain qualities of the neurotransmitter. The goals of this article are to provide some background on each one as well as an overview of both their shared and unique qualities. Gabapentin is a structural analog of the inhibitory neurotransmitter γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Its anticonvulsant, analgesic and anxiolytic properties suggest that it increases GABAergic inhibition; however, the molecular basis for these effects is unknown as gabapentin does not directly modify GABA type A (GABA A) receptor function, nor does it modify synaptic inhibition. Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the major neurotransmitter for fast inhibitory synaptic transmission and tonic inhibitory control, is present in 25–50% of all synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000). L-glutamic acid (glutamate) is responsible for fast excitatory neurotransmission and is present at approximately 80% of brain synapses (Sutoo et al, 2000 Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10] [7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on Gabapentin, marketed for the treatment of seizures and neuropathic pain, has been shown to increase in vivo GABA concentration in the brain of both rodents and humans. Gabapentin effects on By Forest Tennant, PNN Columnist “GABA” is short for the neurotransmitter, gamma aminobutyric acid. GABA is the natural (endogenous) biochemical substance in the brain, spinal cord, and all nerves that control electrical conduction. Without proper GABA function, we experience pain. New research Gabapentin enhanced expression of δGABA A receptors and increased a tonic inhibitory conductance in neurons. This increased expression likely contributes to GABAergic effects as gabapentin caused ataxia and anxiolysis in wild-type mice but not δ subunit null-mutant mice.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 | :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_JessicaOlah_WhatToKnowAboutGaba_4000x2700-c7a290db74574d1eb6fab03c9008b9a0.png) |
 |  |