Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
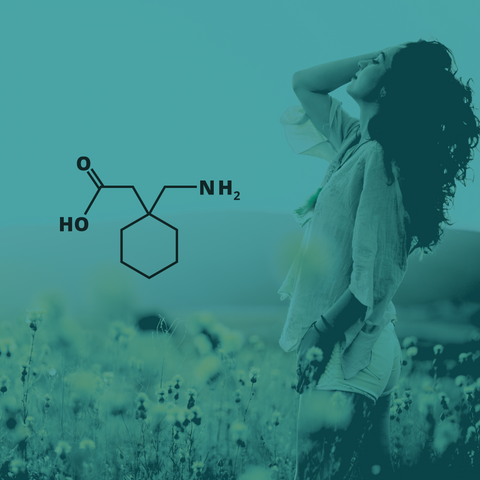
The recommendation for Gabapentin is not to compound a liquid using the tablet or capsule, but to use the suspension. Reports have suggested increased adverse effects when switching generic formulations of antiepileptic drugs, particularly with gabapentin. 45 There are several types of feeding tubes (Box A10.A). These can be further classified according to lumen size (French gauge), number of lumens (single or multiple) and length of use (short-term, long-term/fixed). a. Step 1 is the preferred option; for further explanation, see Choosing a suitable formulation. Keywords: Gabapentin, pregabalin, pain management, adverse effects, pharmacology. Introduction. The gabapentinoid drugs gabapentin and pregabalin are antiepileptic drugs that are considered as first-line treatments for the management of neuropathic pain. 1 Pregabalin is also approved for generalised anxiety disorders in the United Kingdom. The 26 • New drug applications (NDAs) (original or supplemental) where applicants are seeking 27 and/or revising enteral tube administration instructions and related information in Embeda morphine sulfate Capsule Extended‐release (a); do not give via N/G tube E‐Mycin erythromycin Tablet Enteric‐coated Enablex darifenacin Tablet Slow‐release Entocort EC budesonide Capsule Extended‐release; Enteric‐coated (a) Equetro carBAMazepine Capsule Extended‐release (a) Know which medications can be given through the G-tube and tips for giving medication to your child. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. For example, adverse effects from gabapentin, such as dizziness and drowsiness, were only reported in 1 patient (3.1%) in the 3600 mg cohort (grade 3 dizziness) and 2 patients (6.3%) in the 3600 mg cohort (gabapentin was discontinued because of nausea and vomiting partly associated with RT and low adherence to oral hygiene). Enteric-Coated Medications: Enteric-coated formulations are designed to pass through the stomach intact so that drug release can occur in the intestine. This dosage formulation prevents destruction of the drug by stomach acid, reduces GI irritation, and allows Both nutrition and medication administration can be improved or maintained through the appropriate use of enteral alternatives such. as gastrostomy tubes (GT), nasogastric tubes (NG), gastrostomy buttons(G-Buttons; GB), jejunostomy tubes (JT), and nasojejunal tubes (NJ). If your child has a G-tube, most medicines should be given in the gastric port (G-port). This is the port that goes to your child’s stomach. Ask your care team if you have questions about which port the medicine should go into. When the oral route is not available, patients may need to be fed and administered medicines through an enteral tube. Tubes may terminate in the stomach or the jejunum, and they may enter via the nose or through the abdominal wall. prescription and over-the-counter drug product list 40th edition cumulative supplement number 09 : september 2020 additions/deletions for prescription drug product list acetaminophen; butalbital; caffeine tablet;oral butalbital, acetaminophen and caffeine >a> aa strides pharma 325mg;50mg;40mg a 203647 001 sep 21, 2020 sep newa acetaminophen; codeine phosphate solution;oral acetaminophen and Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Solution is suitable for use with the following type of NG and PEG tubes: Ensure that the enteral feeding tube is free from obstruction before administration. 1. Flush the enteral tube with water, using the minimum fl ush volume required. 2. Administer the required dose of Gabapentin Rosemont Oral Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2008;65(24):2347-2357. Administer medications via the oral route when possible. Determine the enteral feeding tube size (e.g., small bore or large bore), insertion site (e Most medications that you normally take by mouth can be taken through your feeding tube. Medications must be in liquid form or crushed into a powder to prevent your feeding tube from getting clogged. Many medications come in a liquid form. Ask your healthcare provider about liquid forms if you take pills, tablets, or capsules. In addition, use of gabapentin for persistent pain in children with SNI resulted in a significant reduction of associated GI symptoms, including decreased emesis and retching, improved feeding tolerance, weight gain, and change from J-tube to G-tube feedings [17,20,21]. Always use a feeding extension set to deliver medication. Never administer medication through the balloon port. Liquid medication is preferred. If liquid medication is thick, it may need to be diluted before administration or it can clog the feeding tube. Gabapentin 330 Galantamine 332 Ganciclovir 334 Glibenclamide 335 Gliclazide 336 Glimepiride 338 Glipizide 339 Glyceryl trinitrate 341 Glycopyrronium bromide 342 Granisetron 343 Griseofulvin 345 Haloperidol 347 Hydralazine hydrochloride 349 Hydrocortisone 350 Hydromorphone hydrochloride 352 Hydroxycarbamide (Hydroxyurea) 353
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |