Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
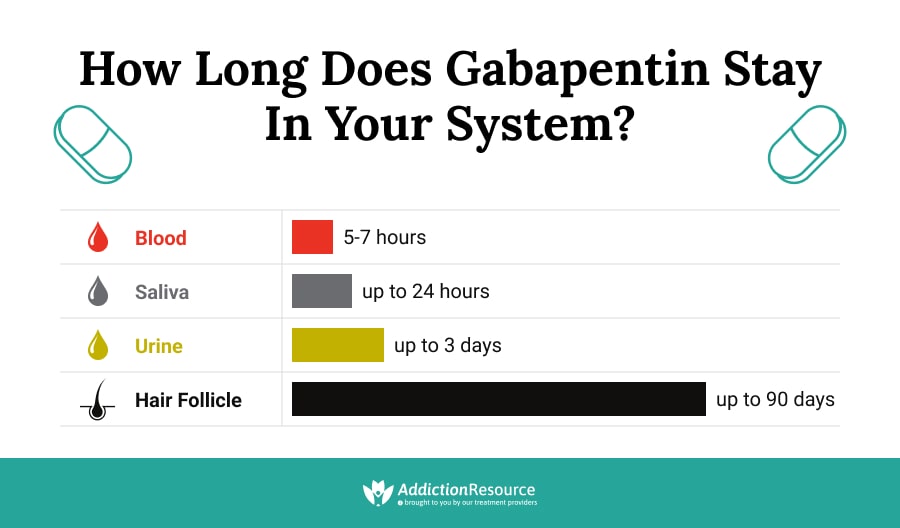 |  |
Adults, normal: 5 to 7 hours; increased half-life with decreased renal function; anuric adult patients: 132 hours; adults during hemodialysis: 3.8 hours. <3% In CrCl <30 mL/minute, half-life is approximately 52 hours (immediate release). Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly Half-life The elimination t 1/2 of gabapentin in patients with normal renal function is 5-7 hours. 16 , 17 , 5 In patients with reduced renal function, the elimination t 1/2 may be prolonged - in patients with a creatinine clearance of 30 mL/min, the reported half-life of gabapentin was approximately 52 hours. 16 , 17 The mean gabapentin half-life ranged from about 6.5 hours (patients with creatinine clearance >60 mL/min) to 52 hours (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) and gabapentin renal clearance from about 90 mL/min (>60 mL/min group) to about 10 mL/min (<30 mL/min). In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Table 2. Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment in Adults Receiving Gabapentin Gastroretentive Tablets60; Cl cr (mL/minute). Adjusted Dosage Regimen. 30–60. 600 mg to 1.8 g once daily; initiate at 300 mg once daily and may titrate according to same schedule recommended for those with normal renal function based on individual patient response and tolerability Knowing the gabapentin half-life can also be important regarding withdrawal, to know when withdrawal symptoms would occur. In general, half-life refers to the time it takes for the amount of drug present in the system to be reduced by 50%. After one half-life of gabapentin, its concentration in the body would be half the original dose. To determine the average amount of time it takes to excrete gabapentin, it is necessary to consider its half-life within the range of 5 to 7 hours. This indicates that after you’ve taken a gabapentin dose, approximately 50% will have been cleared from your system within 5 to 7 hours (on average). In a study in anuric adult subjects (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about 132 hours; during dialysis the apparent half-life of gabapentin was reduced to 3.8 hours. Hemodialysis thus has a significant effect on gabapentin elimination in anuric subjects. This gabapentin half life calculator shows how gabapentin accumulates and how long it stays in your body. Get dose and frequency with ease! Gabapentin is eliminated from the systemic circulation by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Gabapentin is not appreciably metabolized in humans. Gabapentin elimination half-life is 5 to 7 hours and is unaltered by dose or following multiple dosing. Gabapentin elimination rate constant, plasma clearance, and renal clearance are directly The reported half-life (the time it takes for 50% of the drug to be metabolized) is 5 to 7 hours, which necessitates a dosing frequency of 3 to 4 times daily for it to be effective. Most studies report that gabapentin has a duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. Gabapentin is an anticonvulsive medication that received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1993 and has been available in generic form in the USA since 2004. Gabapentin was originally used as a muscle relaxant and an anti-spasmodic. However, it was later discovered that gabapentin has the potential of an anticonvulsive medication and can be used as an adjunct to more Day 1: Single 300 mg dose; Day 2: 600 mg/day (i.e., 300 mg two times a day) (N=11), the apparent elimination half-life of gabapentin on nondialysis days was about In adults with postherpetic neuralgia, gabapentin capsules may be initiated on Day 1 as a single 300 mg dose, on Day 2 as 600 mg/day (300 mg two times a day), and on Day 3 as 900 mg/day (300 mg three times a day). The dose can subsequently be titrated up as needed for pain relief to a dose of 1,800 mg/day (600 mg three times a day). Gabapentin: Gabapentin is indicated for postherpetic neuralgia and serves as adjunctive therapy for managing partial seizures (with or without secondary generalization) in adults and pediatric patients aged 3 or older. For anuric patients (without dialysis), gabapentin half-life is roughly 132 hours. How long does it take for gabapentin to kick in? Some patients report gabapentin kicks in soon after their first dose, while others do not experience full effects for up to 2 weeks. Gabapentin Half-Life. Gabapentin comes in immediate-release and extended-release formulations as a tablet. The half-life of gabapentin is between 5 and 7 hours, which is how long it takes for the drug’s concentration in the body to be reduced by half.[3] The liver is responsible for metabolizing most drugs, but gabapentin works differently. Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat neuropathic pain and also for partial seizures [10][7] of epilepsy. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. [11] . Gabapentin has a half-life of 5 to 7 hours, but it can vary by dosage, formulation, and individual factors. Gabapentin’s half-life and how long it stays in the body influence how long the effects last and possible risks.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |