Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
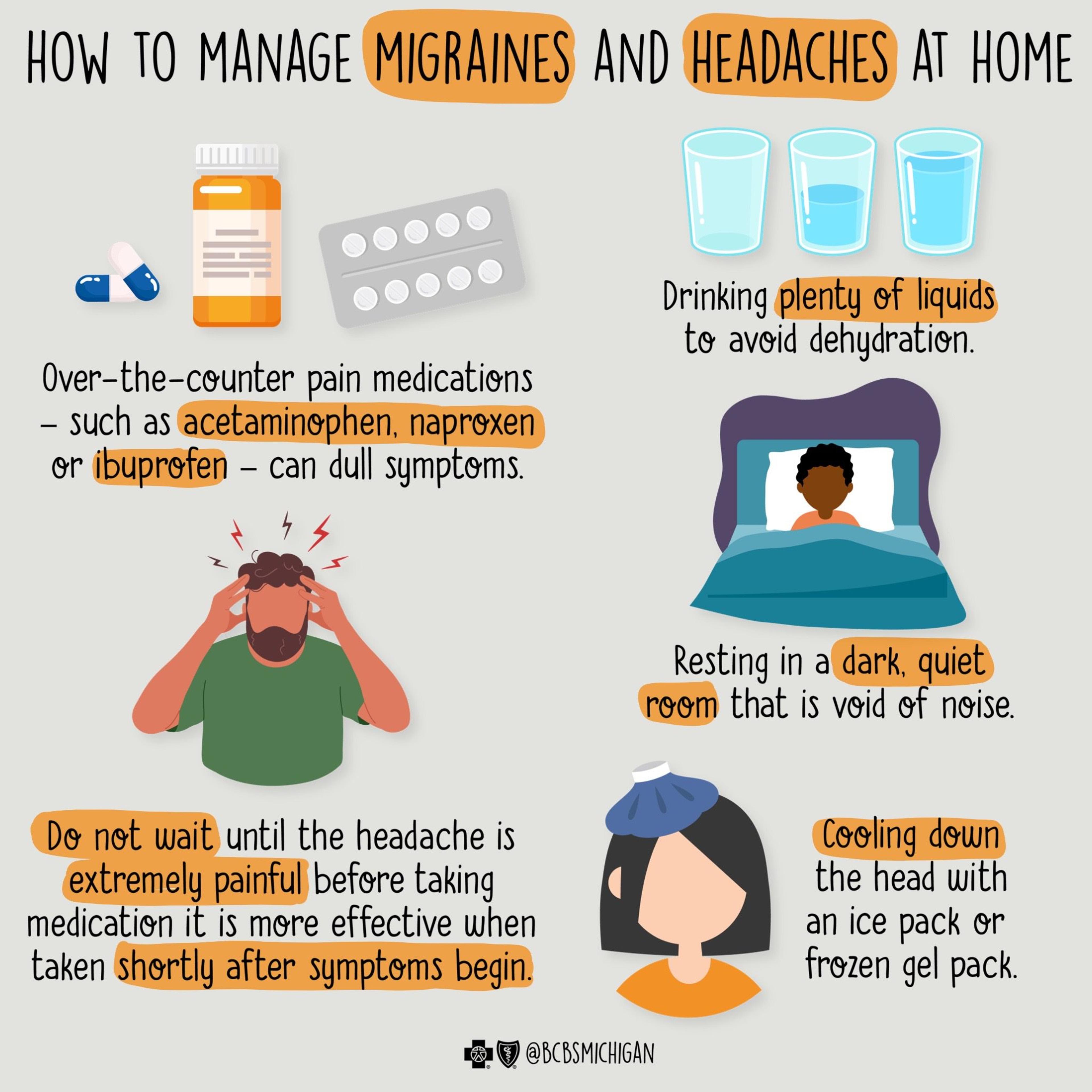
Amitriptyline is effective at preventing tension-type headaches after three months of treatment. • Triptans, ibuprofen, naproxen, aspirin, and high-dose acetaminophen are effective treatments To ease your headache pain until you see your doctor, you might: Avoid activities that worsen your headaches. Try over-the-counter pain relief medications — such as naproxen sodium (Aleve) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others). To avoid rebound headaches, don't take these more than three times a week. Pain relievers available without a prescription are usually the first line of treatment for reducing headache pain. The anti-seizure medicines gabapentin (Gralise Gabapentin (Neurontin) for prophylactic treatment of migraines and headaches, how it works, dosage, review of clinical trials on the effectiveness of gabapentin. The American Academy of Neurology (AAN) and the American Headache Society (AHS) do not list gabapentin as "effective" or "probably effective" for preventing migraines in their 2012 guidelines. Instead, gabapentin is given a level U rating, which means the evidence is conflicting or inadequate to support or refute its use for migraine prevention. A 2016 study showed evidence that gabapentin benefits headache syndromes, but it still wasn’t recommended as a primary therapy. If you’re experiencing migraine attacks or your current First-line medications established as effective based on clinical evidence include divalproex, topiramate, metoprolol, propranolol, and timolol. Medications such as amitriptyline, The recommendations on treatment of menstrual-related migraine are based on the clinical guidelines Headaches in over 12s: diagnosis and management , Primary care management of headache in adults [Becker, 2015], National headache management system for adults , and Pharmacological management of migraine , consensus statements from the Danish At the end of the 12-week treatment phase, the median 4-week migraine rate was 2.7 for the gabapentin-treated patients maintained on a stable dose of 2400 mg/day and 3.5 for the placebo-treated patients (P =.006), compared with 4.2 and 4.1, respectively, during the baseline period. Gabapentin does not decrease the frequency of migraine headaches and is not recommended for prophylactic therapy. or when acute drug treatment is inadequate. The antiepileptic drugs topiramate Objective: Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. do not offer opioids for the acute treatment of tension-type headache; prophylactic treatment. consider a course of up to 10 sessions of acupuncture over 5-8 weeks for the prophylactic treatment of chronic tension-type headache; For NICE guidance regarding management of chronic pain (pain that lasts for more than 3 months) then see linked item Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. A new review indicates that gabapentin may be an effective adjunct therapy for primary headache syndromes, but that there is not enough evidence to support its use as a primary treatment. Gabapentin (GBP), originally an antiepileptic drug, is more commonly used in the treatment of pain, including headache disorders. Off-label GBP is used in headache disorders with some success, some failure, and much debate. Migraine is a common episodic disorder, the hallmark of which is a disabling headache generally associated with nausea and/or light and sound sensitivity. The acute treatment of migraine in adults is reviewed here. Preventive treatment of migraine in adults is discussed separately. (See "Preventive treatment of episodic migraine in adults".) Several prophylactic treatments for chronic daily headache can reduce headache frequency and severity, as well as improve overall quality of life. Nonpharmacologic treatments include relaxation We also debate the role of a new antiepileptic drug, gabapentin, in the management of headache and neck pain. It is now considered to be an emergent treatment for pain syndrome. We delineate its pharmacological, laboratory and clinical profiles, with a review of the world literature. Objective: To compare efficacy and safety of gabapentin (GPT) versus placebo for prophylaxis of chronic daily headache (CDH) (headache at least 15 days/month of greater than 4 hours duration over preceding 6 months). Methods: This is a multicenter randomized placebo-controlled crossover study.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 | |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |