Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
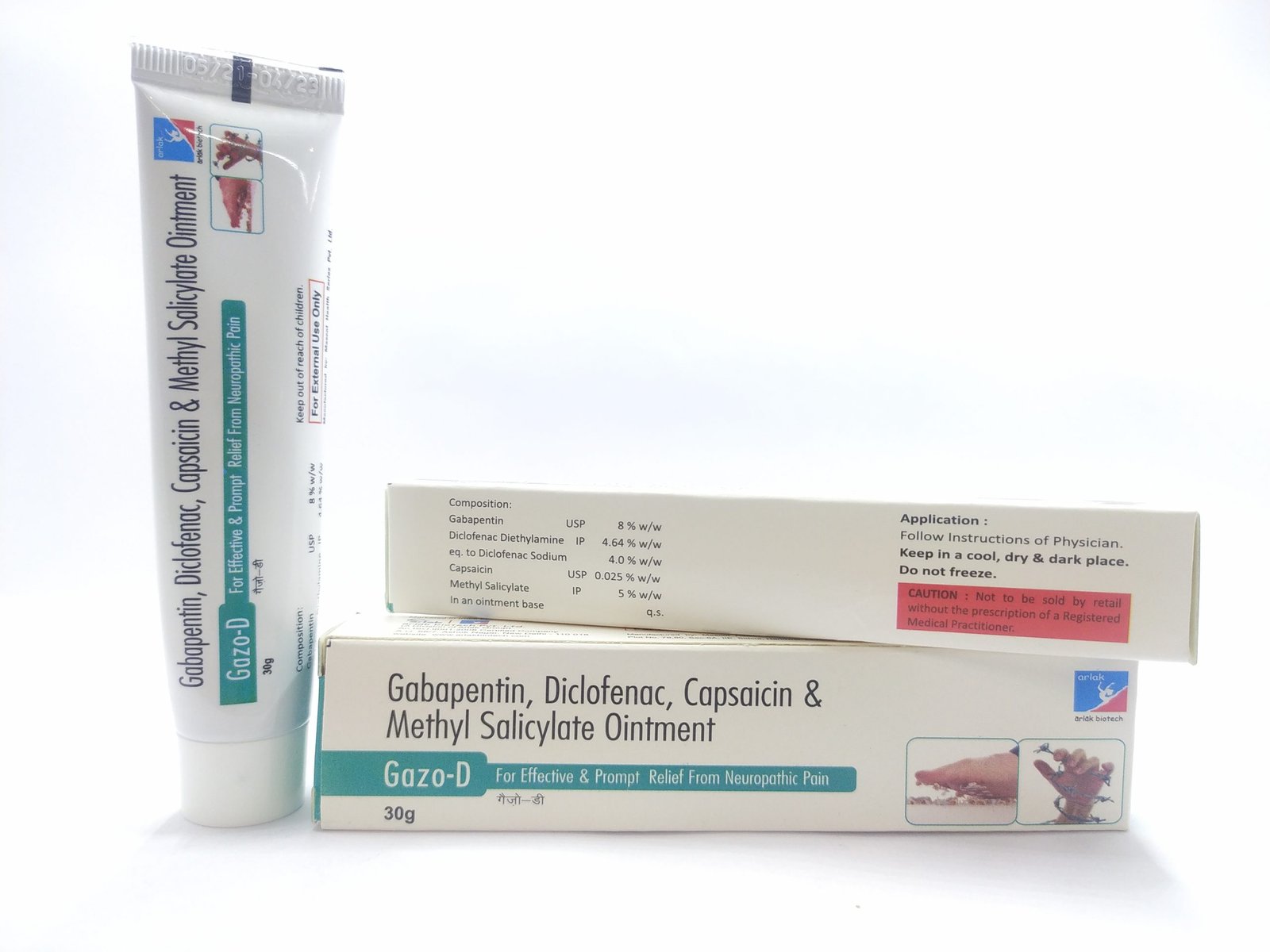 |  |
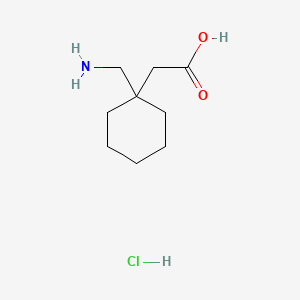
Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant drug that has been used for a number of off-label indications, including neuropathic pain. It is thought to act by binding to calcium channels and modulating calcium influx, or by blocking new synapse formation. Rofecoxib + Aminoguanidine hydrochloride Meloxicam + Aminoguanidine hydrochloride: CCI model of neuropathic pain in rat (pressure test, hot plate test, cold stimuli paw withdrawal test) NA: Improved analgesia outcomes (i.e., higher withdrawal thresholds than monotherapies) Gabapentin + Metamizole: Formalin model in rat: NA Gabapentin is an anticonvulsant and has been used to manage neuropathic pain. Gabapentin is not without side effects and there is also potential for misuse. Side effects associated with gabapentin include somnolence, dizziness, peripheral edema and gait disturbances. Amitriptyline hydrochloride and pregabalin can be used in combination if the patient has an inadequate response to either drug at the maximum tolerated dose. Nortriptyline [unlicensed indication] may be better tolerated than amitriptyline hydrochloride. Gabapentin is also effective for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Gabapentin capsules were started at 300 mg/d and increased to 2700 mg/d within 3 weeks: Gabapentin, 300 mg, bid, P.O. Pregabalin 75 mg, bid, P.O. Intervention time (Weeks) 14 (2W) 8 (Washout period) Comparison: Placebo: Pregabalin: Outcome: Gabapentin was not beneficial in the treatment of CIPN (See Supplementary Table S1 for details) We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Oral gabapentin dosed at 1,200 mg or more daily demonstrated a 50% reduction in pain intensity, with a number needed to treat (NNT) of eight for postherpetic neuralgia and an NNT of six for Gabapentin is commonly used to treat and prevent seizures in people with epilepsy or to treat nerve pain (postherpetic neuralgia) that can occur after a viral infection called shingles. “Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Authors' conclusions: Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Evidence for other types of neuropathic pain is very limited. 197 reviews for gabapentin to treat Peripheral Neuropathy: Rx: C N: X: Generic name: gabapentin systemic Drug class: gamma-aminobutyric acid analogs For consumers: Gabapentin was shown to be better than placebo across all studies for IMMPACT outcomes. The review concentrated on gabapentin doses of 1,200 mg/d or greater and reported that doses at or above this threshold were reasonably effective for treatment of various neuropathic pain types. Gabapentin at doses of 1800 mg to 3600 mg daily (1200 mg to 3600 mg gabapentin encarbil) can provide good levels of pain relief to some people with postherpetic neuralgia and peripheral diabetic neuropathy. First-line drug therapy for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy includes duloxetine, gabapentin, amitriptyline, and pregabalin; however, these medications do not restore sensation to affected extremities. Evidence for long-term benefit and safety of first-line treatment options is lacking. The plasma level of gabapentin does not increase proportionally with dose increase – this means that the risk of side effects is higher when high doses are taken. Moreover, bioavailability of gabapentin falls from 60% to 33% as the total daily dosage increase from 900mg to 3600 mg. Gabapentin is approved to treat seizures and postherpetic neuralgia, a type of nerve pain from shingles. It is thought to work by changing how nerves send messages to your brain. It is also used off-label to treat other neuropathic pain conditions. A RCT compared topical ketamine 5% cream (three times daily) to placebo in the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. 22 After one month, ketamine reduced some aspects of pain but change in pain intensity was no different than with placebo. 22 In patients with complex regional pain syndrome, a double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial Researchers compare four treatments for neuropathy. Researchers publishing in JAMA Neurology describe the results of a unique trial in which 402 people with idiopathic sensory polyneuropathy were randomly assigned to one of four medications: duloxetine, mexiletine, nortriptyline, or pregabalin. After 12 weeks, each person rated their neuropathy Gabapentin and pregabalin are used mostly in the management of diabetes-induced peripheral neuropathy and postherpetic neuralgia. The analgesic effect of gabapentin arises from increased GABA synthesis, α2δ subunit binding of voltage-gated calcium channels, and non-NMDA receptor antagonism.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |