Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
%20Questions%20And%20Answers%202022.png) | 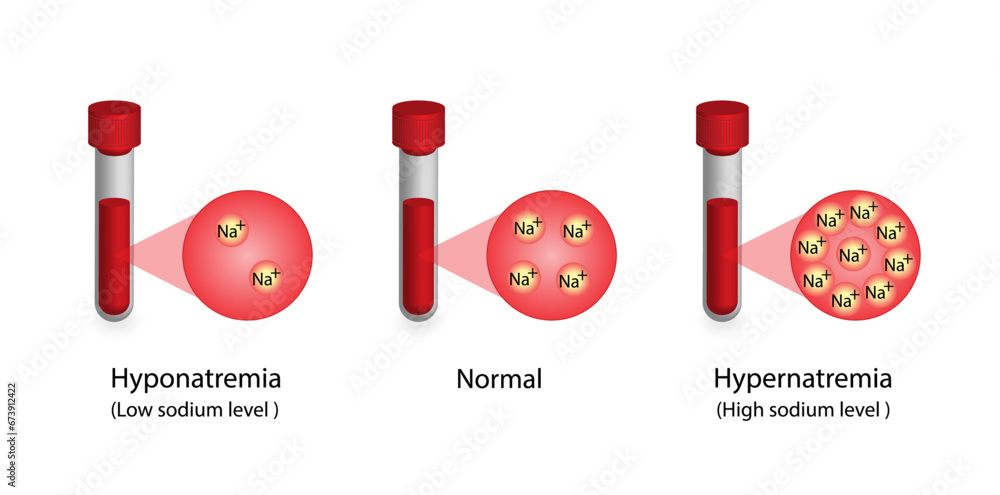 |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Hyponatremia and hypernatremia are electrolyte disorders that can be associated with poor outcomes. Hyponatremia is considered mild when the sodium concentration is 130 to 134 mEq per L, moderate Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which intervention would the nurse include in the plan of care for a client admitted with herpes zoster? Select all that apply. One, some, or all responses may be correct. 1 Acyclovir 2 Silvadene 3 Gabapentin 4 Wet compresses 5 Contact isolation, Which type of laser is used in the treatment of vascular and other pigmented lesions Our study showed a mild increase in hospitalization due to hyponatremia within 90 days of the first prescription but a non–significant decrease in risk during chronic use. Thus, gabapentin seems to carry a very low over-all risk of inducing hyponatremia. Hypernatraemia, defined as a serum sodium level >145 mmol/L, is a relatively common electrolyte disorder, especially among the elderly and critically ill patients. The reported frequency of hypernatraemia in a general hospital population ranges from 0.3% to 3.5% [1,2]. When taking gabapentin, there are steps you can take to lower the risk of hyponatremia. Eating a balanced diet with enough sodium is key. Eating foods high in sodium is important for keeping electrolytes balanced. INTRODUCTION. Hypernatremia is most often due to unreplaced water that is lost from the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting or osmotic diarrhea), skin (sweat), or the urine (arginine vasopressin disorders or an osmotic diuresis due to glycosuria in uncontrolled diabetes mellitus or increased urea excretion resulting from catabolism or recovery from kidney failure) () []. INTRODUCTION. Long QT syndrome (LQTS) is a disorder of myocardial repolarization characterized by a prolonged QT interval on the electrocardiogram (ECG) ().This syndrome is associated with an increased risk of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) and a characteristic life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia also known as torsades de pointes (TdP) (waveform 2A-B). Gabapentin (Neurontin, Gralise, Horizant) is a medicine used to treat partial seizures, nerve pain from shingles and restless leg syndrome. It works on the chemical messengers in your brain and nerves. Gabapentin is from a group of medicines called anticonvulsants. She denied any history of stroke or myocardial infarction. Home medications included 0.5 milligrams (mg) of clonazepam once daily, 100 mg lamotrigine once daily, 600 mg gabapentin twice daily, oxycodone 10 mg once daily pen, 20 mg citalopram twice daily, and paroxetine 25 mg controlled release in the morning and 12.5 mg at bedtime. hyponatremia (Tables 4 and 5). CBZ is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4toyieldanactivemetabolite,carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide, Etiology and evaluation of hypernatremia in adults; Evaluation and management of suspected sepsis and septic shock in adults; Evaluation and management of the first seizure in adults; Hepatic encephalopathy in adults: Clinical manifestations and diagnosis; Hepatic encephalopathy in adults: Treatment; Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus Recognizing the Symptoms of Hyponatremia. Hyponatremia is a condition characterized by low levels of sodium in the blood. In some cases, the use of Gabapentin, a medication commonly prescribed for the treatment of epilepsy or neuropathic pain, can lead to hyponatremia. Expert opinion: Carbamazepine and oxcarbazepine are the most common AEDs which induce hyponatremia in patients with epilepsy. Recently, other AEDs, such as eslicarbazepine, sodium valproate, lamotrigine, levetiracetam and gabapentin have also been reported to cause hyponatremia. Lamotrigine and gabapentin had the lowest risk both during initiation and ongoing treatment and may be advantageous in patients at risk of developing hyponatremia. Keywords: Adverse effect; Antiepileptic drugs; Hyponatremia; SIADH. The most frequent electrolyte disorder in hospitalized patients is hyponatremia [1]. The clinical spectrum in hyponatremia ranges from mild, non-specific symptoms such as fatigue, headache, and gait instability to life-threatening symptoms such as seizures, coma and ultimately death, secondary to brain oedema [2,3]. Pharmaceutical drugs, e.g., thiazide diuretics, antidepressants and While sharing a common property of suppressing seizures, antiseizure medications have many different pharmacologic profiles that are relevant when selecting and prescribing these agents in patients with epilepsy and other conditions. The incidence of epilepsy is highest in old age (>60 years of age), with an estimated 60–135 new cases per 100,000 older adults each year. 1-3 Carbamazepine, valproic acid, phenytoin, and topiramate are frequently used antiepileptic drugs for the control of focal and generalized seizures, and can be initiated as monotherapy. 4-6 These drugs are also often used in treatment of nonepileptic Gabapentin was first conceptualised in the early 1970s during efforts to discover drugs for treating neurological disorders. 7 Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) was known to be a key inhibitory neurotransmitter, whose inhibition could cause seizures. Learn the differences and similarities between gabapentin and an opioid medication. 1. Dizziness is the No. 1 side effect of gabapentin. In studies, almost 30% of people taking gabapentin for postherpetic neuralgia, and over 15% of people taking it for seizures, experienced dizziness. Dizziness is similarly common with Horizant. Herein, we review evidence-based information via PubMed and EMBASE and the relevant literature implicating pharmacologic treatment as an established cause of hypernatraemia and discuss its incidence and the underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
%20Questions%20And%20Answers%202022.png) |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |