Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
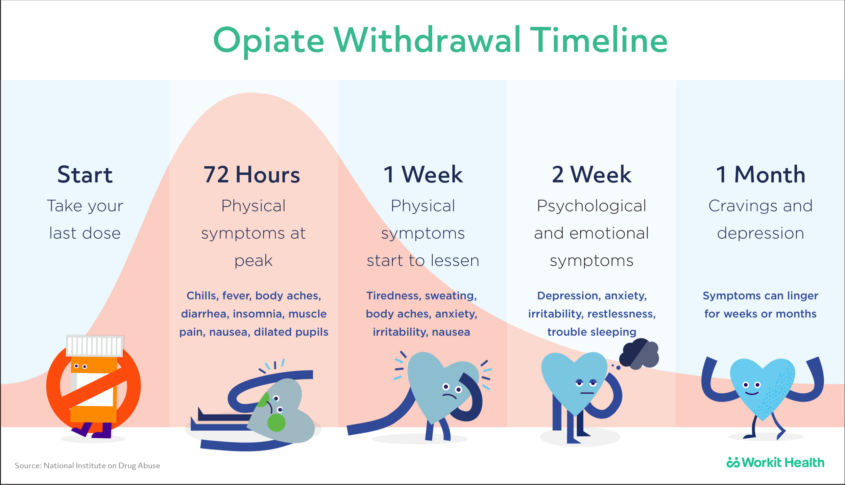
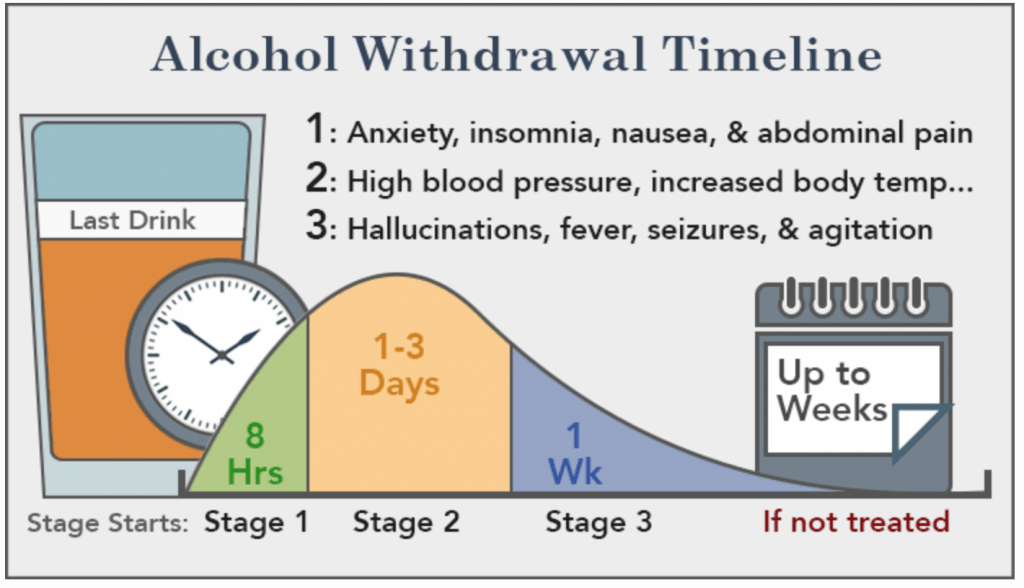
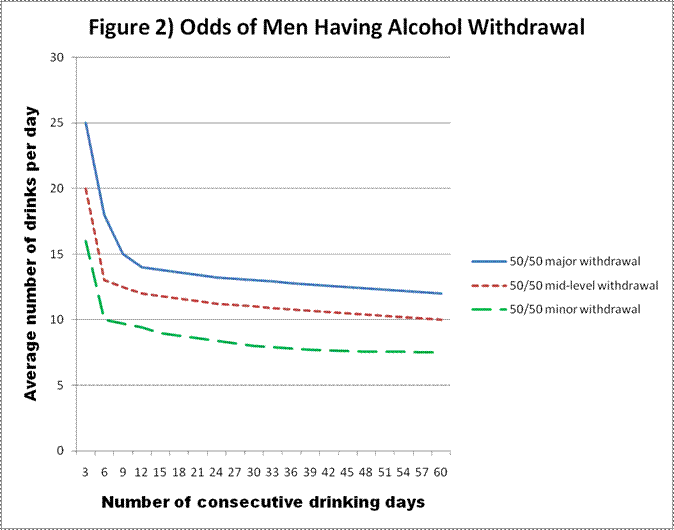
The propensity score for being treated with gabapentin was estimated using a logistic regression model incorporating the following pretreatment variables: age, sex, number of prior admissions with alcohol withdrawal, prior documented alcohol withdrawal seizures or delirium tremens, prior treatment of alcohol withdrawal with gabapentin, prior Gabapentin is effective at reducing drinking among people with alcohol use disorder (AUD) and strong withdrawal symptoms, according to a study published in JAMA Internal Medicine. Some research shows that gabapentin has promise as an alcohol withdrawal treatment, possibly in combination with other medications. Gabapentin can: Help stop the impulse to drink, The mechanism of action of gabapentin may also benefit patients suffering from acute alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to examine if gabapentin can effectively replace/reduce the use of benzodiazepines for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms in hospitalized patients. alcohol withdrawal: seizures, delirium, or death. 1. Proper management of the alcohol withdrawal syndrome can improve engagement in long-term treatment for addiction to alcohol. Complications associated with alcohol withdrawal, however, are estimated to still occur in approximately 500,000 individuals in the United States annually, making it Limited data suggest that gabapentin can provide benefit in managing mild alcohol withdrawal syndrome. There were 5 reported or suspected seizures in the withdrawal studies, suggesting that additional safety data are necessary before gabapentin monotherapy can be routinely considered. Gabapentin can help with alcohol withdrawal by counteracting the physiological effects of the syndrome. Evidence indicates that symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome stem Benzodiazepines are the typical first line treatment for alcohol withdrawal. However, benzodiazepines carry with them significant risks and side effects. As a result, ongoing research has. during treatment. Gabapentin is a medication that is primarily used for seizure control and neuralgia, but. benzodiazepines. We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. The prevalence of alcohol use disorders (AUDs) among hospitalized medically ill patients exceeds 40%. Most AUD patients experience uncomplicated alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS), requiring only supportive medical intervention, while complicated AWS occurs in up to 20% of cases (i.e. seizures, delirium tremens). CIWA was originally designed as a tool for alcohol withdrawal research and is validated only in mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal. Studies on CIWA have frequently excluded patients with seizures. CIWA does not include vital sign assessment, which is an important part of recognizing severe alcohol withdrawal syndrome. Gabapentin is a calcium channel GABAergic modulator that is widely used for pain. Studies showing reduced drinking and decreased craving and alcohol-related disturbances in sleep and affect in the months following alcohol cessation suggest therapeutic potential for alcohol use disorder. This is different from our study that included patients with a history of complicated alcohol withdrawal, including those with alcohol withdrawal seizures or alcohol withdrawal delirium. One important factor was that in our evaluation of the gabapentin protocol, a significant number of patients were found to have received valproate (36.4%). Gabapentin is efficacious for the treatment of acute alcohol withdrawal symptoms 29,30 and also provides short-term relapse prevention after medicated alcohol detoxification, 31 perhaps by an effect on sleep normalization. 32,33 Post hoc analysis has shown effectiveness of treatment with gabapentin, in combination with flumazenil 34 or Conclusions: Our findings demonstrate that using gabapentin with benzodiazepine was associated with a reduction in the cumulative benzodiazepine dosage for alcohol withdrawal. Considering gabapentin as an adjunctive therapy holds promise for patients with comorbidities who could benefit from reducing benzodiazepine dose. Study Objective. Gabapentin has been proved to be beneficial in promoting abstinence, decreasing alcohol cravings, and improving mood and sleep quality when given at higher doses; however, data are limited regarding the efficacy and safety of using high-dose gabapentin as part of the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). Approximately one-half of patients with alcohol use disorder who abruptly stop or reduce their alcohol use will develop signs or symptoms of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The syndrome is due to Early initiation of high-dose gabapentin was associated with a significant reduction in benzodiazepine exposure, faster stabilization of alcohol withdrawal-related symptoms, and shorter hospital length of stay. Future studies evaluating gabapentin's effect on long-term safety and hospital readmissio Conclusions and relevance: These data, combined with others, suggest gabapentin might be most efficacious in people with AUD and a history of alcohol withdrawal symptoms. Future studies should evaluate sleep changes and mood during early recovery as mediators of gabapentin efficacy. Gabapentin has been shown to be safe and effective for mild alcohol withdrawal but is not appropriate as mono-therapy for severe withdrawal owing to risk of seizures. During early abstinence, gabapentin may improve sleep, cravings, and mood—factors associated with relapse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |