Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
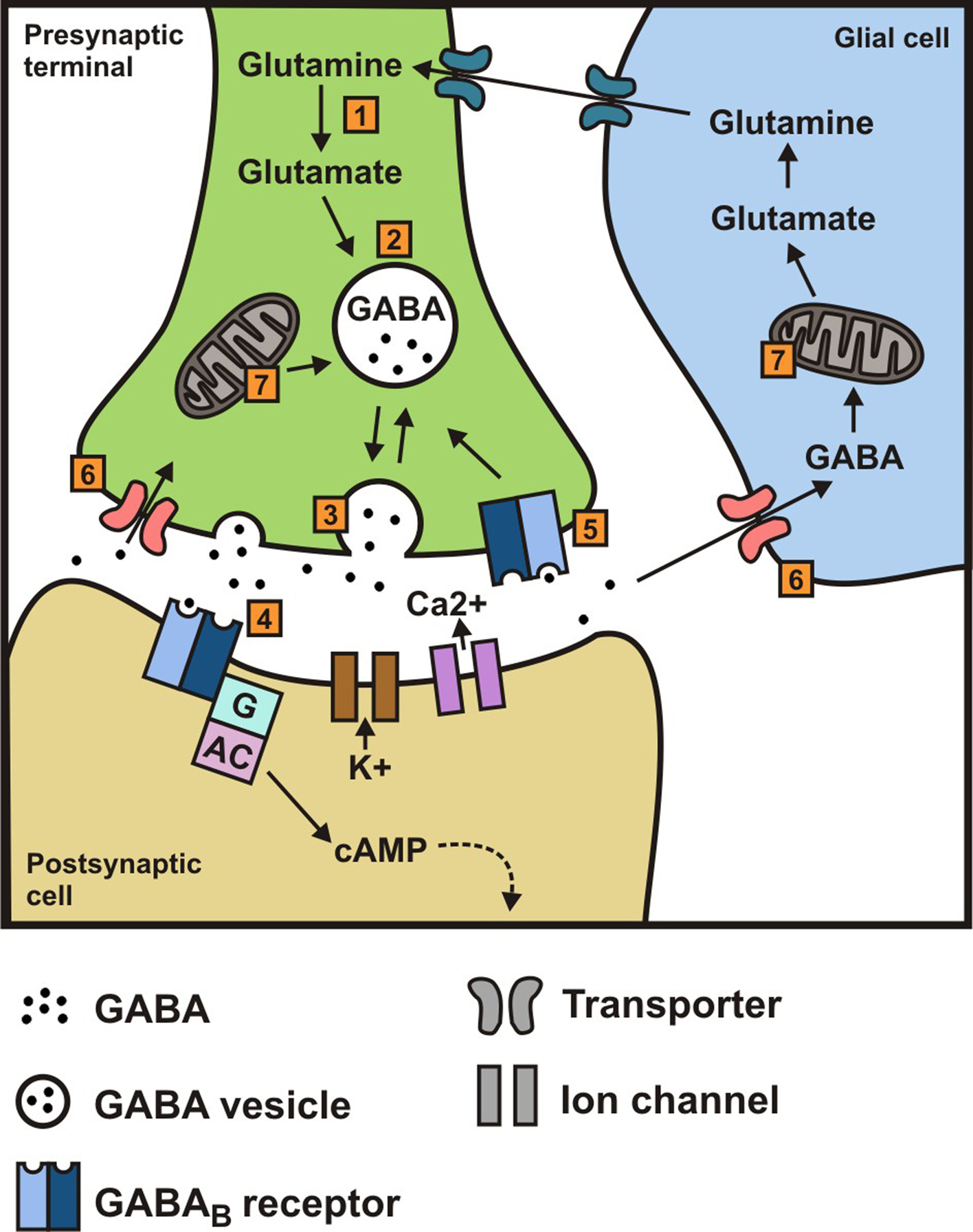
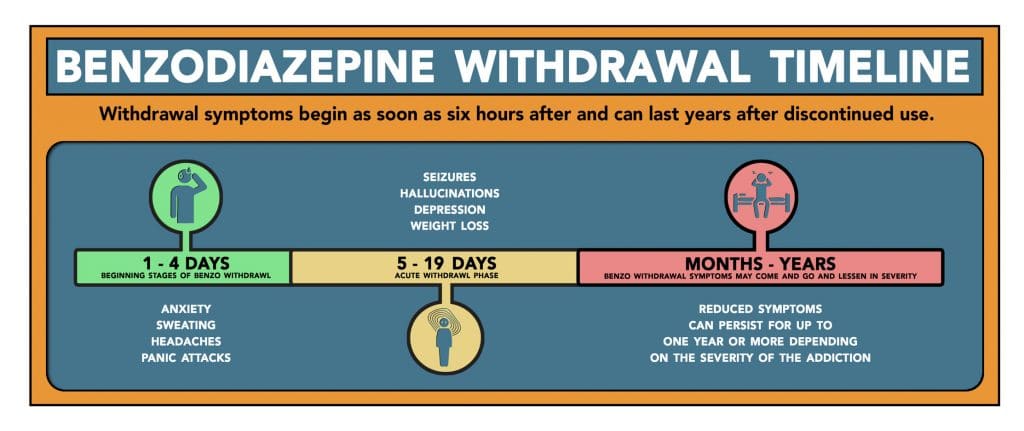
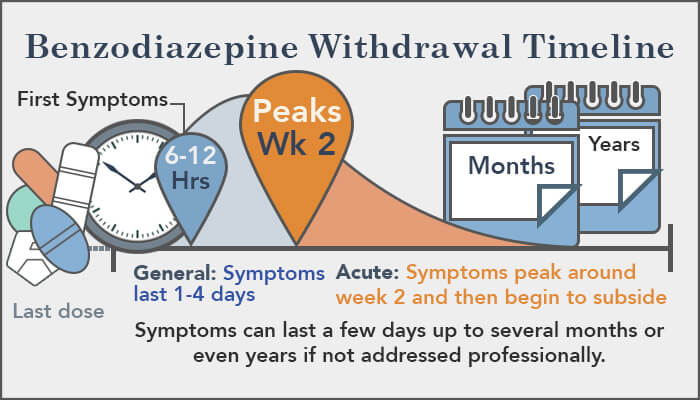
Wanted to see what opinions were on taking gabapentin for the crippling anxiety that comes with benzo withdrawals. I’ve real a couple of success stories where it helped a couple of patients with PAWS and then I’ve also read where the gabapentin didn’t work. Also heard it was a drug that might be Similar to alcohol and benzodiazepine withdrawal, gabapentin affects gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a key neurotransmitter in the brain. Common withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, headaches, and irritability. In severe cases, particularly for those on high doses or with seizure disorders, withdrawal leads to seizures. In 2021, the American Psychiatric Association presented a study on the possibility of treating benzodiazepine dependence, abuse, and withdrawal with gabapentin. According to the psychiatrists, the two drugs share similar mechanisms, making gabapentin an effective adjunct treatment. Different mechanisms underlying the efficacy of gabapentin in benzodiazepine withdrawal can be considered. Although it has no direct effect on GABA receptors or transporters, it has some GABA-ergic activity, which may be sufficient to compensate the benzodiazepine-related GABA activity. Benzodiazepine withdrawal can be a long and difficult process, but there are steps that physicians can take to help their patients survive the process. Tapering the drug slowly and switching to a long half-life benzodiazepine may be helpful, as may adjunctive medications and coping skills. Encouraging acceptance and finding a support system can also be key to surviving benzodiazepine withdrawal. Gabapentin will mask benzo withdrawal symptoms. That may seem like a good thing, but when you finally reduce/eliminate the gabapentin, the benzo withdrawal symptoms may still be there. And/or gabapentin withdrawal may occur. Gabapentin works by showing a high affinity for binding sites throughout the brain corresponding to the presence of the voltage-gated calcium channels, especially α-2-δ-1, which seems to inhibit the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the presynaptic area that participate in epileptogenesis.” Addition of an anticonvulsant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should be considered for high-dosage withdrawal. These results suggest the potential use of gabapentin as an adjunct to the use of benzodiazepines for treating benzodiazepine withdrawal. The limitations of this study included a small sample size and variability in medication management strategies across the sample. Chronic use of a benzodiazepine can cause physiologic dependence and the potential for a withdrawal syndrome upon rapid discontinuation. Benzodiazepine dependance can develop from use of prescribed, illicit (ie, non-prescribed use of compounds used medically), and designer (ie, compounds not used medically) agents. The American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) recommends gabapentin for treating withdrawal symptoms as follows: (I) Gabapentin is an appropriate alternative to benzodiazepines for mild to moderate alcohol withdrawal. (II) Gabapentin is a suitable choice for treating alcohol withdrawal when the physician also intends to utilize it for a related to withdrawal, benzodiazepines are commonly tapered slowly, with psychologi- sant (e.g., gabapentin [Neurontin]) should be considered for high-dosage withdrawal. Efficacy of Gabapentin versus Benzodiazepines in the Management of Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome . Douglas R. Fredona RN, BSN, PCCN, CNRN A masters project completed in partial fulfillment of the requirements al is necessary. Gabapentin, an anxiolytic drug that is also used off-label to treat alcohol withdrawal, is a potential candidate for modulating benzodiazepine withdrawal. Using electronic records from a large inpatient psychiatric facility, a retrospective study of 172 patients presenting with benzodiazepine withdrawal was conducted to determine if the coincidental use of gabapentin for other USA: Gabapentin and benzodiazepine combination is safe for the treatment of benzodiazepine withdrawal, according to findings from a recent study. The results were presented at the American Psychiatric Association Annual Meeting (virtual meeting) held from May 1-3, 2021. "Gabapentin in Addiction Treatment In the last few years, several studies have demonstrated that gabapentin can be a helpful resource for treating substance abuse in various ways. Specifically, it is useful in treating withdrawal and maintaining abstinence in people struggling with alcohol, benzodiazepine, and opioid addiction. Gabapentin has growing evidence to support its use in the treatment of alcohol use disorder, however there is limited evidence regarding its role in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. The purpose of this study was to determine if adjunctive gabapentin reduces the need for benzodiazepine (BZD) administration during alcohol withdrawal. Overall, Neurontin Gabapentin is a valuable treatment option for benzodiazepine withdrawal. Its ability to reduce withdrawal symptoms, stabilize mood, prevent seizures, improve sleep quality, and minimize discomfort make it an effective and supportive medication for individuals navigating the challenges of benzodiazepine withdrawal. Most people I was in treatment with took Gabapentin to ease withdrawal symptoms. since you’re doing a more gradual taper you probably wouldn’t need it, but I don’t think you’re gonna screw anything up by taking it if you think it helps. Researchers found a total daily dose of 600 mg to 1,800 mg of gabapentin reduced withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, they reported no complications with the combination of gabapentin and
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |