Gallery
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
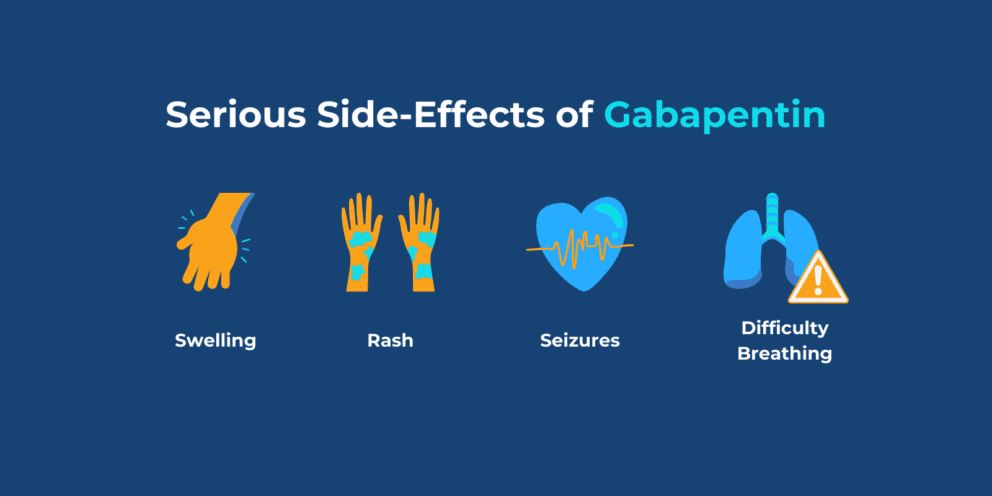
While studies don’t typically show effectiveness for improving symptoms of depression, there is evidence that gabapentin may have some benefit for anxiety disorders. A rat study found that gabapentin produced behavioral changes suggestive of anxiolysis, or feelings of calmness. Evidence does not support the use of gabapentin for bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder (MDD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), stimulant use disorder, or opioid withdrawal. Could gabapentin be more than just an anticonvulsant? As it turns out, the answer is a resounding yes. Today, gabapentin is frequently prescribed off-label for various mental health conditions, joining the ranks of other mood-stabilizing medications like lamotrigine, which has shown promise in treating bipolar disorder and depression. Only two groups have described their experience with gabapentin in either bipolar or unipolar depression (Young et al., 1997, Ghaemi et al., 1998, Young et al., 1999). To our knowledge, this is the first report on the extended adjunctive use of gabapentin in a large cohort of depressed patients resistant to conventional antidepressants. Gabapentin may be effective for treating depression and anxiety, among other things. Although gabapentin was traditionally used to treat seizures, it is now sometimes used as a mood stabilizer for depression and bipolar disorder because it calms neurons in the brain, and it may be effective for anxiety too. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. In 2019, the FDA added a warning and precaution about the possibility of respiratory depression that states: “There is evidence from case reports, human studies, and animal studies associating gabapentin with serious, life-threatening, or fatal respiratory depression when coadministered with CNS depressants, including opioids, or in the Gabapentin is a nerve pain medication and anticonvulsant that has proven to be effective for people who have hard-to-treat depression or other mood disorders. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse. In addition to being used to treat pain, gabapentin is used off label to treat anxiety, alcohol use disorder (AUD), alcohol withdrawal, depression, substance use disorders (SUDs), sleep problems, and more. However, the data to support these off-label uses of gabapentin are mixed, especially for long-term use. Adjunctive gabapentin 300 mg initially, increased by 600 mg a week until patients reported a full night sleep or could no longer tolerate sedative side effects. Study duration was 10 weeks. - Adjunctive gabapentin decreased HAM-D and Bech mania rating scores as early as after the first week of study, and the effects were sustained. Gabapentin has less likely benefit adjunctively for bipolar disorder. Gabapentin has clearer efficacy for alcohol craving and withdrawal symptoms and may have a role in adjunctive treatment of opioid dependence. There is no clear evidence for gabapentin therapy in depression, PTSD prevention, OCD, or other types of substance abuse.
Articles and news, personal stories, interviews with experts.
Photos from events, contest for the best costume, videos from master classes.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |